|
Nelly Martyl
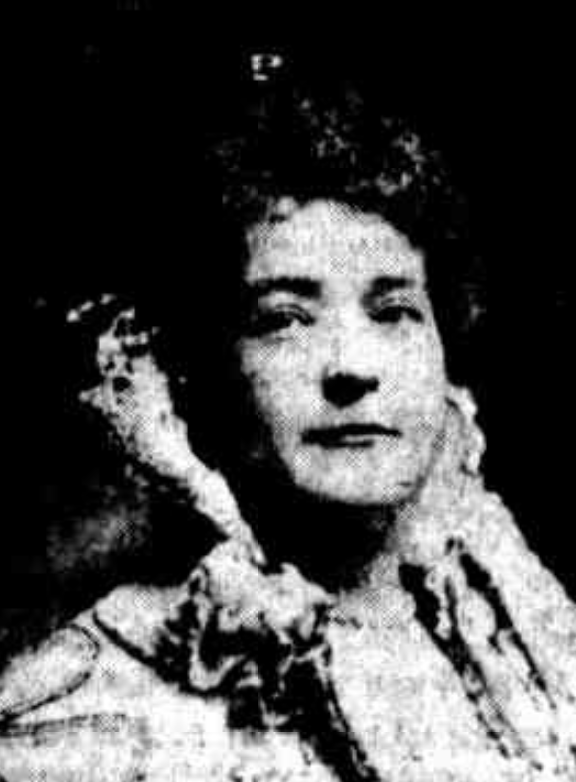
Nelly Martyl (1 April 1884 – 9 November 1953), born Nelly Adèle Anny Martin, was a French opera singer based in Paris who participated in several world premieres. During World War I and the 1918 flu epidemic, she worked as a nurse and received the Croix de Guerre for her service. Early life Nelly Adèle Anny Martin was born in Paris, the daughter of Jules Edouard Martin and Hélène Fleming. Her mother was English. She trained as a singer at the Conservatoire de Paris, studying with teachers Martini and Jacques Isnardon. Career Martyl was a soprano opera singer in Paris. She made her professional debut in 1907 in Gluck's '' Armide''. She joined the Opéra-Comique in 1909, where she appeared as Micaela in Bizet's ''Carmen'', Sophie in Massenet's ''Werther'', Mimi in Puccini's ''La bohème'' and in the title role of Massenet's ''Manon'', among others. Martyl performed in several world premieres, including Le Borne's ''La Catalane'' (1907), Erlanger's ''La Sorcière'' (191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nellie Martel
Ellen Alma "Nellie" Martel, (; 30 September 1855 – 11 August 1940) was an English-Australian suffragist and elocutionist. She stood for the Senate at the 1903 federal election, one of the first four women to stand for federal parliament. Life Born at Beacon in Cornwall to hammer-man John Charleston and Elizabeth, ''née'' Williams (one of her siblings was future Australian Senator David Charleston), she migrated to Australia in 1879, arriving in Sydney in January 1880. She married a Guernsey widower, photographer Charles Martel, at Christ Church Cathedral in Newcastle on 4 April 1885; the couple returned to Britain in 1889. While in England she witnessed her sister's marriage to the engineer Alfred Goninan. After touring France and Italy, Martel and her husband returned to Sydney in 1891 and both joined the Womanhood Suffrage League (WSL); she was elected to its council and organising committee in 1894 and to the finance committee in 1895. Her husband had been de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manon
''Manon'' () is an ''opéra comique'' in five acts by Jules Massenet to a French libretto by Henri Meilhac and Philippe Gille, based on the 1731 novel '' L'histoire du chevalier des Grieux et de Manon Lescaut'' by the Abbé Prévost. It was first performed at the Opéra-Comique in Paris on 19 January 1884, with sets designed by Eugène Carpezat (act 1), Auguste Alfred Rubé and Philippe Chaperon (acts 2 and 3), and Jean-Baptiste Lavastre (act 4). Prior to Massenet's work, Halévy (''Manon Lescaut'', ballet, 1830) and Auber (''Manon Lescaut'', opéra comique, 1856) had used the subject for musical stage works. Massenet also wrote a one-act sequel to ''Manon'', '' Le portrait de Manon'' (1894), involving the Chevalier des Grieux as an older man. The composer worked at the score of ''Manon'' at his country home outside Paris and also at a house at The Hague once occupied by Prévost himself. ''Manon'' is Massenet's most popular and enduring opera and, having "quickly conquer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singers From Paris
Singing is the act of creating musical sounds with the voice. A person who sings is called a singer, artist or vocalist (in jazz and/or popular music). Singers perform music (arias, recitatives, songs, etc.) that can be sung with or without accompaniment by musical instruments. Singing is often done in an ensemble of musicians, such as a choir. Singers may perform as soloists or accompanied by anything from a single instrument (as in art song or some jazz styles) up to a symphony orchestra or big band. Different singing styles include art music such as opera and Chinese opera, Indian music, Japanese music, and religious music styles such as gospel, traditional music styles, world music, jazz, blues, ghazal, and popular music styles such as pop, rock, and electronic dance music. Singing can be formal or informal, arranged, or improvised. It may be done as a form of religious devotion, as a hobby, as a source of pleasure, comfort, or ritual as part of music education or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1953 Deaths
Events January * January 6 – The Asian Socialist Conference opens in Rangoon, Burma. * January 12 – Estonian émigrés found a Estonian government-in-exile, government-in-exile in Oslo. * January 14 ** Marshal Josip Broz Tito is chosen President of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia. ** The Central Intelligence Agency, CIA-sponsored Robertson Panel first meets to discuss the Unidentified flying object, UFO phenomenon. * January 15 – Georg Dertinger, foreign minister of East Germany, is arrested for spying. * January 19 – 71.1% of all television sets in the United States are tuned into ''I Love Lucy'', to watch Lucy give birth to Little Ricky, which is more people than those who tune into Dwight Eisenhower's inauguration the next day. This record has yet to be broken. * January 20 – Dwight D. Eisenhower is First inauguration of Dwight D. Eisenhower, sworn in as the 34th President of the United States. * January 24 ** Mau Mau Upr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1884 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – The Fabian Society is founded in London. * January 5 – Gilbert and Sullivan's '' Princess Ida'' premières at the Savoy Theatre, London. * January 18 – Dr. William Price attempts to cremate his dead baby son, Iesu Grist, in Wales. Later tried and acquitted on the grounds that cremation is not contrary to English law, he is thus able to carry out the ceremony (the first in the United Kingdom in modern times) on March 14, setting a legal precedent. * February 1 – ''A New English Dictionary on historical principles, part 1'' (edited by James A. H. Murray), the first fascicle of what will become ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', is published in England. * February 5 – Derby County Football Club is founded in England. * March 13 – The siege of Khartoum, Sudan, begins (ends on January 26, 1885). * March 28 – Prince Leopold, the youngest son and the eighth child of Queen Victoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeleine Goüin
Magdeleine Goüin, ''countess Bernard de Ganay'' (2 March 1901 – 30 June 1949) was a French racing driver and philanthropist. Early life Goüin was born 2 March 1901 in the 8th arrondissement of Paris. She was a daughter of Édouard Goüin and Suzanne du Buit (future countess of Segur-Lamoignon), and the sister of Henry Goüin, president of the Fondation Royaumont. Career As a racing driver, Goüin won the Rallye Paris – Saint-Raphaël Féminin in 1930 at the wheel of a Renault Reinastella type RM. She finished second the following year at the Rally Paris-Amsterdam behind Suzanne Deutsch de La Meurthe. She became vice-president of the Automobile-Club Feminine de France, which was presided over at the time by Anne de Rochechouart de Mortemart. Philanthropy Goüin created and animated the "tea Rosy", teas of charity which raised funds for the work of Visiting Nurses of France (founded by her mother-in-law the Marquise de Ganay) and the dispensary of the Nelly-Martyl F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of The Aisne
The Second Battle of the Aisne (french: Bataille du Chemin des Dames or french: Seconde bataille de l'Aisne, 16 April – mid-May 1917) was the main part of the Nivelle Offensive, a Franco-British attempt to inflict a decisive defeat on the German armies in France. The Entente strategy was to conduct offensives from north to south, beginning with an attack by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) then the main attack by two French army groups on the Aisne. General Robert Nivelle planned the offensive in December 1916, after he replaced Joseph Joffre as Commander-in-Chief of the French Army. The objective of the attack on the Aisne was to capture the prominent , east–west ridge of the Chemin des Dames, north-east of Paris and then advance northwards to capture the city of Laon. When the French armies met the British advancing from the Arras front, the Germans would be pursued towards Belgium and the German frontier. The offensive began on 9 April, when the British began the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun (french: Bataille de Verdun ; german: Schlacht um Verdun ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front in France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north of Verdun-sur-Meuse. The German 5th Army attacked the defences of the Fortified Region of Verdun (RFV, ) and those of the French Second Army on the right (east) bank of the Meuse. Using the experience of the Second Battle of Champagne in 1915, the Germans planned to capture the Meuse Heights, an excellent defensive position, with good observation for artillery-fire on Verdun. The Germans hoped that the French would commit their strategic reserve to recapture the position and suffer catastrophic losses at little cost to the German infantry. Poor weather delayed the beginning of the attack until 21 February but the Germans captured Fort Douaumont in the first three days. The advance then slowed for several days, despite inflicting many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Red Cross And Red Crescent Movement
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human suffering. Within it there are three distinct organisations that are legally independent from each other, but are united within the movement through common basic principles, objectives, symbols, statutes and governing organisations. History Foundation Until the middle of the nineteenth century, there were no organized or well-established army nursing systems for casualties, nor safe or protected institutions, to accommodate and treat those who were wounded on the battlefield. A devout Calvinist, the Swiss businessman Jean-Henri Dunant traveled to Italy to meet then-French emperor Napoleon III in June 1859 with the intention of discussing difficulties in conducting business in Algeria, which at that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelly Martyl Sings La Marseillaise At A Scottish Hospital During World War I - Original
Cornell Iral Haynes Jr. (born November 2, 1974), better known by his stage name Nelly, is an American rapper, singer, actor and entrepreneur. He embarked on his music career with the hip hop group St. Lunatics in 1993 and signed to Universal Records in 1999. Under Universal, Nelly began his solo career in the year 2000, with his debut album ''Country Grammar'', of which the featured title track and the single "Ride wit Me" were top ten hits. The album peaked at number one the ''Billboard'' 200, and became Nelly's best-selling album to date, selling over 8.4 million copies in the United States. His following album ''Nellyville'' produced the number-one hits "Hot in Herre" and "Dilemma" (featuring Kelly Rowland), along with the top five single " Air Force Ones" (featuring Murphy Lee and St. Lunatics). With the same-day dual release of '' Sweat'' and ''Suit'' (2004) and the compilation ''Sweatsuit'' (2006), Nelly continued to generate many chart-topping hits. ''Sweat'' debuted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Opera House
The Royal Opera House (ROH) is an opera house and major performing arts venue in Covent Garden, central London. The large building is often referred to as simply Covent Garden, after a previous use of the site. It is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet, and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. The first theatre on the site, the Theatre Royal (1732), served primarily as a playhouse for the first hundred years of its history. In 1734, the first ballet was presented. A year later, the first season of operas, by George Frideric Handel, began. Many of his operas and oratorios were specifically written for Covent Garden and had their premieres there. The current building is the third theatre on the site, following disastrous fires in 1808 and 1856 to previous buildings. The façade, foyer, and auditorium date from 1858, but almost every other element of the present complex dates from an extensive reconstruction in the 1990s. The main auditorium seats 2,256 people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amadis (Massenet)
''Amadis'' is an opera in three acts with prologue by Jules Massenet to a French libretto by Jules Claretie based on the Spanish knight-errantry romance '' Amadis de Gaula'', originally of Portuguese origin, by Garci Rodríguez de Montalvo. It was first performed at the Opéra de Monte-Carlo on 1 April 1922, nearly ten years after Massenet's death. Massenet had started to compose the piece in 1895 but shelved it and completed it clandestinely in the last years of his life. ''Amadis'' is one of three operas by Massenet to have been premiered posthumously; the others are ''Panurge'' (1913) and ''Cléopâtre'' (1914). ''Amadis'' has gained no lasting popularity but was revived (and recorded on the Koch Swann label) during the Massenet Festival in Saint-Étienne, France in 1988. Roles Synopsis The story takes place in ancient Brittany Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)