|
Negative Differentiation
The negativity bias,Kanouse, D. E., & Hanson, L. (1972). Negativity in evaluations. In E. E. Jones, D. E. Kanouse, S. Valins, H. H. Kelley, R. E. Nisbett, & B. Weiner (Eds.), ''Attribution: Perceiving the causes of behavior.'' Morristown, NJ: General Learning Press. also known as the negativity effect, is a cognitive bias that, even when positive or neutral things of equal intensity occur, things of a more negative nature (e.g. unpleasant thoughts, emotions, or social interactions; harmful/traumatic events) have a greater effect on one's psychological state and processes than neutral or positive things. In other words, something very positive will generally have less of an impact on a person's behavior and cognition than something equally emotional but negative. The negativity bias has been investigated within many different domains, including the formation of impressions and general evaluations; attention, learning, and memory; and decision-making and risk considerations. Exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Bias
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm (philosophy), norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the Objectivity (philosophy), objective input, may dictate their behavior in the world. Thus, cognitive biases may sometimes lead to perceptual distortion, inaccurate judgment, illogical interpretation, and irrationality. While cognitive biases may initially appear to be negative, some are adaptive. They may lead to more effective actions in a given context. Furthermore, allowing cognitive biases enables faster decisions which can be desirable when timeliness is more valuable than accuracy, as illustrated in Heuristic (psychology), heuristics. Other cognitive biases are a "by-product" of human processing limitations, resulting from a lack of appropriate mental mechanisms (bounded rationality), the impact of an individual's constitution and bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Aversion (psychology)
Risk aversion is a preference for a sure outcome over a gamble with higher or equal expected value. Conversely, rejection of a sure thing in favor of a gamble of lower or equal expected value is known as risk-seeking behavior. The psychophysics of chance induce overweighting of sure things and of improbable events, relative to events of moderate probability. Underweighting of moderate and high probabilities relative to sure things contributes to risk aversion in the realm of gains by reducing the attractiveness of positive gambles. The same effect also contributes to risk seeking in losses by attenuating the aversiveness of negative gambles. Low probabilities, however, are overweighted, which reverses the pattern described above: low probabilities enhance the value of long-shots and amplify aversion to a small chance of a severe loss. Consequently, people are often risk seeking in dealing with improbable gains and risk averse in dealing with unlikely losses. Related theories Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positivity Effect
The positivity effect is the ability to constructively analyze a situation where the desired results are not achieved, but still obtain positive feedback that assists one's future progression. Empirical research findings suggest that the positivity effect can be influenced by internal positive speech, where engaging in constructive self-dialogue can significantly improve one’s ability to perceive and react to challenging situations more optimistically. The findings of a study show that the optimism bias in future-oriented thinking fulfils a self-improvement purpose while also suggesting this bias probably reflects a common underpinning motivational process across various future-thinking domains, either episodic or semantic. In attribution The positivity effect as an attribution phenomenon relates to the habits and characteristics of people when evaluating the causes of their behaviors. To positively attribute is to be open to attributing a person’s inherent disposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollyanna Principle
The Pollyanna principle (also called Pollyannaism or positivity bias) is the tendency for people to remember pleasant items more accurately than unpleasant ones. Research indicates that at the subconscious level, the mind tends to focus on the optimistic; while at the conscious level, it tends to focus on the negative. This subconscious bias is similar to the Barnum effect. Development The name derives from the 1913 novel '' Pollyanna'' by Eleanor H. Porter describing a girl who plays the "glad game"—trying to find something to be glad about in every situation. The novel has been adapted to film several times, most famously in 1920 and 1960. An early use of the name "Pollyanna" in psychological literature was in 1969 by Boucher and Osgood who described a ''Pollyanna hypothesis'' as a universal human tendency to use positive words more frequently and diversely than negative words in communicating. Empirical evidence for this tendency has been provided by computational analyse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Development (journal)
''Child Development'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal covering developmental psychology from the fetal period to adolescence. It was established in 1930 and the editor-in-chief is Glenn Roisman. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Society for Research in Child Development. The journal publishes original contributions on topics in child development from the fetal period through adolescence. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2018 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 5.024. References External links * Developmental psychology journals Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Academic journals established in 1930 English-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
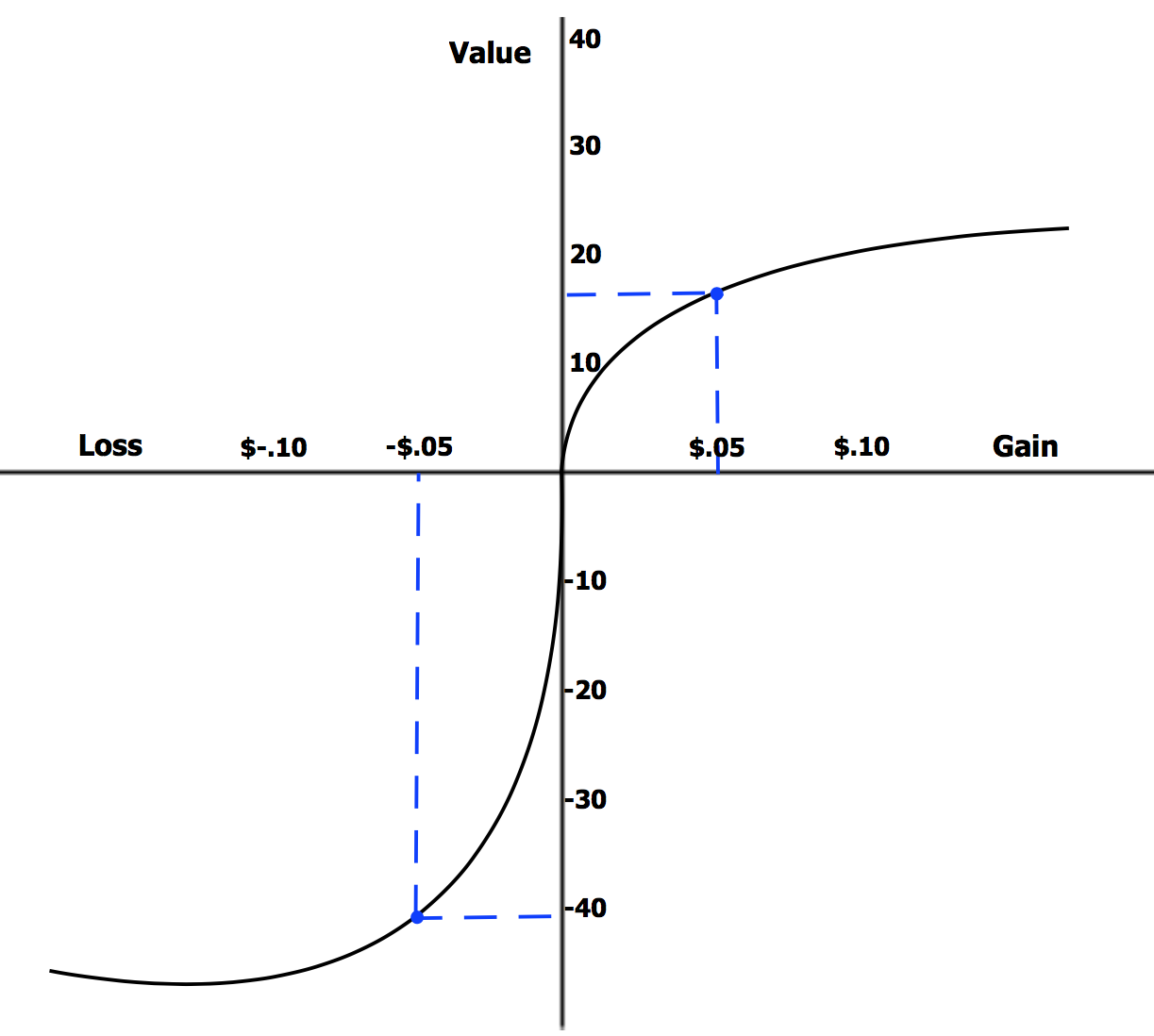
Prospect Theory
Prospect theory is a theory of behavioral economics, judgment and decision making that was developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1979. The theory was cited in the decision to award Kahneman the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Based on results from controlled studies, it describes how individuals assess their loss and gain perspectives in an asymmetric manner (see loss aversion). For example, for some individuals, the pain from losing $1,000 could only be compensated by the pleasure of earning $2,000. Thus, contrary to the expected utility theory (which models the decision that perfectly rational agents would make), prospect theory aims to describe the actual behavior of people. In the original formulation of the theory, the term ''prospect'' referred to the predictable results of a lottery. However, prospect theory can also be applied to the prediction of other forms of behaviors and decisions. Prospect theory challenges the expected utility theory deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos Tversky
Amos Nathan Tversky (; March 16, 1937 – June 2, 1996) was an Israeli cognitive and mathematical psychologist and a key figure in the discovery of systematic human cognitive bias and handling of risk. Much of his early work concerned the foundations of measurement. He was co-author of a three-volume treatise, ''Foundations of Measurement''. His early work with Daniel Kahneman focused on the psychology of prediction and probability judgment; later they worked together to develop prospect theory, which aims to explain irrational human economic choices and is considered one of the seminal works of behavioral economics. Six years after Tversky's death, Kahneman received the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for work he did in collaboration with Amos Tversky. While Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously, Kahneman has commented that he feels "it is a joint prize. We were twinned for more than a decade." Tversky also collaborated with many leading researchers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences together with Vernon L. Smith. Kahneman's published empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. Kahneman became known as the "grandfather of behavioral economics." With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011, Kahneman was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year, his book '' Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. Kah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometrica
''Econometrica'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal of economics, publishing articles in many areas of economics, especially econometrics. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Econometric Society. The current editor-in-chief is Guido Imbens. History ''Econometrica'' was established in 1933. Its first editor was Ragnar Frisch, recipient of the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969, who served as an editor from 1933 to 1954. Although ''Econometrica'' is currently published entirely in English, the first few issues also contained scientific articles written in French. Indexing and abstracting ''Econometrica'' is abstracted and indexed in: * Scopus * EconLit * Social Sciences Citation Index According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Aversion
In cognitive science and behavioral economics, loss aversion refers to a cognitive bias in which the same situation is perceived as worse if it is framed as a loss, rather than a gain. It should not be confused with risk aversion, which describes the rational behavior of valuing an uncertain outcome at less than its expected value. When defined in terms of the pseudo-utility function as in cumulative prospect theory (CPT), the left-hand of the function increases much more steeply than gains, thus being more "painful" than the satisfaction from a comparable gain. Empirically, losses tend to be treated as if they were twice as large as an equivalent gain. Loss aversion was first proposed by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman as an important component of prospect theory. History In 1979, Daniel Kahneman and his associate Amos Tversky originally coined the term "loss aversion" in their initial proposal of prospect theory as an alternative descriptive model of decision makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recognition Memory
Recognition memory, a subcategory of explicit memory, is the ability to recognize previously encountered events, objects, or people.Medina, J. J. (2008)The biology of recognition memory. ''Psychiatric Times''. When the previously experienced event is reexperienced, this environmental content is matched to stored memory representations, eliciting matching signals. As first established by psychology experiments in the 1970s, recognition memory for pictures is quite remarkable: humans can remember thousands of images at high accuracy after seeing each only once and only for a few seconds.Standing, L. (1973). "Learning 10,000 pictures". ''The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology'', 25(2), 207–222. Retrieved Jan 20 2020, from . Recognition memory can be subdivided into two component processes: recollection and familiarity, sometimes referred to as "remembering" and "knowing", respectively. Recollection is the retrieval of details associated with the previously experienced event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impression Formation
Impression formation in social psychology refers to the processes by which different pieces of knowledge about another are combined into a global or summary impression. Social psychologist Solomon Asch is credited with the seminal research on impression formation and conducted research on how individuals integrate information about personality traits. Two major models have been proposed to explain how this process of integration takes place. The configural model suggests that people form cohesive impressions by integrating traits into a unified whole, adjusting individual traits to fit an overall context rather than evaluating each trait independently. According to this model, some traits are more schematic and serve as central traits to shape the overall impression. As an individual seeks to form a coherent and meaningful impression of another individual, previous impressions significantly influence the interpretation of subsequent information. In contrast, the algebraic model tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |