|
Neferkare (Tanis)
Neferkare was an ancient Egyptian ruler ("king") of Tanis during the 26th Dynasty. Biography He was possibly the successor of the better known king Sehetepibenre Pedubast, and should have succeeded him in around 665 BCE, just one year before Psamtik I of the 26th Dynasty proclaimed himself pharaoh. His existence was proposed by the French Egyptologist Pierre Montet, who found in Tanis a few monuments bearing a partially erased royal titulary which was quite similar to the one of Pepi II Neferkare of the Old Kingdom. However, in one of these monuments is mentioned the goddess Mut, "Lady of Isheru", whose cult is typical of a more recent epoch. Furthermore, a cornice from Athribis bears both the cartouches of a ''Neferkare'' and a ''Wahibre''; the latter likely is Psamtik I while the former could be this Tanite ruler. Based upon these findings, it is likely that Psamtik, once he became pharaoh, could no longer tolerate the multitude of rulers with claims of kingship upo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanis
Tanis ( grc, Τάνις or Τανέως ) or San al-Hagar ( ar, صان الحجر, Ṣān al-Ḥaǧar; egy, ḏꜥn.t ; ; cop, ϫⲁⲛⲓ or or ) is the Greek name for ancient Egyptian ''ḏꜥn.t'', an important archaeological site in the north-eastern Nile Delta of Egypt, and the location of a city of the same name. It is located on the Tanitic branch of the Nile, which has long since silted up. The first study of Tanis dates to 1798 during Napoléon Bonaparte's expedition to Egypt. Engineer Pierre Jacotin drew up a map of the site in the '' Description de l'Égypte''. It was first excavated in 1825 by Jean-Jacques Rifaud, who discovered the two pink granite sphinxes now in the Musée du Louvre, and then by François Auguste Ferdinand Mariette between 1860 and 1864, and subsequently by William Matthew Flinders Petrie from 1883 to 1886. The work was taken over by Pierre Montet from 1929 to 1956, who discovered the royal necropolis dating to the Third Intermediate Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isheru
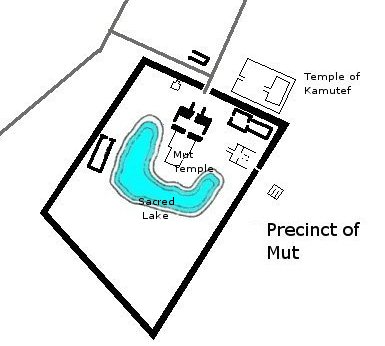
The Precinct of Mut is an Ancient Egyptian temple compound located in the present city of Luxor (ancient Thebes), on the east bank of the Nile in South Karnak. The compound is one of the four key ancient temples that creates the Karnak Temple Complex. It is approximately 325 meters (1,066 feet) south of the precinct of the god Amun. The precinct itself encompasses approximately 90,000 square meters (968,751 square feet) of the entire area. The Mut Precinct contains at least six temples: the Mut Temple, the Contra Temple, and Temples A, B, C, and D. Surrounding the Mut Temple proper, on three sides, is a sacred lake called the Isheru. To the south of the sacred lake is a vast amount of land currently being excavated by Dr. Betsy Bryan and her team from the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. Today, most of the compound is still destroyed, but it is currently being renovated. Surrounding the Mut Temple, the Contra Temple, and Temples A, B, C, and D, is an enclosur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The Twenty-sixth Dynasty Of Egypt
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century BC Pharaohs
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toby Wilkinson
Toby Alexander Howard Wilkinson, (born 1969) is an English Egyptologist and academic. After studying Egyptology at the University of Cambridge, he was Lady Wallis Budge Research Fellow in Egyptology at Christ's College, Cambridge (1993 to 1997) and then a research fellow at the University of Durham (1997 to 1999). He became a Fellow of Clare College, Cambridge in 2003. He was Deputy Vice Chancellor (External Relations) at the University of Lincoln from 2017 to 2021, and then Vice Chancellor of Fiji National University from January 2021 to December 2021. Since 2022, he has been Fellow for Development at Clare College, Cambridge. Wilkinson was awarded the 2011 Hessell-Tiltman Prize for his book ''The Rise and Fall of Ancient Egypt: the History of a Civilisation from 3000 BC to Cleopatra''. Early life Wilkinson was born in 1969. He read Egyptology at Downing College, Cambridge. He graduated with a first class Bachelor of Arts (BA) degree, and was awarded the Thomas Mulvey Egy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22nd Dynasty
The Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt is also known as the Bubastite Dynasty, since the pharaohs originally ruled from the city of Bubastis. It was founded by Shoshenq I. The Twenty-first, Twenty-second, Twenty-third, Twenty-fourth, and Twenty-fifth dynasties of ancient Egypt are often combined under the group designation of the Third Intermediate Period. Rulers The pharaohs of the Twenty-second Dynasty were a series of Meshwesh (ancient Libyan tribe) chieftains, who ruled from c. 943 BC until 716 BC. They had settled in Egypt since the Twentieth Dynasty and were known in Egypt as the 'Great Chiefs of the Ma' (Ma being a synonym of Meshwesh). Manetho states that this Egyptianized ancient Libyan dynasty first ruled over Bubastis, but its rulers almost certainly governed from Tanis, which was their capital and the city where their tombs have been excavated. Another pharaoh who belongs to this group is Tutkheperre Shoshenq. His period of rule within this dynasty is currently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt. Of Meshwesh ancestry, Shoshenq I was the son of Nimlot A, Great Chief of the Ma, and his wife Tentshepeh A, a daughter of a Great Chief of the Ma herself. He is presumed to be the Shishak mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, and his exploits are carved on the Bubastite Portal at Karnak. Chronology The conventional dates for his reign, as established by Kenneth Kitchen, are 945–924 BC but his time-line has recently been revised upwards by a few years to 943–922 BC, since he may well have lived for up to two to three years after his successful campaign in Canaan, conventionally dated to 925 BC. As Edward Wente of the University of Chicago noted (1976) on page 276 of his JNES 35 Book Review of Kitchen's study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was as ''mḥw'' and means ''"north"''. Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into number of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartouche
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a cartouche is an oval with a line at one end tangent to it, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The first examples of the cartouche are associated with pharaohs at the end of the Third Dynasty, but the feature did not come into common use until the beginning of the Fourth Dynasty under Pharaoh Sneferu. While the cartouche is usually vertical with a horizontal line, if it makes the name fit better it can be horizontal, with a vertical line at the end (in the direction of reading). The ancient Egyptian word for cartouche was , and the cartouche was essentially an expanded shen ring. Demotic script reduced the cartouche to a pair of brackets and a vertical line. Of the five royal titularies it was the ''prenomen'' (the throne name), and the "Son of Ra" titulary (the so-called '' nomen'' name given at birth), which were enclosed by a cartouche. At times amulets took the form of a cartouche displaying the name of a king and placed in to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athribis
Athribis ( ar, أتريب; Greek: , from the original Egyptian ''Hut-heryib'', cop, Ⲁⲑⲣⲏⲃⲓ) was an ancient city in Lower Egypt. It is located in present-day Tell Atrib, just northeast of Benha on the hill of Kom Sidi Yusuf. The town lies around 40 km north of Cairo, on the eastern bank of the Damietta branch of the Nile. It was mainly occupied during the Ptolemaic, Roman, and Byzantine eras. Background Athribis was once the capital of the tenth Lower Egyptian nome. The Palermo stone indicates Egyptian occupation of the site dating back to the Old Kingdom, with the earliest mention of Athribis dating to the reign of Sahure. This could perhaps have been confirmed in 2010, with the discovery of a mastaba dating to the late Third Dynasty to early Fourth Dynasty in nearby Quesna. After this, archeological evidence exists for an occupation during the 12th Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom period. Today, much of the preexisting artifacts are being lost every year b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and the 20th centuries. Not only was the last king of the Early Dynastic Period related to the first two kings of the Old Kingdom, but the "cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1938.jpg)




