Cornice on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
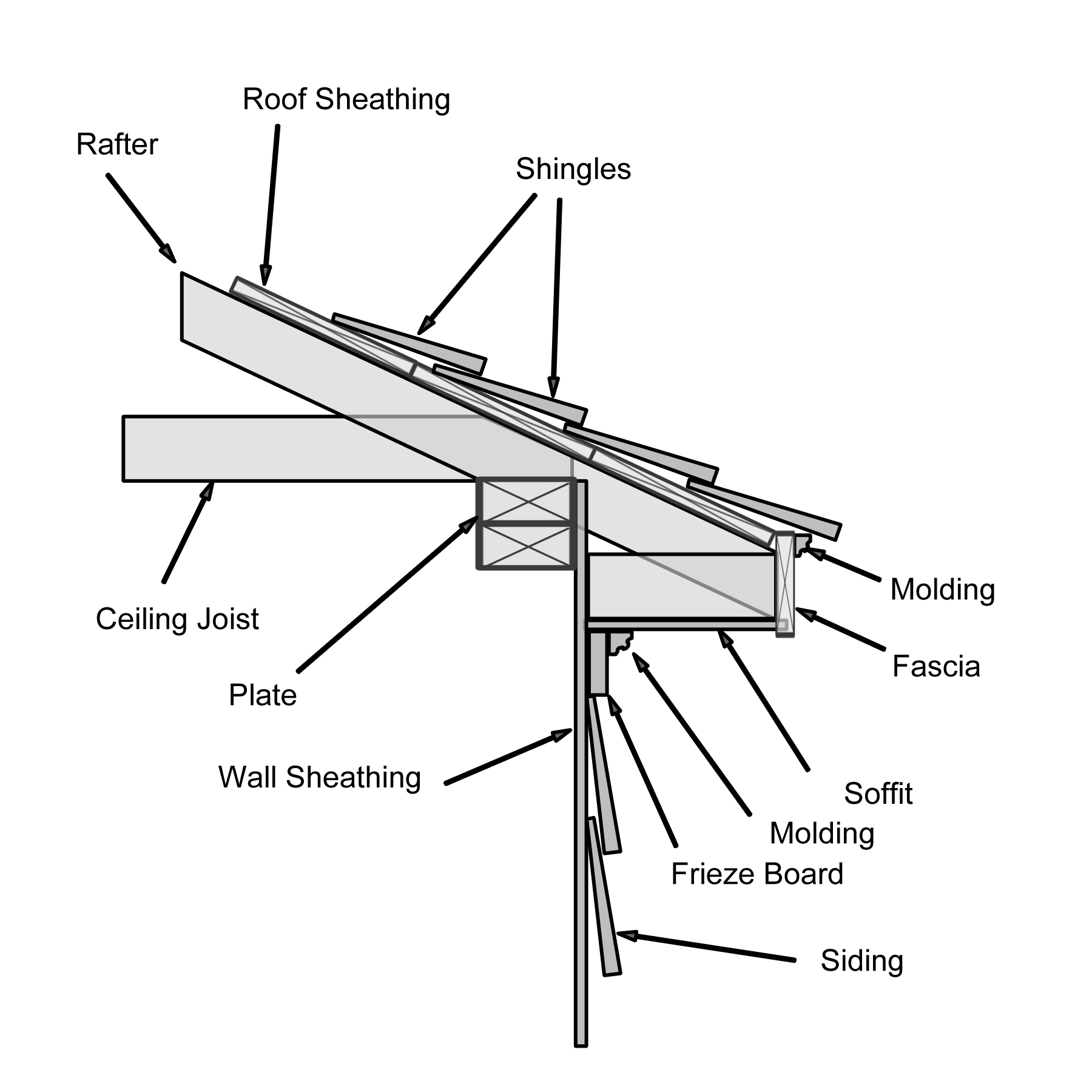 Box cornices enclose the cornice of the building with what is essentially a long, narrow box. A box cornice may further be divided into either the ''narrow'' box cornice or the ''wide'' box cornice type. A narrow box cornice is one in which "the projection of the rafter serves as a nailing surface for the soffit board as well as the fascia trim." This is possible if the slope of the roof is fairly steep and the width of the eave relatively narrow. A wide box cornice, a common practice on houses with gentle roof slopes and wide eaves, requires lookouts to support it and provide a surface to attach the soffits securely. Box cornices often have ventilation screens laid over openings cut in the soffits to allow air to circulate within the cornice.
Box cornices enclose the cornice of the building with what is essentially a long, narrow box. A box cornice may further be divided into either the ''narrow'' box cornice or the ''wide'' box cornice type. A narrow box cornice is one in which "the projection of the rafter serves as a nailing surface for the soffit board as well as the fascia trim." This is possible if the slope of the roof is fairly steep and the width of the eave relatively narrow. A wide box cornice, a common practice on houses with gentle roof slopes and wide eaves, requires lookouts to support it and provide a surface to attach the soffits securely. Box cornices often have ventilation screens laid over openings cut in the soffits to allow air to circulate within the cornice.
 A closed or snub cornice is one in which there is no projection of the rafters beyond the walls of the building and, therefore, no soffit or fascia. This type of cornice is easy to construct but provides little aid in dispersing water away from the building and is sometimes considered to lack aesthetic value.
A closed or snub cornice is one in which there is no projection of the rafters beyond the walls of the building and, therefore, no soffit or fascia. This type of cornice is easy to construct but provides little aid in dispersing water away from the building and is sometimes considered to lack aesthetic value.
 In an open cornice, the shape of the cornice is similar to that of a wide box cornice, except that both the lookouts and the soffit are absent. It is a lower-cost treatment that requires fewer materials and may even have no fascia board, but it lacks the finished appearance of a box cornice.
In an open cornice, the shape of the cornice is similar to that of a wide box cornice, except that both the lookouts and the soffit are absent. It is a lower-cost treatment that requires fewer materials and may even have no fascia board, but it lacks the finished appearance of a box cornice.
File:Italianate1.png, Projecting cornice of a painted wooden
 In
In architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase.
A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
ends, roof eaves
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural sty ...
, and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect.
A building's projecting cornice may appear to be heavy and hence in danger of falling, particularly on commercial buildings, but it often is actually very light and made of pressed metal.
In classical architecture
InAncient Greek architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenes, whose Ancient Greece, culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor, Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC ...
and its successors using the classical order
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform.
Coming down to the present from Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civiliz ...
s in the tradition of classical architecture
Classical architecture typically refers to architecture consciously derived from the principles of Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or more specifically, from ''De archit ...
, the cornice is the topmost element of the entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and ...
, which consists (from top to bottom) of the cornice, the frieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
, and the architrave
In classical architecture, an architrave (; , also called an epistyle; ) is the lintel or beam, typically made of wood or stone, that rests on the capitals of columns.
The term can also apply to all sides, including the vertical members, ...
.
Where a triangular pediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
is above the entablature, the cornice continues all round the triangle, the two sides being "raking cornices". The vertical space below the cornice is typically decorated by dentils (little teeth) or the larger modillion
A modillion is an ornate bracket, more horizontal in shape and less imposing than a corbel. They are often seen underneath a Cornice (architecture), cornice which helps to support them. Modillions are more elaborate than dentils (literally transl ...
s. The soffit
A soffit is an exterior architectural feature, generally the horizontal, aloft underside of the roof edge. Its archetypal form, sometimes incorporating or implying the projection of rafters or trusses over the exterior of supporting walls, is t ...
, or horizontal space under a projecting cornice, may be elaborately carved with vegetal designs.
In modern residential architecture
Rake
A ''rake'' is an architectural term for an eave or cornice that runs along thegable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
of the roof of a modern residential structure. It may also be called a ''sloping cornice'', a ''raking cornice''. The trim and rafters at this edge are called ''rakes'', ''rake board'', ''rake fascia'', ''verge-boards'', ''barge-boards'' or ''verge-'' or ''barge-rafters''. It is a sloped timber on the outside facing edge of a roof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of tempera ...
running between the ridge
A ridge is a long, narrow, elevated geomorphologic landform, structural feature, or a combination of both separated from the surrounding terrain by steep sides. The sides of a ridge slope away from a narrow top, the crest or ridgecrest, wi ...
and the eave
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural sty ...
. On a typical house, any gable will have two rakes, one on each sloped side. The rakes are often supported by a series of lookouts (sometimes also called ''strong arms'') and may be trimmed with a '' rake fascia'' board (which is not a true fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
...
) on the outside facing edge and a ''rake soffit
A soffit is an exterior architectural feature, generally the horizontal, aloft underside of the roof edge. Its archetypal form, sometimes incorporating or implying the projection of rafters or trusses over the exterior of supporting walls, is t ...
'' along the bottom.
Types
The cornices of a modern residential building will usually be one of three types: a ''box'' cornice, a ''close'' or ''closed'' cornice, or an ''open'' cornice.Box cornice
 Box cornices enclose the cornice of the building with what is essentially a long, narrow box. A box cornice may further be divided into either the ''narrow'' box cornice or the ''wide'' box cornice type. A narrow box cornice is one in which "the projection of the rafter serves as a nailing surface for the soffit board as well as the fascia trim." This is possible if the slope of the roof is fairly steep and the width of the eave relatively narrow. A wide box cornice, a common practice on houses with gentle roof slopes and wide eaves, requires lookouts to support it and provide a surface to attach the soffits securely. Box cornices often have ventilation screens laid over openings cut in the soffits to allow air to circulate within the cornice.
Box cornices enclose the cornice of the building with what is essentially a long, narrow box. A box cornice may further be divided into either the ''narrow'' box cornice or the ''wide'' box cornice type. A narrow box cornice is one in which "the projection of the rafter serves as a nailing surface for the soffit board as well as the fascia trim." This is possible if the slope of the roof is fairly steep and the width of the eave relatively narrow. A wide box cornice, a common practice on houses with gentle roof slopes and wide eaves, requires lookouts to support it and provide a surface to attach the soffits securely. Box cornices often have ventilation screens laid over openings cut in the soffits to allow air to circulate within the cornice.
Close cornice
 A closed or snub cornice is one in which there is no projection of the rafters beyond the walls of the building and, therefore, no soffit or fascia. This type of cornice is easy to construct but provides little aid in dispersing water away from the building and is sometimes considered to lack aesthetic value.
A closed or snub cornice is one in which there is no projection of the rafters beyond the walls of the building and, therefore, no soffit or fascia. This type of cornice is easy to construct but provides little aid in dispersing water away from the building and is sometimes considered to lack aesthetic value.
Open cornice
 In an open cornice, the shape of the cornice is similar to that of a wide box cornice, except that both the lookouts and the soffit are absent. It is a lower-cost treatment that requires fewer materials and may even have no fascia board, but it lacks the finished appearance of a box cornice.
In an open cornice, the shape of the cornice is similar to that of a wide box cornice, except that both the lookouts and the soffit are absent. It is a lower-cost treatment that requires fewer materials and may even have no fascia board, but it lacks the finished appearance of a box cornice.
Cavetto cornice
Ancient Egyptian
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
architectural tradition made special use of large cavetto mouldings as a cornice, with only a short fillet (plain vertical face) above, and a torus
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanarity, coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses inclu ...
moulding (convex semi-circle) below. This cavetto cornice is sometimes also known as an "Egyptian cornice", "hollow and roll" or "gorge cornice". It has been suggested to be a reminiscence in stone architecture of the primitive use of bound bunches of reeds as supports for buildings, the weight of the roof bending their tops out.
The cavetto cornice, often forming less than a quarter-circle, influenced Egypt's neighbours and as well as appearing in early Ancient Greek architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenes, whose Ancient Greece, culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor, Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC ...
, it is seen in Syria and ancient Iran
The history of Iran (also known as Name of Iran, Persia) is intertwined with Greater Iran, which is a socio-cultural region encompassing all of the areas that have witnessed significant settlement or influence exerted by the Iranian peoples and ...
, for example at the Tachara
The Tachara, or the Tachar Château, also referred to as the Palace of Darius the Great, was the exclusive building of Darius I at Persepolis, Iran. It is located 70 km northeast of the modern city of Shiraz in Fars province.
History and ...
palace of Darius I
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
at Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and ...
, completed in 486 BC. Inspired by this precedent, it was then revived by Ardashir I
Ardashir I (), also known as Ardashir the Unifier (180–242 AD), was the founder of the Sasanian Empire, the last empire of ancient Iran. He was also Ardashir V of the Kings of Persis, until he founded the new empire. After defeating the last Par ...
(r. 224–41 AD), the founder of the Sasanian dynasty.
The cavetto took the place of the cymatium in many Etruscan temples, often painted with vertical "tongue" patterns, and combined with the distinctive "Etruscan round moulding", often painted with scales. A typical example may be seen at the reconstructed Etruscan temple at Villa Giulia.
Additional more obscure varieties of cornice include the ''architrave'' cornice, ''bracketed'' cornice, and ''modillion'' cornice.
Cornice return
A ''cornice return'' is an architectural detail that occurs where a roof's horizontal cornice connects to a gable's rake. It is a short horizontal extension of the cornice that occurs on each side of the gable end of the building (see picture of Härnösands rådhus with two of these). The two most common types of cornice return are the ''Greek return'' and the ''soffit return'' (also called a ''boxed'' or ''box'' soffit return). The former includes a sloped hip shape on the inside of the cornice under the eaves, which is sheathed or shingled like the rest of the roof above it and is considered very attractive; the latter is a simple return without these features.As window treatment
The term cornice may also be used to describe a form of hard window treatment along the top edge of a window. In this context, a cornice represents a board (usually wood) placed above the window to conceal the mechanism for opening and closing drapes. If covered in a layer of cloth and given padding, it is sometimes called a soft cornice rather than a hard cornice.Gallery
Italianate
The Italianate style was a distinct 19th-century phase in the history of Classical architecture. Like Palladianism and Neoclassicism, the Italianate style combined its inspiration from the models and architectural vocabulary of 16th-century It ...
residence
File:Louis Sullivan - cornice detail - Wainwright Building, Seventh + Chestnut Streets, Saint Louis, St. Louis City County, MO.jpg, The Wainwright Building by Louis Sullivan
Louis Henry Sullivan (September 3, 1856 – April 14, 1924) was an American architect, and has been called a "father of skyscrapers" and "father of modernism". He was an influential architect of the Chicago school (architecture), Chicago ...
File:Cornice plaster MET 40-170-267.jpg, Cornice with running leaf pattern from Nishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Ni ...
, 10th century, exhibited in the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an Encyclopedic museum, encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the List of largest museums, third-largest museum in the world and the List of larg ...
(New York City)
File:DecorazioneASquame.jpg, Roman cornice of ionic order, from Imperial palace on the Palatine hill in Rome (Flavian epoch)
File:Valence-Corniche-Crabes-Coquillages.jpg, Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
corniche with crabs, shells and seaweeds, in Valence (France)
File:Architecture v11 1905 p229.jpg, Bracketed cornice
File:Jassoy building storefront, Stillwater, Minnesota - DPLA - 903b364123cfa7c5cd7a54b5f8088247 (cropped).jpg, Elaborate cornice on Jassoy Building in Stillwater, Minnesota
See also
*Eaves
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural sty ...
* Geison
References
{{Authority control Columns and entablature Architectural elements