|
National Unity And Armed Forces Day
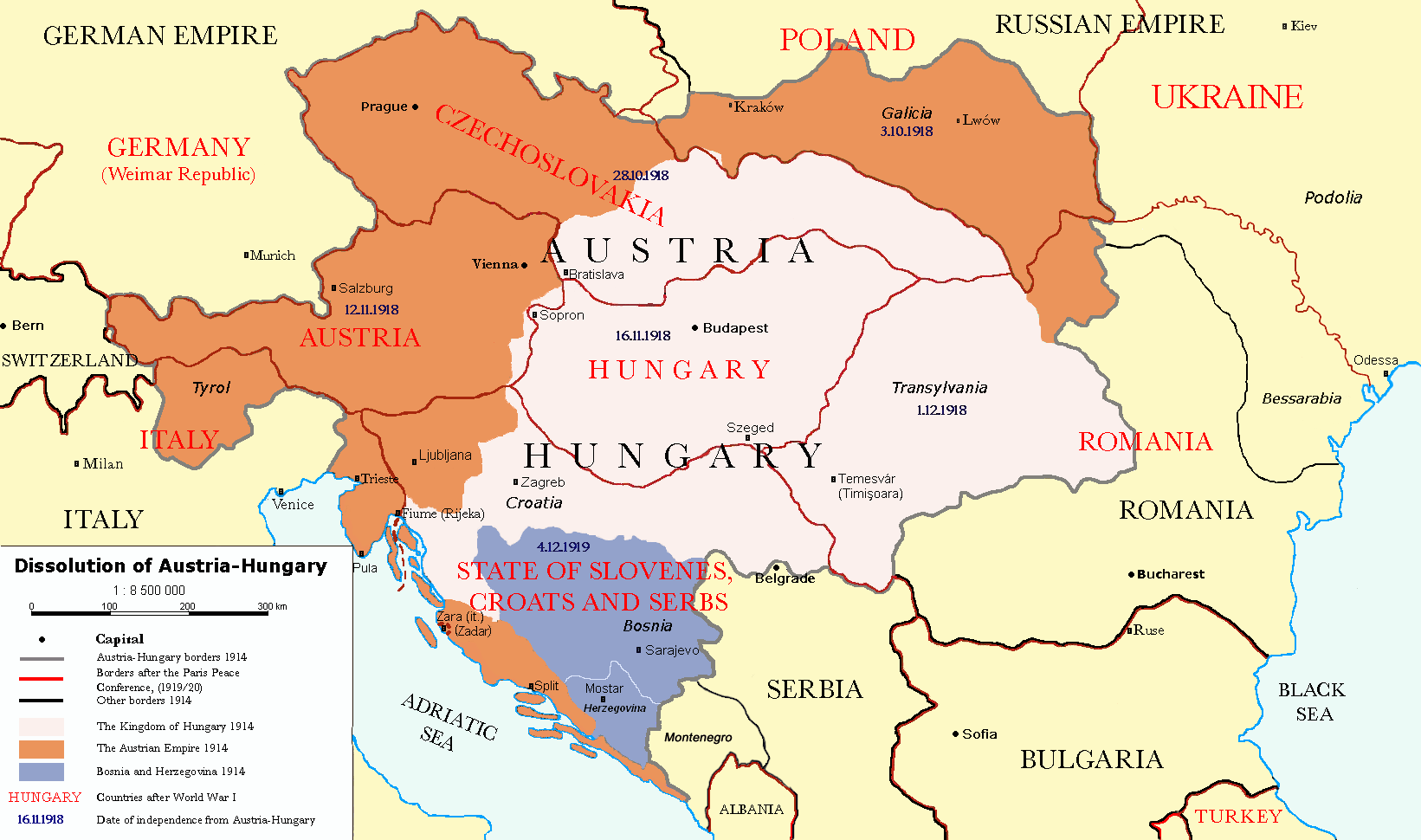
National Unity and Armed Forces Day () is an Public holidays in Italy, Italian national day since 1919 which commemorates the victory in World War I, a war event considered the completion of the process of unification of Italy. It is celebrated every 4 November, which is the anniversary of the armistice of Villa Giusti becoming effective in 1918 declaring Austria-Hungary's surrender. History Italy entered the First World War in 1915 with the aim of completing national unity: for this reason, the Italian intervention in the First World War is also considered the Fourth Italian War of Independence, in a historiographical perspective that identifies in the latter the conclusion of the unification of Italy, whose military actions began during the revolutions of 1848 with the First Italian War of Independence. The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919), Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919) and the Treaty of Rapallo (1920), Treaty of Rapallo (1920) allowed the annexation of Trent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Italy
The president of Italy, officially titled President of the Italian Republic (), is the head of state of Italy. In that role, the president represents national unity and guarantees that Politics of Italy, Italian politics comply with the Constitution of Italy, Constitution. The president is the commander-in-chief of the Italian Armed Forces and chairs the High Council of the Judiciary (Italy), High Council of the Judiciary. The president serves a seven-year term, with no term limits. The incumbent president is former Constitutional Court of Italy, constitutional judge Sergio Mattarella, who was 2015 Italian presidential election, elected on 31 January 2015, and 2022 Italian presidential election, re-elected on 29 January 2022. Qualifications for office The framers of the Constitution of Italy intended for the president to be an elder statesman of some stature. Article 84 states that any Italian citizen who is fifty or older on election day and enjoys civil and political rights c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920 Festa Delle Bandiere
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number) * One of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (1987 film), a 1987 science fiction film * ''19-Nineteen'', a 2009 South Korean film * ''Diciannove'', a 2024 Italian drama film informally referred to as "Nineteen" in some sources Science * Potassium, an alkali metal * 19 Fortuna, an asteroid Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle * "Stone in Focus", officially "#19", a composition by Aphex Twin * "Nineteen", a song from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' by Bad4Good * "Nineteen", a song from the 2001 al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Rome (1924)
The Treaty of Rome was agreed on 27 January 1924, when Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes agreed that Fiume would be annexed to Italy as the Province of Fiume, and the town of Sušak would be part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Fiume and Sušak would have a joint administration of the port facilities. Both towns are now in the city of Rijeka, Croatia. Background After Fiume was under Gabriele D'Annunzio's Italian Regency of Carnaro, the Treaty of Rapallo (1920) created the independent Free State of Fiume, which was immediately recognised by other states, including the United States, France and the United Kingdom. The state survived only one year ''de facto'' and four years ''de jure''. The joint administration of the port was never created. On 24 April 1921, the first general elections for its parliament occurred, and it elected President Riccardo Zanella, the leader of the Autonomist Fiuman Movement. On 3 March 1922, a movement directed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zadar
Zadar ( , ), historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian, ; see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited city in Croatia. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar serves as the seat of Zadar County and of the wider northern Dalmatian region. The city proper covers with a population of 75,082 , making it the second-largest city of the region of Dalmatia and the fifth-largest city in the country. Today, Zadar is a historical center of Dalmatia, Zadar County's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, educational, and transportation centre. Zadar is also the episcopal see of the Archdiocese of Zadar. Because of its rich heritage, Zadar is today one of the most popular Croatian tourist destinations, named "entertainment center of the Adriatic" by ''The Times'' and "Croatia's new capital of cool" by ''The Guardian''. UNESCO's World Heritage Site list included the fortified city of Zadar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), Kingdom of Croatia, the Republic of Venice, the Austrian Empire, and presently the Croatia, Republic of Croatia. Dalmatia is a narrow belt stretching from the island of Rab (island), Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar, Šibenik, and Dubrovnik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvarner Gulf
The Kvarner Gulf (, or ; ; or ) sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal waters. The largest islands within the Kvarner are Cres, Krk, Pag, Rab and Lošinj. A portion of the Kvarner Bay, located between Cres, Krk, Rab and Pag is also called (literally "little Kvarner"; or ), and the portion east of Krk and Rab is called Senj Channel (after the mainland town of Senj). The bay is notable for its depth (more than 100 meters), which allows for the city of Rijeka at its northernmost point to have a sea port that can accommodate Capesize ships. Environment The bay is home to many beaches and tourist locations because of its beautiful waters and warm climate. Important Bird Area Collectively, the islands of the Kvarner Gulf form the Kvarner Islands Important Bird Area (IBA), designated as such by BirdLife International because it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at the top of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Kvarner Gulf, the peninsula is shared by three countries: Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy,Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries'' John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe'' Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), 90% of its area being part of Croatia. Most of Croatian Istria is part of Istria County. Geography The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria mountain range; the rivers Dragonja/Dragogna, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian March
The Julian March ( Croatian and ), also called Julian Venetia (; ; ; ), is an area of southern Central Europe which is currently divided among Croatia, Italy, and Slovenia.''Contemporary History on Trial: Europe Since 1989 and the Role of the Expert Historian'' by Harriet Jones, Kjell Ostberg, Nico Randeraad p. 155 The term was coined in 1863 by the Italian Graziadio Isaia Ascoli, a native of the area, to demonstrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol ( ; ; ), often known in English as Trentino-South Tyrol or by its shorter Italian name Trentino-Alto Adige, is an Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Italy, located in the Northern Italy, northern part of the country. The region has a population of 1.1 million, of whom 62% speak Italian language as their mother tongue, 30% speak German language, German and several foreign languages are spoken by immigrant communities. Since the 1970s, most legislative and administrative powers have been transferred to the two self-governing Provinces of Italy, provinces that make up the region: the province of Trento, commonly known as Trentino, and the province of Bolzano, commonly known as South Tyrol (). In South Tyrol, South Tyrol#Languages, German remains the sizeable majority language. From the 9th century until 1801, the region was part of the Holy Roman Empire. After being part of the short-lived Italian Republic (N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Rapallo (1920)
The Treaty of Rapallo was an agreement between the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes in the aftermath of the First World War. It was intended to settle the Adriatic question, which referred to Italian claims over territories promised to the country in return for its entry into the war against Austria-Hungary, claims that were made on the basis of the 1915 Treaty of London. The wartime pact promised Italy large areas of the eastern Adriatic. The treaty, signed on 12 November 1920 in Rapallo, Italy, generally redeemed the promises of territorial gains in the former Austrian Littoral by awarding Italy territories generally corresponding to the peninsula of Istria and the former Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, with the addition of the Snežnik Plateau, in addition to what was promised by the London treaty. The articles regarding Dalmatia were largely ignored. Instead, in Dalmatia, Italy received the city of Zadar and several islands. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919)
The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye () was signed on 10 September 1919 by the victorious Allies of World War I on the one hand and by the Republic of German-Austria on the other. Like the Treaty of Trianon with Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946), Hungary and the Treaty of Versailles with the Weimar Republic, it contained the Covenant of the League of Nations, Covenant of the League of Nations and as a result was not ratified by the United States but was followed by the US–Austrian Peace Treaty (1921), US–Austrian Peace Treaty of 1921. The treaty signing ceremony took place at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye. Background As a preamble, on 21 October 1918, 208 German-speaking delegates of the Austrian Imperial Council (Austria), Imperial Council had convened in a "provisional national assembly of German-Austria" at the Palais Niederösterreich, Lower Austrian Landtag. When the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Army culminated at the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, the Social D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Italian War Of Independence
The First Italian War of Independence (), part of the ''Risorgimento'' or unification of Italy, was fought by the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) and Italian volunteers against the Austrian Empire and other conservative states from 23 March 1848 to 22 August 1849 in the Italian peninsula. The conflict was preceded by the outbreak of the Sicilian revolution of 1848 against the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies. It was precipitated by riots in the cities of Milan (Five Days of Milan, Five Days) and Venice, which rebelled against Austria and established governments. The part of the conflict which was fought by King Charles Albert of Sardinia against Austria in Northern Italy was a royal war and popular war, royal war and consisted of two campaigns. In both campaigns, the Kingdom of Sardinia attacked the Austrian Empire and after initial victories, Sardinia was decisively defeated and lost the war. The decisive events of the first and second campaigns we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |