Julian March on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Julian March ( Croatian and ), also called Julian Venetia (; ; ; ), is an area of southern
p. 155 The term was coined in 1863 by the Italian
The term was later endorsed by Italian irredentists, who sought to annex regions in which ethnic Italians made up most (or a substantial portion) of the population: the Austrian Littoral,
"Clash of civilisations"
, ''Italian Historical Society Journal,'' Vol.12, No.2, p.4 A contemporary Italian autonomous region, bordering on
 The term "Julian March" is a partial translation of the Italian name "Venezia Giulia" (or "Julian Venetia"), coined by the Italian Jewish historical linguist Graziadio Ascoli, who was born in Gorizia. The term "
The term "Julian March" is a partial translation of the Italian name "Venezia Giulia" (or "Julian Venetia"), coined by the Italian Jewish historical linguist Graziadio Ascoli, who was born in Gorizia. The term "
 At the end of the
At the end of the
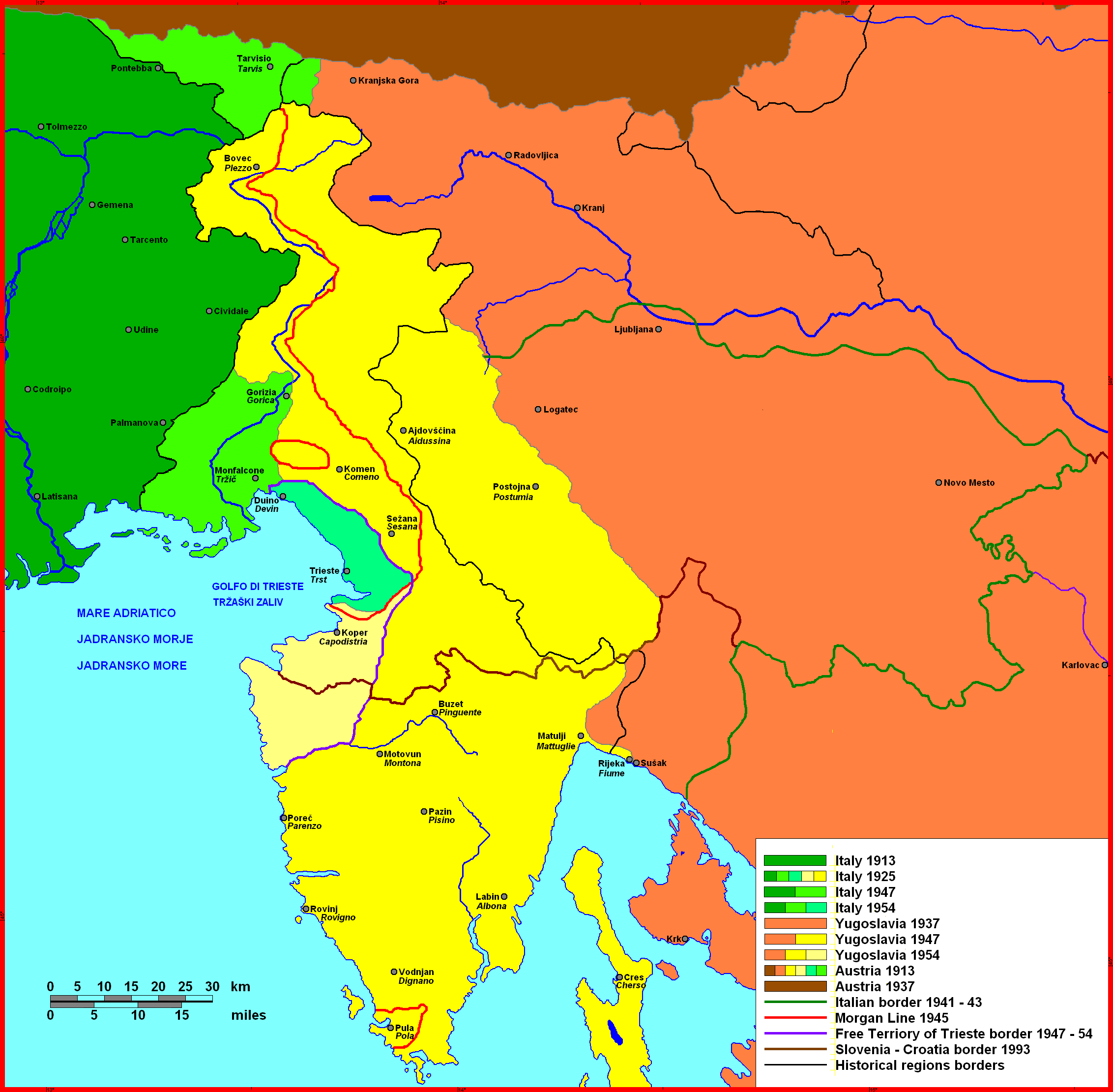 The Kingdom of Italy annexed the region after World War I according to the Treaty of London and later Treaty of Rapallo, comprising most of the former
The Kingdom of Italy annexed the region after World War I according to the Treaty of London and later Treaty of Rapallo, comprising most of the former
 The Western allies adopted the term "Julian March" as the name for the territories which were contested between Italy and the People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia between 1945 and 1947. The
The Western allies adopted the term "Julian March" as the name for the territories which were contested between Italy and the People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia between 1945 and 1947. The
 Two major ethnolinguistic clusters were unified in the region. The western portion was inhabited primarily by Italians (Italian language, Italian, Venetian language, Venetian and Friulian language, Friulian were the three major languages), with a small Istriot language, Istriot-speaking minority. The eastern and northern areas were inhabited by South Slavs (
Two major ethnolinguistic clusters were unified in the region. The western portion was inhabited primarily by Italians (Italian language, Italian, Venetian language, Venetian and Friulian language, Friulian were the three major languages), with a small Istriot language, Istriot-speaking minority. The eastern and northern areas were inhabited by South Slavs (
 The standard Italian language was common among educated people in Trieste,
The standard Italian language was common among educated people in Trieste,
File:Flag of the Austrian Littoral.svg, alt=, Official flag of the Austrian Littoral, Austrian Litoral (1849–1919)
File:Flag of the Austrian Littoral with coat of arms.svg, alt=, Official flag of the Austrian Littoral, Austrian Litoral (1849–1919) (with coat of arms)
The Problem of Trieste and the Italo-Yugoslav Border by Glenda SlugaIstituto Giuliano: an Italian association dedicated to the promotion of culture and tradition in the Julian MarchIstituto regionale per la storia del movimento di liberazione nel Friuli-Venezia Giulia: an Italian association dedicated to the study of the history of resistance war in Friuli and Julian March
{{Authority control Friuli-Venezia Giulia Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy History of Istria Italians of Croatia Modern history of Slovenia 1860s neologisms
Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
which is currently divided among Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, and Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
.''Contemporary History on Trial: Europe Since 1989 and the Role of the Expert Historian'' by Harriet Jones, Kjell Ostberg, Nico Randeraadp. 155 The term was coined in 1863 by the Italian
linguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
Graziadio Isaia Ascoli, a native of the area, to demonstrate that the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City ...
, Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
, Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
, and Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
(then all part of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
) shared a common Italian linguistic identity. Ascoli emphasized the Augustan partition of Roman Italy
Roman Italy is the period of ancient Italian history going from the founding of Rome, founding and Roman expansion in Italy, rise of ancient Rome, Rome to the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire; the Latin name of the Italian peninsula ...
at the beginning of the Empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
, when ''Venetia et Histria
Venetia et Histria (Latin: ''Regio X Venetia et Histria'') was an administrative subdivision in the northeast of Roman Italy. It was originally created by Augustus as the tenth ''regio'' in 7 AD alongside the nine other ''regiones''. The region h ...
'' was ''Regio X'' (the Tenth Region).Marina Cattaruzza, ''Italy and Its Eastern Border, 1866–2016'', Routledge 2016 - ch. IThe term was later endorsed by Italian irredentists, who sought to annex regions in which ethnic Italians made up most (or a substantial portion) of the population: the Austrian Littoral,
Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
, Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
. The Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was built upon th ...
promised the regions to Italy in the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in exchange for Italy's joining the Allied Powers in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The secret 1915 Treaty of London promised Italy territories largely inhabited by Italians (such as Trentino) in addition to those largely inhabited by Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
or Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
; the territories housed 421,444 Italians, and about 327,000 ethnic Slovenes.Lipušček, U. (2012) ''Sacro egoismo: Slovenci v krempljih tajnega londonskega pakta 1915'', Cankarjeva založba, Ljubljana. Cresciani, Gianfranco (2004"Clash of civilisations"
, ''Italian Historical Society Journal,'' Vol.12, No.2, p.4 A contemporary Italian autonomous region, bordering on
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
, is named Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and a ...
("Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
and Julian Venetia").
Etymology
March
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 2 ...
" in "Julian March" refers to a medieval European designation for a borderland or frontier district, more specifically, a buffer zone between different realms.
In an 1863 newspaper article, Ascoli focused on a wide geographical area north and east of Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
which was under Austrian rule; he called it Triveneto
The Triveneto () or (; ; ; ), also often referred to as North-Eastern Italy or simply North-EastNot to be misunderstood with the statistical region Northeast Italy, which includes Emilia-Romagna, too. ( or ), is a historical region of Italy. The ...
("the three Venetian regions"). Ascoli divided Triveneto into three parts:
*Euganean Venetia (''Venezia Euganea'' or ''Venezia propria''; Venetia in the strict sense), made up of Italy's Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
region and most of the territory of Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
(roughly corresponding to the present Italian provinces of Udine
Udine ( ; ; ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the middle of the Friuli-Venezia Giulia region, between the Adriatic Sea and the Carnic Alps. It is the capital of the Province of Udine, Regional decentralization entity ...
and Pordenone
Pordenone (; Venetian language, Venetian and ) is a city and (municipality) in the Italy, Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, the capital of the Province of Pordenone, Regional decentralization entity of Pordenone.
The name comes from Lati ...
)
*Tridentine Venetia ('' Venezia Tridentina''): the present Italian region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol ( ; ; ), often known in English as Trentino-South Tyrol or by its shorter Italian name Trentino-Alto Adige, is an Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Italy, located in the ...
*Julian Venetia (''Venezia Giulia''): "Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
... including the land between the Venetia in the strict sense of the term, the Julian Alps
The Julian Alps (, , , , ) are a mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps that stretches from northeastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2,864 m at Mount Triglav, the highest peak in Slovenia. A large part of the Julian Alps is inclu ...
, and the sea"
According to this definition, Triveneto overlaps the ancient Roman region of ''Regio X – Venetia et Histria'' introduced by Emperor Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
in his administrative reorganization of Italy at the beginning of the first century AD. Ascoli (who was born in Gorizia) coined his terms for linguistic and cultural reasons, saying that the languages spoken in the three areas were substantially similar. His goal was to stress to the ruling Austrian Empire the region's Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and Venetian roots and the importance of the Italian linguistic element.
The term "Venezia Giulia" did not catch on immediately, and began to be used widely only in the first decade of the 20th century. It was used in official administrative acts by the Italian government in 1922–1923 and after 1946, when it was included in the name of the new region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and a ...
.
History
Early Middle Ages to the Republic of Venice
 At the end of the
At the end of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
and the beginning of the Migration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories ...
, the area had linguistic boundaries between speakers of Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
(and its dialects
A dialect is a variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standardized varieties as well as vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or iso ...
) and the Germanic- and Slavic-language speakers who were moving into the region. Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
first arrived in present-day Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
and its surrounding areas between the fourth and sixth centuries. They were followed by the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
, who appeared on the borders of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
around the sixth century and settled in the Eastern Alps
The Eastern Alps are usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley, up to the Splügen Pass at the Main chain of the Alps, Alpine divide, and down the Liro (Como), Liro River to Lake Como in the south. ...
between the sixth and eighth centuries. In Byzantine Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, on the east shore of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
, several city-states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
had limited autonomy. The Slavs retained their languages in the interior, and local Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
(followed by Venetian and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
) continued to be spoken on the coast.
Beginning in the early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, two main political powers shaped the region: the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
and the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
(the dukes and, later, archdukes of Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
). During the 11th century, Venice began building an overseas empire ('' Stato da Màr'') to establish and protect its commercial routes in the Adriatic and southeastern Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
s. Coastal areas of Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
and Dalmazia were key parts of these routes since Pietro II Orseolo
Pietro II Orseolo (961−1009) was the Doge of Venice from 991 to 1009, and a member of the House of Orseolo. He began the period of eastern expansion of Venice that lasted for the better part of 500 years. He secured his influence in the Dalma ...
, the Doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ) – in Italian, was the doge or highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice (697–1797). The word derives from the Latin , meaning 'leader', and Venetian Italian dialect for 'duke', highest official of the ...
, established Venetian rule in the high and middle Adriatic around 1000.F. C. Lane, ''Venice. A maritime Republic'', The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1973 The Venetian presence was concentrated on the coast, replacing Byzantine rule and confirming the political and linguistic separation between coast and interior. The Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
began expanding toward the Italian interior ('' Stato da Tera'') in 1420, acquiring the Patriarchate of Aquileia
The Patriarchate of Aquileia was an episcopal see and ecclesiastical province in northeastern Italy, originally centered in the ancient city of Aquileia, situated near the northern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It emerged in the 4th century as a m ...
(which included a portion of modern Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
—the present-day provinces of Pordenone
Pordenone (; Venetian language, Venetian and ) is a city and (municipality) in the Italy, Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, the capital of the Province of Pordenone, Regional decentralization entity of Pordenone.
The name comes from Lati ...
and Udine
Udine ( ; ; ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the middle of the Friuli-Venezia Giulia region, between the Adriatic Sea and the Carnic Alps. It is the capital of the Province of Udine, Regional decentralization entity ...
—and part of internal Istria).
The Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
held the March of Carniola
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 ...
, roughly corresponding to the central Carniola
Carniola ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region still tend to identify with its traditional parts Upp ...
n region of present-day Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
(part of their holdings in Inner Austria), since 1335. During the next two centuries, they gained control of the Istrian cities of Pazin
Pazin (, ) is a town in western Croatia, the administrative seat of Istria County. It is known for the medieval Pazin Castle, the former residence of the Istrian margraves.
Geography
The town had a population of 8,638 in 2011, of which 4,386 li ...
and Rijeka-Fiume, the port of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
(with Duino
Duino (, ) is today a seaside resort on the northern Adriatic Sea, Adriatic coast. It is a ''hamlet (place), hamlet'' of Duino-Aurisina, a municipality (''comune'') of the Friuli–Venezia Giulia region of northeastern Italy. The settlement, pict ...
), Gradisca and Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
(with its county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
in Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
).
Republic of Venice to 1918
The region was relatively stable from the 16th century to the 1797fall of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice was dissolved and dismembered by the French general Napoleon Bonaparte and the Habsburg monarchy on 12 May 1797, ending approximately 1,100 years of its existence. It was the final action of Napoleon's Italian campaign ...
, which was marked by the Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
between Austria and France. The Habsburgs gained Venetian lands on the Istrian Peninsula and the Quarnero (Kvarner) islands, expanded their holdings in 1813 with Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's defeats and the dissolution of the French Illyrian provinces
The Illyrian Provinces were an autonomous province of France during the First French Empire that existed under Napoleonic Rule from 1809 to 1814. The province encompassed large parts of modern Italy and Croatia, extending their reach further e ...
. Austria gained most of the republic's territories, including the Adriatic coast, Istria and portions of present-day Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
(such as the city of Karlstadt).
Habsburg rule abolished political borders which had divided the area for almost 1,000 years. The territories were initially assigned to the new Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
, which became the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City ...
in 1849. This was established as a crown land
Crown land, also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. Today, in Commonwealth realm ...
(''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, consisting of three regions: the Istrian peninsula, Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (; ; ), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled "Goritz", was a crown land of the Habsburg dynasty within the Austrian Littoral on the Adriatic Sea, in what is now a multilingual border area of ...
, and the city of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
.
The Italian-Austrian war of 1866, followed by the passage of what was then known as Veneto (the current Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
and Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
regions, except for the province of Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
) to Italy, did not directly affect the Littoral; however, a small community of Slavic speakers in northeastern Friuli (an area known as Slavia Friulana – Beneška Slovenija) became part of the Kingdom of Italy. Otherwise, the Littoral lasted until the end of the Austrian Empire in 1918.
The Italians in Julian March supported the Italian Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
: as a consequence, the Austrians saw the Italians as enemies and favored the Slav communities of Julian March. During the meeting of the Council of Ministers of 12 November 1866, Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
outlined a wide-ranging project aimed at the Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people, and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nati ...
or Slavization of the areas of the empire with an Italian presence:
Istrian Italians were more than 50% of the total population of Istria for centuries, while making up about a third of the population in 1900.
Kingdom of Italy (1918–1943)
 The Kingdom of Italy annexed the region after World War I according to the Treaty of London and later Treaty of Rapallo, comprising most of the former
The Kingdom of Italy annexed the region after World War I according to the Treaty of London and later Treaty of Rapallo, comprising most of the former Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City ...
(Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (; ; ), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled "Goritz", was a crown land of the Habsburg dynasty within the Austrian Littoral on the Adriatic Sea, in what is now a multilingual border area of ...
, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
), south-western portions of the former Duchy of Carniola
The Duchy of Carniola (, , ) was an imperial estate of the Holy Roman Empire, established under House of Habsburg, Habsburg rule on the territory of the former East Frankish March of Carniola in 1364. A hereditary land of the Habsburg monarc ...
, and the current Italian municipalities of Tarvisio
Tarvisio ( German and ; ) is a (municipality) in the Regional Decentralization Entity of Udine, in the autonomous Friuli-Venezia Giulia region of Italy.
Geography
The town is in the Canal Valley (''Val Canale'') between the Carnic Alps and Ka ...
, Pontebba and Malborghetto Valbruna which had been Carinthian (aside from Fusine in Valromana in eastern Tarvisio, which had been part of Carniola). The annexed areas included many partially or fully Slovene or Croat areas. The island of Krk
Krk (; ; ; ; archaic German: ''Vegl'', ; ) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of Primorje-Gorski Kotar county. Krk is tied with Cres as the largest Adriatic island, depending o ...
and the municipality of Kastav
Kastav is a town in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County, western part of Croatia, built on a 365 m high hill overlooking the Kvarner Gulf on the northern coast of the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic. It is in close vicinity of Rijeka, the largest port in Croatia ...
, which had formerly been part of the Austrian Littoral, became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () has been its colloq ...
(renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929).
Rijeka-Fiume, which had enjoyed special status
Special or specials may refer to:
Policing
* Specials, Ulster Special Constabulary, the Northern Ireland police force
* Specials, Special Constable, an auxiliary, volunteer, or temporary; police worker or police officer
* Special police forces
...
within the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen
The Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen (), informally Transleithania (meaning the lands or region "beyond" the Leitha River), were the Hungarian territories of Austria-Hungary, throughout the latter's entire existence (30 March 1867 – 16 ...
(the Hungarian part of Austria-Hungary), became an independent city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
in the Treaty of Rapallo: the Free State of Fiume
The Free State of Fiume () was an independent free state that existed from 1920 to 1924. Its territory of comprised the city of Fiume (today Rijeka, Croatia) and rural areas to its north, with a corridor to its west connecting it to the Kingdo ...
. It was abolished following the 1924 Treaty of Rome and divided between Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.
The new provinces of Gorizia (which was merged with the Province of Udine
The province of Udine (; ; ; ; ) was a province in the autonomous Friuli-Venezia Giulia region of Italy, bordering Austria and Slovenia, with the capital in the city of Udine. Abolished on 30 September 2017, it was reestablished in 2019 as the Re ...
between 1924 and 1927), Trieste, Pola and Fiume (after 1924) were created. Tarvisio, Pontebba, Malborghetto Valbruna, and the westernmost part of the former Littoral around Cervignano del Friuli remained part of Udine (and so Euganean Venetia) after 1927.
Italians lived primarily in cities and along the coast, and Slavs inhabited the interior. Fascist
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural soci ...
persecution, "centralising, oppressive and dedicated to the forcible Italianisation of the minorities", caused the emigration of about 105,000 Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
and Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
from the Julian March—around 70,000 to Yugoslavia and 30,000 to Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
. Several thousand Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
moved from Yugoslavia to Italy after 1918, many to Istria and Trieste.
In response to the Fascist Italianization
Italianization ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or assimilation. It is also known for a process organized by the Kingdom of Italy to force cultural and ethnic assimilation of the nati ...
of Slovene areas, the militant anti-Fascist
Anti-fascism is a political movement in opposition to fascist ideologies, groups and individuals. Beginning in European countries in the 1920s, it was at its most significant shortly before and during World War II, where the Axis powers were op ...
organization TIGR
TIGR (an acronym of the place-names ''Trieste, Trst'', ''Istria, Istra'', ''Gorizia, Gorica'', and ''Rijeka, Reka''), fully the Revolutionary Organization of the Julian March T.I.G.R. (), was a Militant (word), militant Anti-fascism, anti-fascis ...
emerged in 1927. TIGR co-ordinated Slovene resistance against Fascist Italy
Fascist Italy () is a term which is used in historiography to describe the Kingdom of Italy between 1922 and 1943, when Benito Mussolini and the National Fascist Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. Th ...
until it was dismantled by the secret police
image:Putin-Stasi-Ausweis.png, 300px, Vladimir Putin's secret police identity card, issued by the East German Stasi while he was working as a Soviet KGB liaison officer from 1985 to 1989. Both organizations used similar forms of repression.
Secre ...
in 1941, and some former members joined the Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, and Slovene language, Slovene: , officially the National Liberation Army and Partisan Detachments of Yugoslavia sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska i partizanski odr ...
. The Slovene Partisans emerged that year in the occupied Province of Ljubljana
The Province of Ljubljana (, , ) was the central-southern area of Slovenia. In 1941, it was annexed by the Kingdom of Italy, and after 1943 occupied by Nazi Germany. Created on May 3, 1941, it was abolished on May 9, 1945, when the Slovene Parti ...
, and spread by 1942 to the other Slovene areas which had been annexed by Italy twenty years earlier.
German occupation and resistance (1943–1945)
After the Italian armistice of September 1943, many local uprisings took place. The town ofGorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
was temporarily liberated by partisans, and a liberated zone in the Upper Soča
Soča (, in Slovene) or Isonzo (, in Italian; other names: ; ; or ') is a long river that flows through western Slovenia () and northeastern Italy ().
An Alpine river in character, its source lies in the Trenta Valley in the Julian Alps ...
Valley known as the Kobarid Republic lasted from September to November 1943. The German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
began to occupy the region and encountered severe resistance from Yugoslav partisans, particularly in the lower Vipava Valley
The Vipava Valley (; , , ) is a valley in the Slovenian Littoral, roughly between the village of Podnanos to the east and the border with Italy to the west. The main towns are Ajdovščina and Vipava.
Geography
The narrow valley of the Vipav ...
and the Alps. Most of the lowlands were occupied by the winter of 1943, but Yugoslav resistance remained active throughout the region and withdrew to the mountains.
In the aftermath of the fall 1943 Italian armistice, the first of what became known as the Foibe massacres
The foibe massacres (; ; ), or simply the foibe, refers to ethnic cleansing, mass killings and deportations both during and immediately after World War II, mainly committed by Yugoslav Partisans and OZNA in the Italian Empire, then-Italian terri ...
occurred (primarily in present-day Croatian Istria). The Germans established the Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral, officially part of the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic (, ; RSI; , ), known prior to December 1943 as the National Republican State of Italy (; SNRI), but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò (, ), was a List of World War II puppet states#Germany, German puppe ...
but under ''de facto'' German administration, that year. Many areas, (especially north and north-east of Gorizia) were controlled by the partisan resistance, which was also active on the Karst Plateau
The Karst Plateau or the Karst region (, ), also locally called Karst, is a karst plateau region extending across the border of southwestern Slovenia and northeastern Italy.
It lies between the Vipava Valley, the low hills surrounding the val ...
and interior Istria. The Nazis tried to repress the Yugoslav guerrillas with reprisals against the civilian population; entire villages were burned down, and thousands of people were interned in Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps (), including subcamp (SS), subcamps on its own territory and in parts of German-occupied Europe.
The first camps were established in March 1933 immediately af ...
. However, the Yugoslav resistance took over most of the region by the spring of 1945.
Italian resistance in the operational zone was active in Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
and weaker in the Julian March, where it was confined to intelligence and underground resistance in the larger towns (especially Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and Pula
Pula, also known as Pola, is the largest city in Istria County, west Croatia, and the List of cities and towns in Croatia, seventh-largest city in the country, situated at the southern tip of the Istria, Istrian peninsula in western Croatia, wi ...
). In May 1945, the Yugoslav Army entered Trieste; over the following days, virtually the entire Julian March was occupied by Yugoslav forces. Retaliation against real (and potential) political opponents occurred, primarily to the Italian population.
Contested region (1945–1954)
 The Western allies adopted the term "Julian March" as the name for the territories which were contested between Italy and the People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia between 1945 and 1947. The
The Western allies adopted the term "Julian March" as the name for the territories which were contested between Italy and the People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia between 1945 and 1947. The Morgan Line
The Morgan Line (, ) was the line of demarcation set up after World War II in the region known as Julian March which prior to the war belonged to the Kingdom of Italy. The Morgan Line was the border between two military administrations in the reg ...
was drawn in June 1945, dividing the region into two militarily administered zones. Zone B was under Yugoslav administration and excluded the cities of Pula, Gorizia, Trieste, the Soča
Soča (, in Slovene) or Isonzo (, in Italian; other names: ; ; or ') is a long river that flows through western Slovenia () and northeastern Italy ().
An Alpine river in character, its source lies in the Trenta Valley in the Julian Alps ...
Valley and most of the Karst Plateau, which were under joint British-American administration. During this period, many Italians left the Yugoslav-occupied area.
In 1946, U.S. President Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
ordered an increase in U.S. troops in their occupation zone (Zone A) and the reinforcement of air forces in northern Italy after Yugoslav forces shot down two U.S. Army transport planes. An agreement on the border was chosen from four proposed solutions at the Paris Peace Conference, 1946, Paris Peace Conference that year. Yugoslavia acquired the northern part of the region east of Gorizia, most of Istria and the city of Fiume. A Free Territory of Trieste was created, divided into two zones—one under Allied and the other under Yugoslav military administration. Tensions continued, and in 1954 the territory was abolished and divided between Italy (which received the city of Trieste and its surroundings) and Yugoslavia, under the terms of the London Memorandum.
Since 1954
In Slovenia the Julian March is known as the Slovene Littoral, encompassing the regions of Goriška and Slovenian Istria. In Croatia, the traditional name ofIstria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
is used. After the divisions of 1947 and 1954, the term "Julian March" survived in the name of the Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and a ...
region of Italy.
The Treaty of Osimo was signed on 10 November 1975 by the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Italian Republic in Osimo, Italy, to definitively divide the Free Territory of Trieste between the two states: the port city of Trieste with a narrow coastal strip to the north-west (Zone A) was given to Italy; a portion of the north-western part of the Istrian peninsula (Zone B) was given to Yugoslavia. The treaty became effective on 11 October 1977. For the Italian Government, the treaty was signed by Mariano Rumor, Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Italy), Minister for Foreign Affairs. For Yugoslavia, the treaty was signed by Miloš Minić, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Yugoslavia), Federal Secretary for Foreign Affairs.
Ethnolinguistic structure
 Two major ethnolinguistic clusters were unified in the region. The western portion was inhabited primarily by Italians (Italian language, Italian, Venetian language, Venetian and Friulian language, Friulian were the three major languages), with a small Istriot language, Istriot-speaking minority. The eastern and northern areas were inhabited by South Slavs (
Two major ethnolinguistic clusters were unified in the region. The western portion was inhabited primarily by Italians (Italian language, Italian, Venetian language, Venetian and Friulian language, Friulian were the three major languages), with a small Istriot language, Istriot-speaking minority. The eastern and northern areas were inhabited by South Slavs (Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
and Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
), with small Montenegrins (ethnic group), Montenegrin (Peroj) and Serbs, Serb minorities.
Other ethnic groups included Istro-Romanians in eastern Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Carinthian Ethnic Germans, Germans in the Canale Valley and smaller German language, German- and Hungarian language, Hungarian-speaking communities in larger urban centres, primarily members of the former Austro-Hungarian elite. This is illustrated by the 1855 ethnographic map of the Austrian Empire compiled by Karl von Czoernig-Czernhausen and issued by the Austrian Imperial and Royal, ''k. u. k.'' department of statistics. According to the 1910–1911 Austrian census, the Austrian Littoral (which would be annexed by Italy from 1920 to 1924) had a population of 978,385. Italian was the everyday language (''Umgangsprache'') of 421,444 people (43.1 percent); 327,230 (33.4 percent) spoke Slovene, and 152,500 (15.6 percent) spoke Croatian. About 30,000 people (3.1 percent) spoke German, 3,000 (0.3 percent) spoke Hungarian, and small clusters of Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian and Czech language, Czech speakers existed. The Friulian language, Friulian, Venetian language, Venetian and Istriot languages were considered Italian; an estimated 60,000 or more "Italian" speakers (about 14 percent) spoke Friulian.
Romance languages
Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
, Istria and Fiume/Rijeka. In Trieste (and to a lesser extent in Istria), Italian was the predominant language in primary education. The Italian-speaking elite dominated the governments of Trieste and Istria under Austro-Hungarian rule, although they were increasingly challenged by Slovene and Croatian political movements. Before 1918, Trieste was the only self-governing Austro-Hungarian unit in which Italian speakers were the majority of the population.
Most of the Romance languages, Romance-speaking population did not speak standard Italian as their native language, but two other closely related Romance languages: Friulian and Venetian.It should be understood that Italian language's division among regional dialects has always been very pronounced. Due to the lack of a central Italian state, a standard Italian language did not actually exist until the second half of the 19th century, nor there was, until then, an agreement among scholars on this language's features. As a result, only 2.5% of Italy's population could speak the Italian standardized language properly when the nation was unified in 1861. See for example the Italian language#History, Italian language historic evolution and There was no attempt to introduce Venetian into education and administration.
Friulian was spoken in the south-western lowlands of the county of Gorizia and Gradisca (except for the Monfalcone-Grado area, where Venetian was spoken), and in the town of Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
. Larger Friulian-speaking centres included Cormons, Cervignano del Friuli, Cervignano, and Gradisca d'Isonzo. A dialect of Friulian (Tergestine) was spoken in Trieste and Muggia, evolving into a Venetian dialect during the 18th century. According to contemporary estimates, three-quarters of the Italians in the county of Gorizia and Gradisca were native Friulian speakers—one-quarter of the county's population, and seven to eight percent of the population of the Julian March.
Venetian dialects were concentrated in Trieste, Rijeka and Istria, and the Istro-Venetian dialect was the predominant language of the west Istrian coast. In many small west Istrian towns, such as Koper (Capodistria), Piran (Pirano) or Poreč (Parenzo), the Venetian-speaking majority reached 90 percent of the population and 100 percent in Umag (Umago) and Muggia. Venetian was also a strong presence on Istria's Cres-Lošinj archipelago and in the peninsula's eastern and interior towns such as Motovun, Labin, Plomin and, to a lesser extent, Buzet and Pazin
Pazin (, ) is a town in western Croatia, the administrative seat of Istria County. It is known for the medieval Pazin Castle, the former residence of the Istrian margraves.
Geography
The town had a population of 8,638 in 2011, of which 4,386 li ...
. Although Istro-Venetian was strongest in urban areas, clusters of Venetian-speaking peasants also existed. This was especially true for the area around Buje and Grožnjan in north-central Istria, where Venetian spread during the mid-19th century (often in the form of a Venetian-Croat pidgin). In the county of Gorizia and Gradisca, Venetian was spoken in the area around Monfalcone and Ronchi dei Legionari, Ronchi (between the lower Isonzo River and the Karst Plateau) in an area popularly known as Bisiacaria and in the town of Grado, Italy, Grado. In Trieste the local Venetian dialect (known as Triestine) was widely spoken, although it was the native language of only about half the city's population. In Rijeka-Fiume, a form of Venetian known as Fiumano emerged during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and became the native language of about half the city's population.
In addition to these two large language groups, two smaller Romance communities existed in Istria. In the south-west, on the coastal strip between Pula and Rovinj, the archaic Istriot language was spoken. In some villages of eastern Istria, north of Labin, the Istro-Romanian language was spoken by about 3,000 people.
South Slavic languages
Slovene language, Slovene was spoken in the north-eastern and southern parts of Gorizia and Gradisca (by about 60 percent of the population), in northern Istria and in the Inner Carniolan areas annexed by Italy in 1920 (Postojna, Vipava, Slovenia, Vipava, Ilirska Bistrica and Idrija). It was also the primary language of one-fourth to one-third of the population of Trieste. Smaller Slovene-speaking communities lived in the Canale Valley (Carinthian Slovenes), in Rijeka and in larger towns outside the Slovene Lands (especiallyPula
Pula, also known as Pola, is the largest city in Istria County, west Croatia, and the List of cities and towns in Croatia, seventh-largest city in the country, situated at the southern tip of the Istria, Istrian peninsula in western Croatia, wi ...
, Monfalcone, Gradisca d'Isonzo and Cormons). Slavia Friulana – Beneška Slovenija, the community living since the eighth century in small towns (such as Resia, Friuli, Resia) in the valleys of the Natisone, Torre River, Torre and Judrio Rivers in Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
, has been part of Italy since 1866.
A variety of Slovene dialects were spoken throughout the region. The Slovene linguistic community in the Julian March was divided into as many as 11 dialects (seven larger and four smaller dialects), belonging to three of the Slovene dialects#Regional groups, seven dialect groups into which Slovene is divided. Most Slovenes were fluent in standard Slovene, with the exception of some northern Istrian villages (where primary education was in Italian and the Slovene national movement penetrated only in the late 19th century) and the Carinthian Slovenes in the Canale Valley, who were Germanisation, Germanised until 1918 and frequently spoke only the local dialect.
Slovene-Italian bilingualism was present only in some north-west Istrian coastal villages and the confined semi-urban areas around Gorizia and Trieste, while the vast majority of Slovene speakers had little (or no) knowledge of Italian; German language, German was the predominant second language of the Slovene rural population.
Croatian was spoken in the central and eastern Istrian peninsula, on the Cres-Lošinj archipelago; it was the second-most-spoken language (after Venetian) in the town of Rijeka. The Kajkavian dialect of Serbo-Croatian was spoken around Buzet in north-central Istria; Čakavian was predominant in all other areas, frequently with strong Kajkavian and Venetian vocabulary influences. Italian-Croatian bilingualism was frequent in western Istria, on the Cres-Lošinj archipelago and in Rijeka, but rare elsewhere.
Linguistic minorities
German was the predominant language in secondary and higher education throughout the region until 1918, and the educated elite were fluent in German. Many Austrian civil servants used German in daily life, especially in larger urban centres. Most of the German speakers would speak Italian, Slovene or Croatian on social and public occasions, depending on their political and ethnic preferences and location. Among the rural population, German was spoken by about 6,000 people in the Canale Valley. In the major urban areas (primarily Trieste and Rijeka), Hungarian language, Hungarian, Serbian language, Serbian, Czech language, Czech and Greek language, Greek were spoken by smaller communities.Flags
See also
*Austrian Riviera *Battles of the Isonzo *Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
*London Pact
*Trieste#History, History of Trieste
*Venetian Slovenia
*Operation Unthinkable
Notes
References
External links
The Problem of Trieste and the Italo-Yugoslav Border by Glenda Sluga
{{Authority control Friuli-Venezia Giulia Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy History of Istria Italians of Croatia Modern history of Slovenia 1860s neologisms