|
Natan Andrei
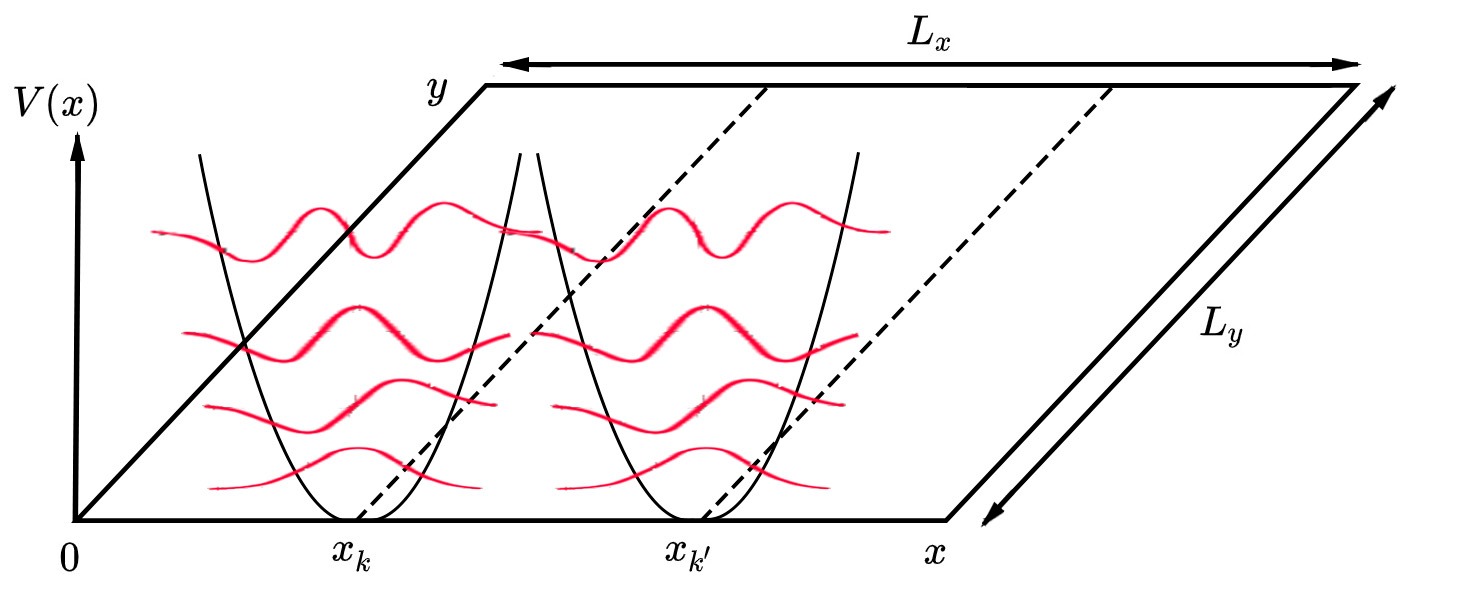
Natan Andrei is an American theoretical physicist who deals with solid state physics and particle physics. He is a distinguished professor at Rutgers University. Andrei received his doctorate in 1979 from Princeton University under supervision of David Gross. In 1989 he was at the Institute for Advanced Study. In 2004 he became a Fellow of the American Physical Society. Independently of Paul Wiegmann, he succeeded in 1980 in finding the exact solution of the Kondo problem. In 2017, both were awarded the Lars Onsager Prize. With John H. Lowenstein, he solved the Chiral Gross–Neveu model using Bethe ansatz technique. He deals with the relations between conformal and exactly integrable field theories and string theory in loop space. In solid state physics, he is primarily concerned with highly correlated electron systems (high-temperature superconductors, quantum Hall effect The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert Einstein was concer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lars Onsager Prize
The Lars Onsager Prize is a prize in theoretical statistical physics awarded annually by the American Physical Society. Prize recipients receive a medal, certificate, and $10,000. It was established in 1993 by Drs. Russell and Marian Donnelly in memory of Lars Onsager. Recipients See also * List of physics awards Notes Awards of the American Physical Society Awards established in 1993 {{sci-award-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The American Physical Society
The American Physical Society honors members with the designation ''Fellow'' for having made significant accomplishments to the field of physics Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which rel .... The following lists are divided chronologically by the year of designation. * List of American Physical Society Fellows (1921–1971) * List of American Physical Society Fellows (1972–1997) * List of American Physical Society Fellows (1998–2010) * List of American Physical Society Fellows (2011–) References {{reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physicists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Hall Effect
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exhibits steps that take on the quantized values : R_ = \frac = \frac , where is the Hall voltage, is the channel current, is the elementary charge and is Planck's constant. The divisor can take on either integer () or fractional () values. Here, is roughly but not exactly equal to the filling factor of Landau levels. The quantum Hall effect is referred to as the integer or fractional quantum Hall effect depending on whether is an integer or fraction, respectively. The striking feature of the integer quantum Hall effect is the persistence of the quantization (i.e. the Hall plateau) as the electron density is varied. Since the electron density remains constant when the Fermi level is in a clean spectral gap, this situation correspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-temperature Superconductivity
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-c or HTS) are defined as materials that behave as superconductors at temperatures above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. The adjective "high temperature" is only in respect to previously known superconductors, which function at even colder temperatures close to absolute zero. In absolute terms, these "high temperatures" are still far below ambient, and therefore require cooling. The first high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986, by IBM researchers Bednorz and Müller, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-c materials are type-II superconductors. The major advantage of high-temperature superconductors is that they can be cooled by using liquid nitrogen, as opposed to the previously known superconductors which require expensive and hard-to-handle coolants, primarily liquid helium. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross–Neveu Model
The Gross–Neveu (GN) model is a quantum field theory model of Dirac fermions interacting via four-fermion interactions in 1 spatial and 1 time dimension. It was introduced in 1974 by David Gross and André Neveu as a toy model for quantum chromodynamics (QCD), the theory of strong interactions. It shares several features of the QCD: GN theory is asymptotically free thus at strong coupling the strength of the interaction gets weaker and the corresponding \beta function of the interaction coupling is negative, the theory has a dynamical mass generation mechanism with \mathbb_2 chiral symmetry breaking, and in the large number of flavor (N \to \infty) limit, GN theory behaves as t'Hooft's large N_c limit in QCD. It consists of N Dirac fermions \psi_1, \psi_2, \cdots, \psi_N. The Lagrangian density is :\mathcal=\bar \psi_a \left(i\partial\!\!\!/-m \right) \psi^a + \frac\left bar \psi_a \psi^a\right2. Einstein summation notation is used, \psi^a is a two component spinor object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kondo Effect
In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities, resulting in a characteristic change i.e. a minimum in electrical resistivity with temperature. The cause of the effect was first explained by Jun Kondo, who applied third-order perturbation theory to the problem to account for scattering of s-orbital conduction electrons off d-orbital electrons localized at impurities ( Kondo model). Kondo's calculation predicted that the scattering rate and the resulting part of the resistivity should increase logarithmically as the temperature approaches 0 K. Experiments in the 1960s by Myriam Sarachik at Bell Laboratories provided the first data that confirmed the Kondo effect. Extended to a lattice of ''magnetic impurities'', the Kondo effect likely explains the formation of ''heavy fermions'' and ''Kondo insulators'' in intermetallic compounds, especially those involving rare earth elements such as cerium, praseodymium, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms a theoretical basis of materials science. It also has direct applications, for example in the technology of transistors and semiconductors. Background Solid materials are formed from densely packed atoms, which interact intensely. These interactions produce the mechanical (e.g. hardness and elasticity), thermal, electrical, magnetic and optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric pattern ( crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary water ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Wiegmann
Paul B. Wiegmann (Павел Борисович Вигман) is a Russian physicist. He is the Robert W. Reneker Distinguished Service Professor in the Department of Physics at the University of Chicago, James Franck Institute and Enrico Fermi Institute. He specializes in theoretical condensed matter physics. He made pioneering contributions to the field of quantum integrable systems. He found exact solutions of O(3) Non-linear Sigma Model, , Wess–Zumino–Witten model (together with Alexander Polyakov), Anderson impurity model and Kondo model. Notable Achievements and Scientific Recognition In 2003, Paul Wiegmann was elected a Fellow of the American Physical Society, the official citation indicating that the recognition was "For exact solutions of models of interacting electronic systems and quantum field theory, including the multi-channel Kondo problem and the Anderson model for magnetic impurities." Awards and Distinguished Appointments *Lady Davis Fellowship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. The society publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious ''Physical Review'' and '' Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. APS is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021 the organization has been led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |