|
Nanoviridae
''Nanoviridae'' is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. The family contains 2 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: stunting. Taxonomy The recognized genera are: * '' Babuvirus'' * '' Nanovirus'' Virus structure and genome Viruses in the family ''Nanoviridae'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and round geometries, and T=1 symmetry. The diameter is around 18–19 nm. Life cycle Viral replication is nuclear. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the ssDNA rolling circle model. After infection of a host cell, the small DNA molecules that have become encapsidated with the genomic ssDNA act as primers. They bind to complementary regions and help in initiation of DNA synthesis by host polymerases. On completion of synthesis, there will be a double stranded intermediate that is transcribed unidirectionally. Most individual nanovirus particles only encode for a single protein Protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
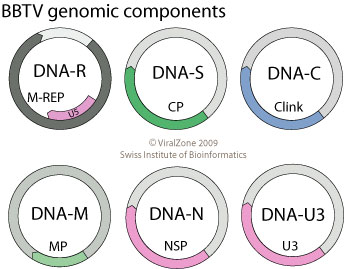
Babuvirus
''Babuvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Nanoviridae''. ''Musa'' species serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: stunting, severe necrosis and early plant death. BBTV induces banana bunchy top disease (BBTD). Taxonomy The genus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species: * ''Babuvirus abacae'', Abaca bunchy top virus * ''Babuvirus cardamomi'', Cardamom bushy dwarf virus * ''Babuvirus musae'', Banana bunchy top virus Structure and genome Viruses in the genus ''Babuvirus'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and round geometries, and T=1 symmetry. The diameter is around 18-19 nm. Genomes are multipartite with 6 to 8 circular segments. Genome size is around 81 kb in totsl. Life cycle Viral replication is nuclear. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the ssDNA rolling ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanovirus
''Nanovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Nanoviridae''. Legume plants serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: stunting, severe necrosis and early plant death. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species: * ''Nanovirus astragali'', Milk vetch dwarf virus * ''Nanovirus astragalirani'', Milk vetch chlorotic dwarf virus * ''Nanovirus flavipisi'', Pea yellow stunt virus * ''Nanovirus flaviviciae'', Faba bean yellow leaf virus * ''Nanovirus medicagonis'', Black medic leaf roll virus * ''Nanovirus necroflaviviciae'', Faba bean necrotic yellows virus * ''Nanovirus necropisi'', Pea necrotic yellow dwarf virus * ''Nanovirus necropumiliviciae'', Faba bean necrotic stunt virus * ''Nanovirus petroselini'', Parsley severe stunt associated virus * ''Nanovirus sophorae'', Sophora yellow stunt virus * ''Nanovirus trifolii'', Subterranean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long molecules of DNA or RNA that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primer (molecular Biology)
A primer is a short, single-stranded nucleic acid used by all living organisms in the initiation of DNA synthesis. A synthetic primer is a type of oligo, short for oligonucleotide. DNA polymerases (responsible for DNA replication) are only capable of adding nucleotides to the 3’-end of an existing nucleic acid, requiring a primer be bound to the template before DNA polymerase can begin a complementary strand. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides after binding to the RNA primer and synthesizes the whole strand. Later, the RNA strands must be removed accurately and replaced with DNA nucleotides. This forms a gap region known as a nick that is filled in using a ligase. The removal process of the RNA primer requires several enzymes, such as Fen1, Lig1, and others that work in coordination with DNA polymerase, to ensure the removal of the RNA nucleotides and the addition of DNA nucleotides. Living organisms use solely RNA primers, while laboratory techniques in biochemistry and mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerases
In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme ( EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by copying a DNA template strand using base-pairing interactions or RNA by half ladder replication. A DNA polymerase from the thermophilic bacterium, ''Thermus aquaticus'' (''Taq'') ( PDBbr>1BGX EC 2.7.7.7) is used in the polymerase chain reaction, an important technique of molecular biology. A polymerase may be template-dependent or template-independent. Poly-A-polymerase is an example of template independent polymerase. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase also known to have template independent and template dependent activities. By function *DNA polymerase (DNA-directed DNA polymerase, DdDP) **Family A: DNA polymerase I; Pol γ, θ, ν **Family B: DNA polymerase II; Pol α, δ, ε, ζ **Family C: DNA polymerase III holoenzyme **Family X: Pol β, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many RNA viruses is composed of negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Background A DNA transcription unit encoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |