|
Nanocages
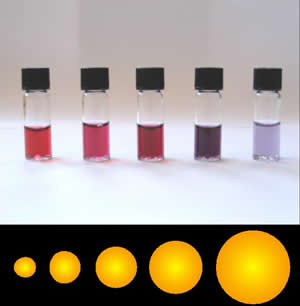
Gold Nanocages are hollow, porous gold nanoparticles ranging in size from 10 to over 150 nm. They are created by reacting silver nanoparticles with chloroauric acid (hydrogen, HGold, Auchlorine, Cl4) in boiling water. Whereas gold nanoparticles absorb light in the visible spectrum of light (at about 550 nm), gold nanocages absorb light in the near-infrared, where biological tissues absorb the least light. Because they are also biocompatible, gold nanocages are promising as a contrast agent for optical coherence tomography. Gold nanocages also absorb light and heat up (Photothermal effect), killing surrounding cancer Cell (biology), cells. Nanocages have been functionalized with cancer-specific antibodies. See also * Colloidal gold * Gold nanorods References Nanoparticles by composition Nanoparticles by morphology {{chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Nanocages Synthesis
Gold is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a Brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under Standard conditions for temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in Free element, free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as Gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in Rock (geology), rocks, Vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Tissue
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Nanorods
In nanotechnology, nanorods are one morphology of nanoscale objects. Each of their dimensions range from 1–100 nm. They may be synthesized from metals or semiconducting materials. Standard aspect ratios (length divided by width) are 3-5. Nanorods are produced by direct chemical synthesis. A combination of ligands act as shape control agents and bond to different facets of the nanorod with different strengths. This allows different faces of the nanorod to grow at different rates, producing an elongated object. One potential application of nanorods is in display technologies, because the reflectivity of the rods can be changed by changing their orientation with an applied electric field. Another application is for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Nanorods, along with other noble metal nanoparticles, also function as theragnostic agents. Nanorods absorb in the near IR, and generate heat when excited with IR light. This property has led to the use of nanorods as can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloidal Gold
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is usually either wine-red coloured (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue/purple (for larger spherical particles or nanorods). Due to their optical, electronic, and molecular-recognition properties, gold nanoparticles are the subject of substantial research, with many potential or promised applications in a wide variety of areas, including electron microscopy, electronics, nanotechnology, materials science, and biomedicine. The properties of colloidal gold nanoparticles, and thus their potential applications, depend strongly upon their size and shape. For example, rodlike particles have both a transverse and longitudinal absorption peak, and anisotropy of the shape affects their self-assembly. History Used since ancient times as a method of staining glass colloidal gold was used in the 4th-century Lycurgus Cup, which changes color dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing s. It is also common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photothermal Effect
Photothermal effect is a phenomenon associated with electromagnetic radiation. It is produced by the photoexcitation of material, resulting in the production of thermal energy (heat). It is sometimes used during treatment of blood vessel lesions, laser resurfacing, laser hair removal and laser surgery. External linksQuantities, Terminology, and Symbols in Photothermal and Related SpectroscopiesResearch paper from IUPAC The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...Amazing Nano Materials: Photothermal and Photoacoustic Effects Photochemistry {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). It is used for medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing (NDT). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution. Depending on the properties of the light source (superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub-micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range). Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiopharmaceuticals, which emit radiation themselves. In x-ray imaging, contrast agents enhance the radiodensity in a target tissue or structure. In magnetic resonance imaging, contrast agents shorten (or in some instances increase) the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues in order to alter the contrast in the image. Contrast agents are commonly used to improve the visibility of blood vessels and the gastrointestinal tract. The types of contrast agent are classified according to their intended imaging modalities. Radiocontrast media For radiography, which is based on X-rays, iodine and barium are the most common types of contrast agent. Various sorts of iodinated contrast agents exist, with variations occurring between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium ( gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm ( near infrared). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well. The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. '' Unsaturated colors'' such as pink, or purple variations like magenta, for example, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |