|
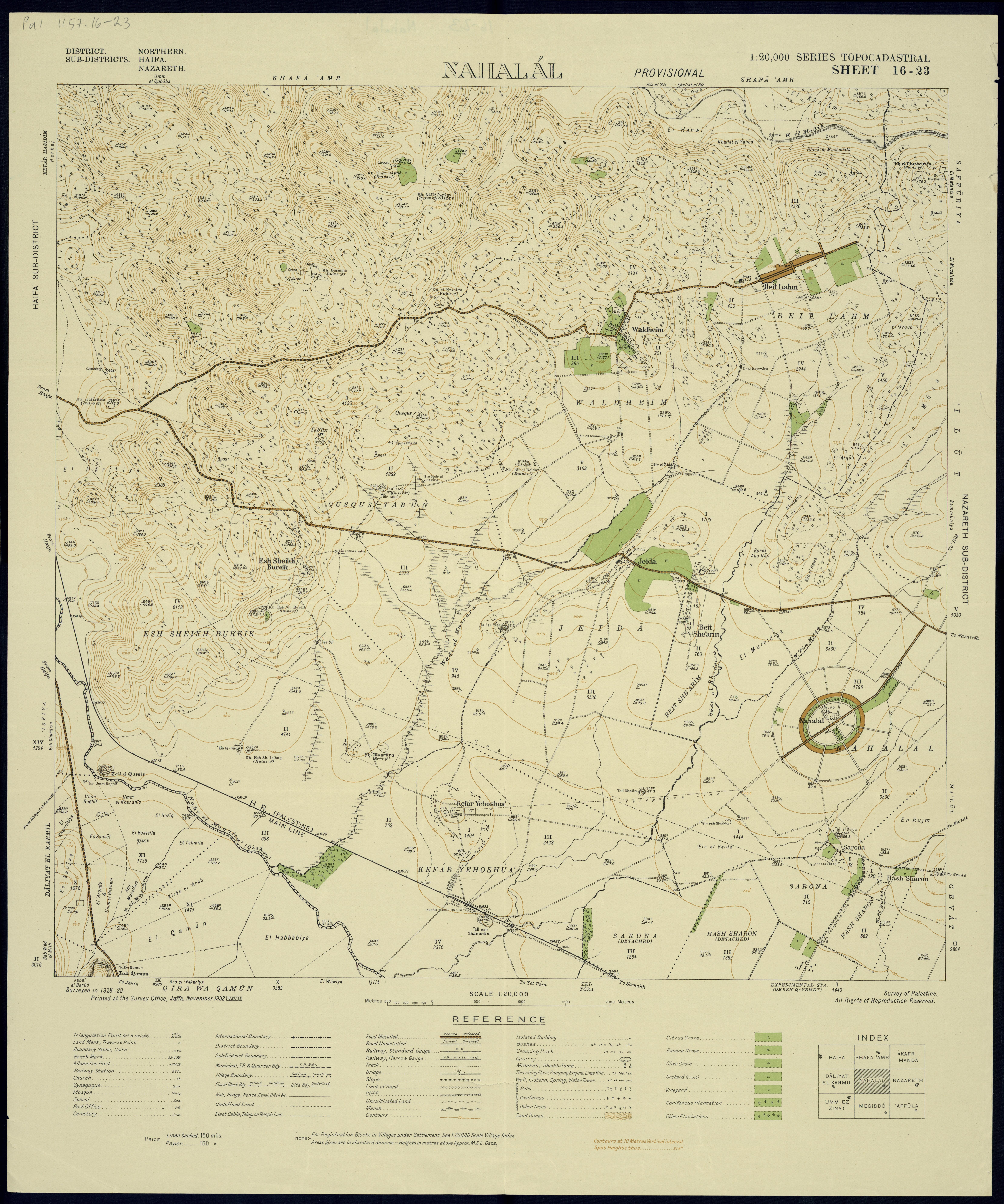
Nahalal
Nahalal () is a moshav in Northern District (Israel), northern Israel. Covering , it falls under the jurisdiction of the Jezreel Valley Regional Council. In it had a population of . Nahalal is best known for its general layout, as designed by Richard Kauffmann: slightly oval round, similar to a spoke wheel, with its public buildings at the "hub" and individual plots of agricultural land radiating from it like spokes with symmetrically placed roads creating eight equal Circular sector, sectors, an inner ring of residential buildings, and an outer ring road.Richard Kauffmann''Die Bebauungsplaene der Kleinsiedlungen Kfar-Nahalal und Kfar-Jecheskiel''('The construction plans for the agricultural small housing estates Kfar Nahalal and Kfar Yehezkel, Kfar Jecheskiel'), published by the Department for Agricultural Colonization of the Zionist Executive, Jerusalem (1923), in German. In the Hebrew Bible Nahalal was a Levitical city mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. According to the Book of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Kauffmann
Richard Kauffmann (1887–1958) was a German-Jewish architect who migrated to Israel (region), Palestine in 1920. His architecture was influenced by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, a proponent of the International Style, and was applied to the local landscape, laying the architectural groundwork for the nascent State of Israel as well as that of several cities including Hadar HaCarmel in Haifa, Nahalal, Afula and the White City (Tel Aviv), White City, as Tel Aviv's International style (architecture), International Style architecture became known. Biography Early life, World War I, work in Europe Richard Kauffmann was born in 1887 in Frankfurt, Germany. In 1907, he began to study art at the Städelschule, but transferred to architecture studies in Amsterdam the following year. In 1909, he moved to the Technical University of Munich, graduating in 1912. In 1914, he opened an office in Frankfurt. During the First World War Kauffmann fought on the Eastern Front, where he became aware of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kfar Yehezkel
Kfar Yehezkel (, ''lit.'' Yehezkel Village) is a moshav in northern Israel. Located in the Jezreel Valley, six kilometres southeast of Afula, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gilboa Regional Council. In the moshav had a population of . History Kfar Yehezkel was founded on 16 December 1921 by pioneers of the Second Aliyah.Family Affair: The Broidas, Kfar Yehezkel Haaretz, 16 April 2009 Settlers from Tel Hai and Hamara, which was evacuated because of Arab attacks from Lebanon, were also among the founding members. It was the second ''moshav ovdim'' in |
Shimron
Tel Shimron (Hebrew: תל שמרון) is an archaeological site and nature reserve in the Jezreel Valley. Shimron was a major city in the north of Israel mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. In later times it was also known as Shim'on. It became an administrative center under Assyrian, Babylonian and Persian rule. During the early Roman period, the city was expanded and fortified by Herod, who renamed it Sebastiya in honor of emperor Augustus. In Late Antiquity, it was known as Simonias (Hebrew: סימונייה), as attested to by Flavius Josephus. The Arabic name of the site is Tell Samunia, also written Samunieh. Tel Shimron is located on the western edge of the Nazareth range, on the intersection of the Lower Galilee and the Jezreel Valley. That location, particularly due to its proximity to the Acre (Akko) Plain, made it an important trade route. Since 2016, the site is being excavated in cooperation with the Jezreel Valley Regional Project. Surveys and excavations Gué ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma'alul
Ma'alul () was a Palestinians, Palestinian village, with a mixed population of primarily Muslims with a substantial minority of Palestinian Christians, that was depopulated and destroyed by Israel during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. Located six kilometers west of the city of Nazareth, many of its inhabitants became Internally Displaced Palestinians, internally displaced refugees, after taking refuge in NazarethRabinowitz, 1997, p27/ref> and the neighbouring town of Yafa an-Naseriyye. Despite having never left the territory that came to form part of Israel, the majority of the villagers of Maalul, and other Palestinian villages like Indur, Andor and Al-Mujidal, were declared "absentees", allowing the confiscation of their land under the Land and Property laws in Israel#The 'Absentees Property Law', Absentees Property Law. Today, much of the former village's lands are owned by the Jewish National Fund. All that remains of its former structures are two Church (building), churches, a mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshav
A moshav (, plural ', "settlement, village") is a type of Israeli village or town or Jewish settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 and 1914, during what is known as the second wave of ''aliyah''. A resident or a member of a moshav can be called a "moshavnik" (). There is an umbrella organization, the Moshavim Movement. The moshavim are similar to kibbutzim with an emphasis on communitarian, individualist labour. They were designed as part of the Zionist state-building programme following the green revolution in the British Mandate of Palestine during the early 20th century, but in contrast to the collective farming kibbutzim, farms in a moshav tended to be individually owned but of fixed and equal size. Workers produced crops and other goods on their properties through individual or pooled labour with the profit and foodstuffs going to provide for themselves. Moshavim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshavim Movement
The Moshavim Movement (, ''Tnu'at HaMoshavim'') is one of the main Settlement movement (Israel), settlement movements in Israel, whose members are cooperative villages organized as moshavim and moshav shitufi, moshavim shitufiim. History Founded in 1920 with the establishment of the first moshav, Nahalal, in the Jezreel Valley in the north of Israel, the movement today has a membership of 253 moshavim from the total of 440 moshavim and moshavim shitufiim in Israel. The member moshavim have access to a range of mutual help instruments maintained by the Moshavim Movement. These include a mutual insurance company, a mutual help fund, a mortgage bank for moshavim, and a pension and retirement fund for individual moshav members. In the past, the Moshavim Movement created a system of regional service cooperatives (''mif'alim ezoriim'' in Hebrew) for supply of farm inputs and for marketing and processing of farm products for its members. These regional cooperatives were essentially simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jezreel Valley Regional Council
Jezreel Valley Regional Council (, ''Mo'atza Azorit Emek Yizra'el'') is a regional council in northern Israel that encompasses most of the settlements in the Jezreel Valley. It includes 15 kibbutzim, 15 moshavim, 6 community settlements and two Bedouin villages. Despite its name, some of these settlements are not located in the Jezreel Valley proper, but in the vicinity. List of communities Kibbutzim * Alonim * Dovrat * Ein Dor * Gazit * Gevat * Ginegar * Hanaton * Harduf * HaSolelim * Kfar HaHoresh * Merhavia * Mizra * Ramat David *Sarid *Yifat Moshavim * Alonei Abba * Alon HaGalil * Balfouria * Beit She'arim (moshav) * Beit Zeid * Bethlehem of Galilee *HaYogev * Kfar Barukh * Kfar Gidon *Kfar Yehoshua * Merhavia *Nahalal * Sde Ya'akov *Tel Adashim * Zippori Community settlements *Adi * Ahuzat Barak * Givat Ela *Hoshaya Hoshaya () is a national-religious community settlement (Israel), community in northern Israel. Located to the south-east of Shefa-'Amr, on Route 77 between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merarites
The Merarites were one of the four main divisions among the Levites in Biblical times. The Bible claims that the Merarites were all descended from the eponymous Merari, a son of Levi, although some biblical scholars regard this as a postdictional metaphor, providing an origin myth of the connectedness of the clan to others in the Israelite confederation.''Jewish Encyclopedia'' The Bible ascribes a specific religious function to the Merarites, namely care of the framework - posts, crossbars, courtyard, tent pegs, etc. - of the sanctuary. This differentiation of religious activity between the Merarites and other Levites, in particular the Aaronids, is found only in the Priestly Code, and not in passages that textual scholars attribute to other authors. According to the Book of Joshua, rather than possessing a continuous territory, the Merarites possessed several cities scattered throughout the geographic region of Gilead, as well as in the south of the Galilee, the latter being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountains, and its western boundary is defined in various ways. Narrow definitions, in which Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe are counted as separate regions, include Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. In contrast, broader definitions include Moldova and Romania, but also some or all of the Balkans, the Baltic states, the Caucasus, and the Visegrád Group, Visegrád group. The region represents a significant part of Culture of Europe, European culture; the main socio-cultural characteristics of Eastern Europe have historically largely been defined by the traditions of the Slavs, as well as by the influence of Eastern Christianity as it developed through the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire and the Ottoman Empire. Another definition was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beirut
Beirut ( ; ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, just under half of Lebanon's population, which makes it the List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, fourth-largest city in the Levant region and the List of largest cities in the Arab world, sixteenth-largest in the Arab world. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint of Lebanon's Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. Beirut has been inhabited for more than 5,000 years, making it one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world. Beirut is Lebanon's seat of government and plays a central role in the Economy of Lebanon, Lebanese economy, with many banks and corporations based in the city. Beirut is an important Port of Beirut, seaport for the country and region, and rated a Global City, Beta- World City by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. Beirut was severely damaged by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |