|
Moshav
A moshav (, plural ', "settlement, village") is a type of Israeli village or town or Jewish settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 and 1914, during what is known as the second wave of ''aliyah''. A resident or a member of a moshav can be called a "moshavnik" (). There is an umbrella organization, the Moshavim Movement. The moshavim are similar to kibbutzim with an emphasis on communitarian, individualist labour. They were designed as part of the Zionist state-building programme following the green revolution in the British Mandate of Palestine during the early 20th century, but in contrast to the collective farming kibbutzim, farms in a moshav tended to be individually owned but of fixed and equal size. Workers produced crops and other goods on their properties through individual or pooled labour with the profit and foodstuffs going to provide for themselves. Moshavim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshav Shitufi
A moshav shitufi (, lit. ''collective moshav'', pl. ''moshavim shitufiim'') is a type of cooperative State of Israel, Israeli village, whose organizational principles place it between the kibbutz and the moshav on the scale of cooperation. Ideology A classic moshav (formally known as ''moshav ovdim'', or ''workers' moshav'') is a village-level service cooperative that takes care of farm services (such as marketing, supply, and credit) for its members, while all production and consumption activities are handled at the level of families and households. A classical kibbutz is a village-level production cooperative, with all production, consumption, and service decisions handled collectively. Moshav shitufi is an intermediate form, in which production and services are handled collectively, while consumption decisions remain the responsibility of the households. Moshav shitufi members are engaged in agriculture and industry in the village and also work in various professions outside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshavim Movement
The Moshavim Movement (, ''Tnu'at HaMoshavim'') is one of the main Settlement movement (Israel), settlement movements in Israel, whose members are cooperative villages organized as moshavim and moshav shitufi, moshavim shitufiim. History Founded in 1920 with the establishment of the first moshav, Nahalal, in the Jezreel Valley in the north of Israel, the movement today has a membership of 253 moshavim from the total of 440 moshavim and moshavim shitufiim in Israel. The member moshavim have access to a range of mutual help instruments maintained by the Moshavim Movement. These include a mutual insurance company, a mutual help fund, a mortgage bank for moshavim, and a pension and retirement fund for individual moshav members. In the past, the Moshavim Movement created a system of regional service cooperatives (''mif'alim ezoriim'' in Hebrew) for supply of farm inputs and for marketing and processing of farm products for its members. These regional cooperatives were essentially simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Farming
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-owners jointly engage in farming activities as a collective; and state farms, which are owned and directly run by a centralized government. The process by which farmland is aggregated is called collectivization. In some countries (including the Soviet Union, the Eastern Bloc countries, China and Vietnam), there have been both state-run and cooperative-run variants. For example, the Soviet Union had both kolkhozy (cooperative-run farms) and sovkhozy (state-run farms). Pre-20th century history Case studies Mexico Under the Aztec Empire, central Mexico was divided into small territories called ''calpulli'', which were units of local administration concerned with farming as well as education and religion. A calpulli consisted of a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
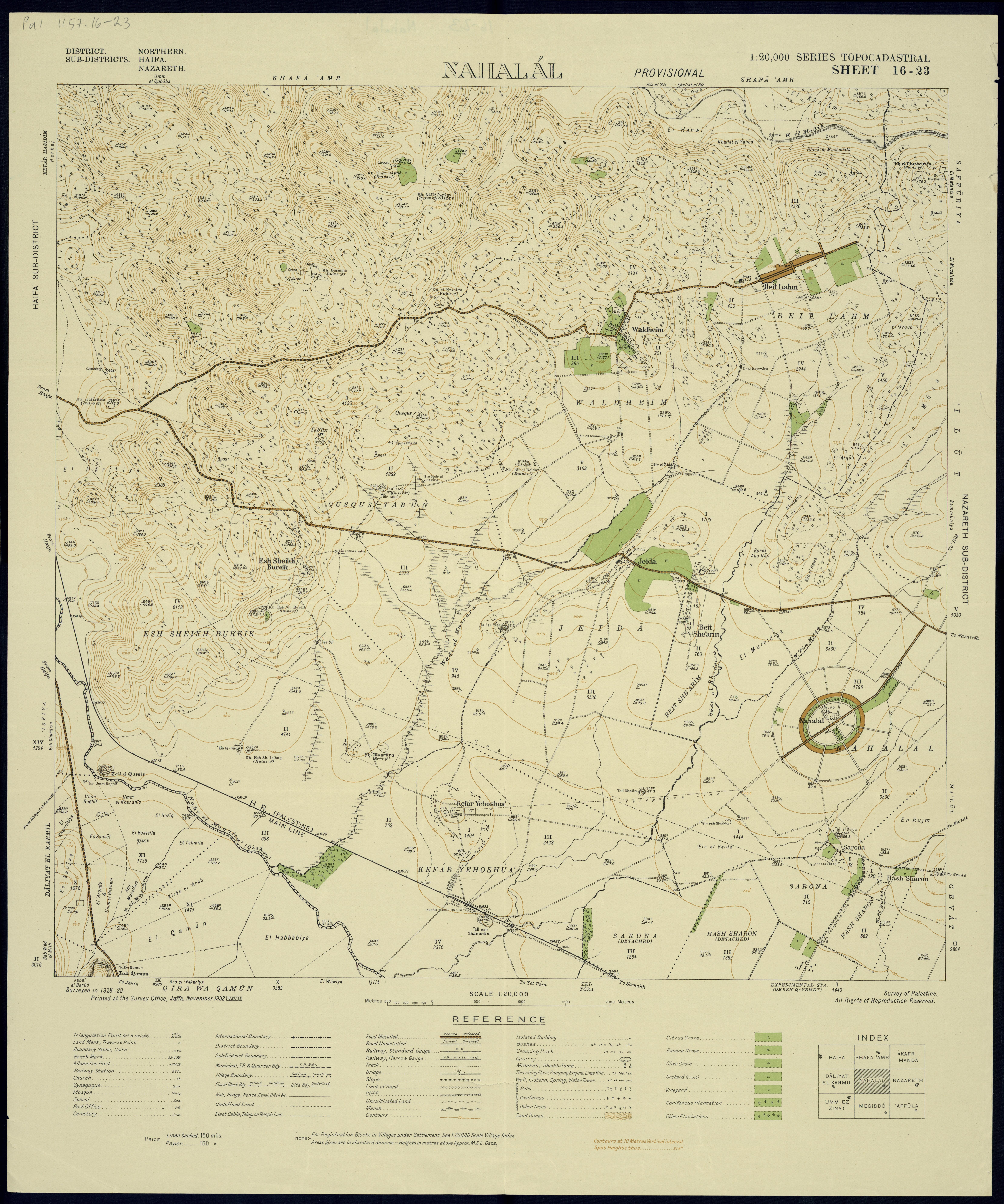
Nahalal
Nahalal () is a moshav in Northern District (Israel), northern Israel. Covering , it falls under the jurisdiction of the Jezreel Valley Regional Council. In it had a population of . Nahalal is best known for its general layout, as designed by Richard Kauffmann: slightly oval round, similar to a spoke wheel, with its public buildings at the "hub" and individual plots of agricultural land radiating from it like spokes with symmetrically placed roads creating eight equal Circular sector, sectors, an inner ring of residential buildings, and an outer ring road.Richard Kauffmann''Die Bebauungsplaene der Kleinsiedlungen Kfar-Nahalal und Kfar-Jecheskiel''('The construction plans for the agricultural small housing estates Kfar Nahalal and Kfar Yehezkel, Kfar Jecheskiel'), published by the Department for Agricultural Colonization of the Zionist Executive, Jerusalem (1923), in German. In the Hebrew Bible Nahalal was a Levitical city mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. According to the Book of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibbutzim
A kibbutz ( / , ; : kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1910, was Degania. Today, farming has been partly supplanted by other economic branches, including industrial plants and high-tech enterprises. Kibbutzim began as utopian communities, a combination of socialism and Zionism. In recent decades, some kibbutzim have been privatized and changes have been made in the communal lifestyle. A member of a kibbutz is called a ''kibbutznik'' ( / ; plural ''kibbutznikim'' or ''kibbutzniks''), the suffix ''-nik'' being of Slavic origin. In 2010, there were 270 kibbutzim in Israel with a total population of 126,000. Their factories and farms account for 9% of Israel's industrial output, worth US$8 billion, and 40% of its agricultural output, worth over US$1.7 billion. Some kibbutzim had also developed substantial high-tech and military industries. For example, in 2010, Kibbutz Sasa, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibbutz
A kibbutz ( / , ; : kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1910, was Degania Alef, Degania. Today, farming has been partly supplanted by other economic branches, including Factory, industrial plants and high-tech Business, enterprises. Kibbutzim began as utopian communities, a combination of socialism and Zionism. In recent decades, some kibbutzim have been Privatization, privatized and changes have been made in the communal lifestyle. A member of a kibbutz is called a ''kibbutznik'' ( / ; plural ''kibbutznikim'' or ''kibbutzniks''), the suffix ''-nik'' being of Slavic languages, Slavic origin. In 2010, there were 270 kibbutzim in Israel with a total population of 126,000. Their factories and farms account for 9% of Israel's industrial output, worth US$8 billion, and 40% of its agricultural output, worth over US$1.7 billion. Some kibbutzim had also developed substantial high-tech and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Zionist
Labor Zionism () or socialist Zionism () is the left-wing, socialist variant of Zionism. For many years, it was the most significant tendency among Zionists and Zionist organizations, and was seen as the Zionist faction of the historic Jewish labour movements of Eastern Europe and Central Europe. Labor Zionism eventually developing local movements in most countries with sizable Jewish populations. Unlike the "political Zionist" tendency founded by Theodor Herzl and advocated by Chaim Weizmann, Labor Zionists did not believe that a Jewish state would be created by simply appealing to the international community or to powerful nations such as the United Kingdom, Germany, or the former Ottoman Empire. Rather, they believed that a Jewish state could only be created through the efforts of the Jewish working class making ''aliyah'' to the Land of Israel and raising a country through the creation of a Labor Jewish society with rural ''kibbutzim'' and ''moshavim'', and an urban Jewis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yishuv
The Yishuv (), HaYishuv Ha'ivri (), or HaYishuv HaYehudi Be'Eretz Yisra'el () was the community of Jews residing in Palestine prior to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The term came into use in the 1880s, when there were about 25,000 Jews living in that region, and continued to be used until 1948, by which time there were some 630,000 Jews there. The term is still in use to denote the pre-1948 Jewish residents in Palestine, corresponding to the southern part of Ottoman Syria until 1918, OETA South in 1917–1920, and Mandatory Palestine in 1920–1948. A distinction is sometimes drawn between the '' Old Yishuv'' and the '' New Yishuv''. The Old Yishuv refers to all the Jews living in Palestine before the first Zionist immigration wave (''aliyah'') of 1882, and to their descendants until 1948. The Old Yishuv residents were religious Jews, living mainly in Jerusalem, Safed, Tiberias, and Hebron. There were smaller communities in Jaffa, Haifa, Peki'in, Acre, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews (), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () in plural and ''Mizrahi'' () in singular, and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are terms used in Israeli discourse to refer to a grouping of Jews, Jewish communities that lived in the Muslim world. ''Mizrahi'' is a political sociological term that was coined with the creation of the Israel, State of Israel. It translates as "Easterner" in Hebrew. The term ''Mizrahi'' is almost exclusively applied to descendants of Jewish communities from North Africa, Central Asia, West Asia, and parts of the North Caucasus. This includes Iraqi Jews, Iranian Jews, Bukharan Jews, Bukharian Jews, Kurdish Jews, Afghan Jews, Mountain Jews, Georgian Jews, and the small community of History of the Jews in Bahrain, Bahraini Jews. The aforementioned groups are believed to derive their ancestry in large part from the Babylonian captivity. Yemenite Jews are also ''Mizrahi'' Jews, though they differ from other ''Mizra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the ), or Marj Ibn Amir (), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. It is bordered to the north by the highlands of the Lower Galilee region, to the south by the Samarian highlands, to the west and northwest by the Mount Carmel range, and to the east by the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan Valley, with Mount Gilboa marking its southern extent. The largest settlement in the valley is the city of Afula, which lies near its center. Name The Jezreel Valley takes its name from the ancient city of Jezreel (city), Jezreel (known in Hebrew as Yizre'el; ; known in Arabic as Zir'in, Zir'ēn, ) which was located on a low hill overlooking the southern edge of the valley. The word ''Jezreel'' comes from the Hebrew, and means "God sows" or "El (god), El sows".Cheyne and Black, ''Encyclopedia Biblica'' The Arabic name of the valley is Marj Bani Amir (), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Town Of Bayt Zakariah, June 2015
Israeli may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel * Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel * Modern Hebrew, a language * ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008 * Guni Israeli (born 1984), Israeli basketball player See also * Israel (other) * Israelites (other), the ancient people of the Land of Israel * List of Israelis Israelis ( ''Yiśraʾelim'') are the citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel. The largest ethnic groups in Israel are Israeli Jews, Jews (75%), followed by Arab-Israelis, Palestinians and Arabs (20%) and other minorities (5%). _ ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |