|
NTERA-2
The NTERA-2 (also designated NTERA2/D1, NTERA2, or NT2) cell line is a clonally derived, pluripotent human embryonal carcinoma cell line. Characteristics NTERA-2 cells exhibit biochemical and developmental properties similar to the cells of the early embryo, and can be used to study the early stages of human neurogenesis. The cells exhibit a high nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio, prominent nucleoli, and the expression of the glycolipid antigen SSEA-3. They also express nestin and vimentin, which are found in neuroepithelial precursor cells, as well as microtubule-associated proteins expressed in human neuroepithelium. NTERA-2 cells also accumulate cytoplasmic glycogen. Differentiation NTERA-2 cells differentiate when exposed to retinoic acid and lose expression of SSEA-3. Differentiation produces neurons via asymmetric cell division, and these cells form interconnected axon networks and express tetanus toxin receptors and neurofilament proteins. By 10–14 days of exposure to retinoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroepithelium
Neuroepithelial cells, or neuroectodermal cells, form the wall of the closed neural tube in early embryonic development. The neuroepithelial cells span the thickness of the tube's wall, connecting with the pial surface and with the ventricular or lumenal surface. They are joined at the lumen of the tube by junctional complexes, where they form a pseudostratified layer of epithelium called neuroepithelium. Neuroepithelial cells are the stem cells of the central nervous system, known as neural stem cells, and generate the intermediate progenitor cells known as radial glial cells, that differentiate into neurons and glia in the process of neurogenesis. Embryonic neural development Brain development During the third week of embryonic growth the brain begins to develop in the early fetus in a process called morphogenesis. Neuroepithelial cells of the ectoderm begin multiplying rapidly and fold in forming the neural plate, which invaginates during the fourth week of embryonic gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopaminergic
Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), dopamine being a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain. Dopaminergic brain pathways facilitate dopamine-related activity. For example, certain proteins such as the dopamine transporter (DAT), vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), and dopamine receptors can be classified as dopaminergic, and neurons that synthesize or contain dopamine and synapses with dopamine receptors in them may also be labeled as ''dopaminergic''. Enzymes that regulate the biosynthesis or metabolism of dopamine such as aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase or DOPA decarboxylase, monoamine oxidase (MAO), and catechol ''O''-methyl transferase (COMT) may be referred to as ''dopaminergic'' as well. Also, any endogenous or exogenous chemical substance that acts to affect dopamine receptors or dopamine release through indirect actions (for example, on neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Stem Cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre- implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the inner cell mass (embryoblast) using immunosurgery results in destruction of the blastocyst, a process which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage have the same moral considerations as embryos in the post-implantation stage of development. Researchers are currently focusing heavily on the therapeutic potential of embryonic stem cells, with clinical use being the goal for many laboratories. Potential uses include the treatment of diabetes and heart disease. The cells are being studied to be used as clinical therapies, models of genetic disorders, and cellular/DNA repair. However, adverse effects in the research and clinical processes such as tumors and un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and other glial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Oligodendrocytes do this by creating the myelin sheath. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only one axon. Each oligodendrocyte forms one segment of myelin for several adjacent axons. Oligodendrocytes are found only in the central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. These cells were originally thought to have been produced in the ventral neural tube; however, research now shows oligodendrocytes originate from the ventral ventricular zone of the embryonic spinal cord and possibly have some concentrations in the forebrain. They are the last c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuronal Process
A neurite or neuronal process refers to any projection from the cell body of a neuron. This projection can be either an axon or a dendrite. The term is frequently used when speaking of immature or developing neurons, especially of cells in culture, because it can be difficult to tell axons from dendrites before differentiation is complete. Neurite development The development of a neurite requires a complex interplay of both extracellular and intracellular signals. At every given point along a developing neurite, there are receptors detecting both positive and negative growth cues from every direction in the surrounding space. The developing neurite sums together all of these growth signals in order to determine which direction the neurite will ultimately grow towards. While not all of the growth signals are known, several have been identified and characterized. Among the known extracellular growth signals are netrin, a midline chemoattractant, and semaphorin, ephrin and collaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofilament
Neurofilaments (NF) are classed as type IV intermediate filaments found in the cytoplasm of neurons. They are protein polymers measuring 10 nm in diameter and many micrometers in length. Together with microtubules (~25 nm) and microfilaments (7 nm), they form the neuronal cytoskeleton. They are believed to function primarily to provide structural support for axons and to regulate axon diameter, which influences nerve conduction velocity. The proteins that form neurofilaments are members of the intermediate filament protein family, which is divided into six types based on their gene organization and protein structure. Types I and II are the keratins which are expressed in epithelia. Type III contains the proteins vimentin, desmin, peripherin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Type IV consists of the neurofilament proteins L, M, H and internexin. Type V consists of the nuclear lamins, and type VI consists of the protein nestin. The type IV interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanus Toxin
Tetanus toxin (TeNT) is an extremely potent neurotoxin produced by the vegetative cell of ''Clostridium tetani'' in anaerobic conditions, causing tetanus. It has no known function for clostridia in the soil environment where they are normally encountered. It is also called spasmogenic toxin, tentoxilysin, tetanospasmin or, tetanus neurotoxin. The LD50 of this toxin has been measured to be approximately 2.5–3 ng/kg, making it second only to the related botulinum toxin (LD50 2 ng/kg) as the deadliest toxin in the world. However, these tests are conducted solely on mice, which may react to the toxin differently from humans and other animals. ''C. tetani'' also produces the exotoxin tetanolysin, a hemolysin, that causes destruction of tissues. Distribution Tetanus toxin spreads through tissue spaces into the lymphatic and vascular systems. It enters the nervous system at the neuromuscular junctions and migrates through nerve trunks and into the central nervous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons ( pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Cell Division
An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates. This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise to daughter cells of equivalent fates. Notably, stem cells divide asymmetrically to give rise to two distinct daughter cells: one copy of the original stem cell as well as a second daughter programmed to differentiate into a non-stem cell fate. (In times of growth or regeneration, stem cells can also divide symmetrically, to produce two identical copies of the original cell.) In principle, there are two mechanisms by which distinct properties may be conferred on the daughters of a dividing cell. In one, the daughter cells are initially equivalent but a difference is induced by signaling between the cells, from surrounding cells, or from the precursor cell. This mechanism is known as extrinsic asymmetric cell division. In the second mechanism, the prospective daughter cells are inherently different at the time of division of the moth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
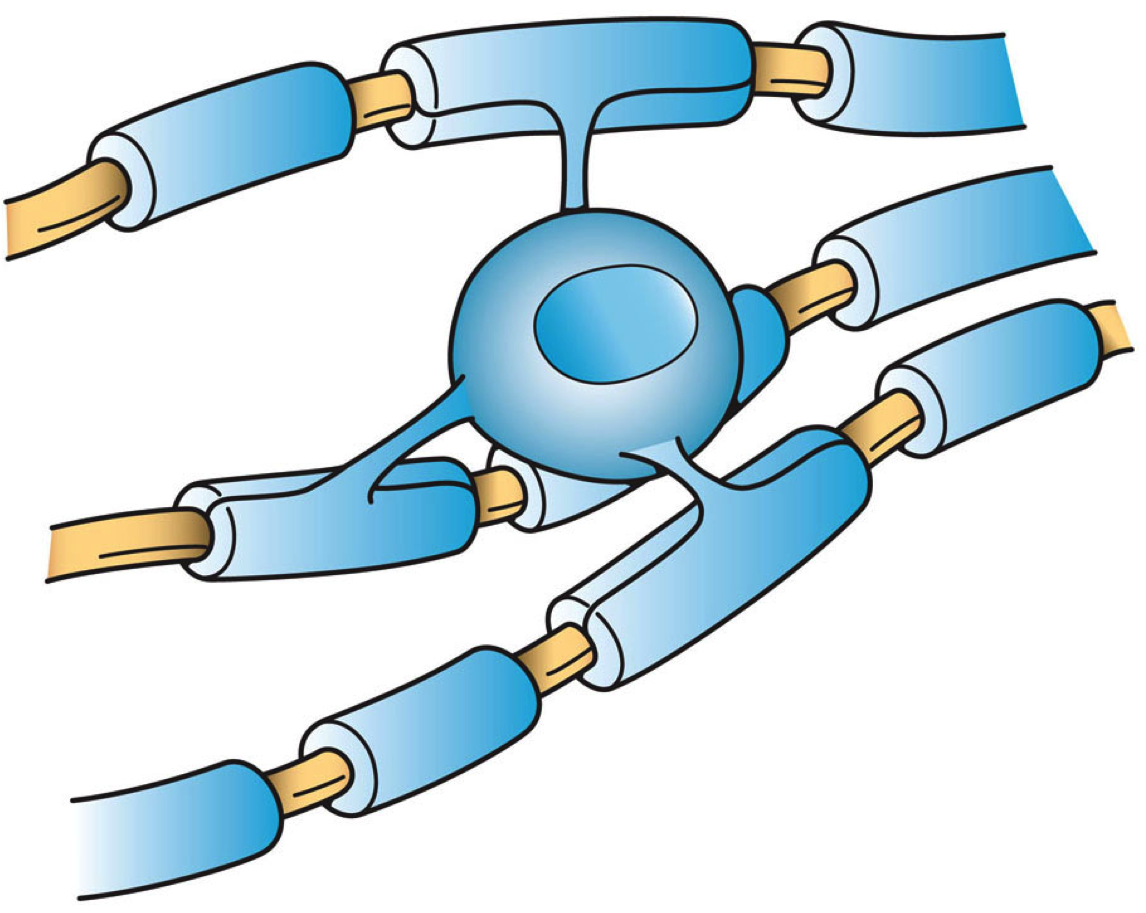
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, electrically excitable cell (biology), cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to Stimulus (physiology), stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the Sense, sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to gland, glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |