|
NOAA-E
NOAA-8, known as NOAA-E before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was first of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment. Launch NOAA-8 was launched on an Atlas E launch vehicle on 28 March 1983 from Vandenberg Air Force Base at Vandenberg Space Launch Complex 3 (SLW-3W). Spacecraft The NOAA-8 satellite had a mass of . The satellite was based upon the DMSP Block 5D satellite bus developed for the U.S. Air Force, and it was capable of maintaining an Earth-pointing accuracy of better than ± 0.1° with a motion rate of less than 0.035 degrees/second. Instruments Primary sensors included the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Infrared Observation Satellite
Television InfraRed Observation Satellite (TIROS) is a series of early weather satellites launched by the United States, beginning with TIROS-1 in 1960. TIROS was the first satellite that was capable of remote sensing of the Earth, enabling scientists to view the Earth from a new perspective: space. The program, promoted by Harry Wexler, proved the usefulness of satellite weather observation, at a time when military reconnaissance satellites were secretly in development or use. TIROS demonstrated at that time that "the key to genius is often simplicity". TIROS is an acronym of "Television InfraRed Observation Satellite" and is also the plural of "tiro" which means "a young soldier, a beginner". The Advanced Research Projects Agency (now DARPA) initiated the TIROS program in 1958 and transferred the program to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1959. Participants in the TIROS program also included, Signal Corps (United States Army), United States Army S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously) or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
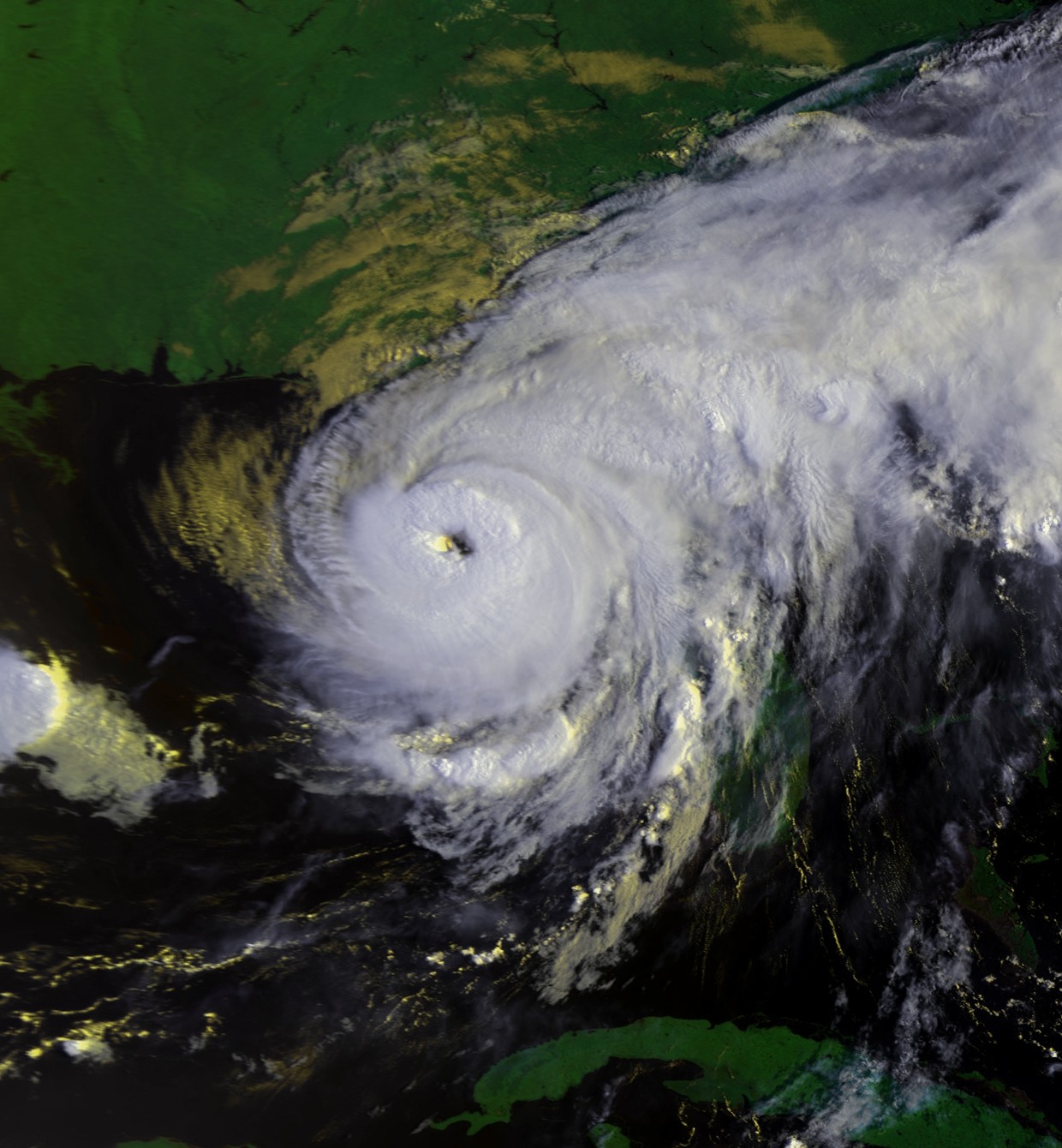
Elena 02 Sep 1985 1411Z N8
Elena may refer to: People * Elena (given name), including a list of people and characters with this name * Raymond Elena (1931-2024), French former professional racing cyclist. * Joan Ignasi Elena (born 1968), Catalan politician * Francine Elena (born 1986), British poet Geography * Elena (town), a town in Veliko Tarnovo Province, Bulgaria ** Elena Municipality * Elena (village), a village in Haskovo Province Film and television * ''Elena'' (2011 film), a 2011 Russian film * ''Elena'' (2012 film), a Brazilian film * ''Elena'' (TV series), a Mexican telenovela * ''Elena of Avalor'', an American TV series * ''Daniele Cortis'', a 1947 Italian film also known as ''Elena'' Music * ''Elena'' (Cavalli), a 1659 opera by Francesco Cavalli * ''Elena'' (Mayr), an 1814 opera by Mayr * "Elena" (song), a 1979 song by The Marc Tanner Band * ''Elena'', an EP by Puerto Muerto Other * ''Elena'' (play), a Cebuano play by Vicente Sotto * Extra Low ENergy Antiproton ring, a storage ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argos (satellite System)
Argos is a global satellite-based system that collects, processes, and Dissemination, disseminates (spreads, distributes) environmental data from fixed and mobile platforms around the world. The worldwide tracking and environmental monitoring system is the results froFranco-American cooperation.In addition to satellite data collection, the main feature of the Argos system is its to ability to Geopositioning, geographically locate the data source from any location on Earth using the Doppler effect; which refers to the apparent change in the wavelength due to relative motion between its source and observer. Argos is operated by CLS/Argos, based in Toulouse, France, and its United States subsidiary, CLS America. History and utilization Argos was established in 1978 and has provided data to environmental research and protection groups. It is a component of many global research programs including the Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere program (TOGA), Tagging of Pacific Pelagics ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its origins to 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established by transfer of personnel from the Army Air Forces with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in United States order of precedence, order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, airlift, rapid global mobility, Strategic bombing, global strike, and command and control. The United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force, which serves as the USAF's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held. Bus-derived satellites are less customized than specially-produced satellites, but have specific equipment added to meet customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission. They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are most commonly used in spacecraft which occupy low Earth orbit missions. Examples Some satellite bus examples include: * Boeing DS&S 702 * Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100 * Moog Inc. SL-OMV, Meteor, Meteorite * * INVAP ARSAT-3K * Airbus D&S Eurostar * ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus * NASA Ames MCSB * SSL 1300 * family * Orbital ATK Star Bus family, inc GEOStar * Mitsubishi Electric DS2000 * Spacecraft bus of the Jam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Meteorological Satellite Program
The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) monitors meteorological, oceanographic, and solar-terrestrial physics for the United States Department of Defense. The program is managed by the United States Space Force with on-orbit operations provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The (originally classified) mission of the satellites was revealed in March 1973. They provide cloud cover imagery from polar orbits that are Sun-synchronous at nominal altitude of . History Early in 1963 The Aerospace Corporation recommended that the U.S. Air Force develop a dedicated military meterological satellite, and the Defense Department agreed. The main emphasis would be on cloud-cover photography, but planners expected to add more sophisticated equipment when it became available. Later, when civilian weather satellites improved their capabilities and could satisfy most military requirements, the Defense Department continued to prefer a separate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage rocket, but the term is more general and also encompasses vehicles like the Space Shuttle. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to high operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles use chemical prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Environment
Space environment is a branch of astronautics, aerospace engineering and space physics that seeks to understand and address conditions existing in space that affect the design and operation of spacecraft. A related subject, space weather, deals with dynamic processes in the solar-terrestrial system that can give rise to effects on spacecraft, but that can also affect the atmosphere, ionosphere and geomagnetic field, giving rise to several other kinds of effects on human technologies. Effects on spacecraft can arise from radiation, space debris and meteoroid impact, upper atmospheric drag and spacecraft charging, spacecraft electrostatic charging. Various mitigation strategies have been adopted. Radiation Radiation in space usually comes from three main sources: # The Van Allen radiation belts # Solar proton events and solar energetic particles; and # Galactic cosmic rays. For long-duration missions, the high doses of radiation can damage electronic components and solar cells. A maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud cover is correlated to the sunshine duration as the least cloudy locales are the sunniest ones while the cloudiest areas are the least sunny places, as clouds can block sunlight, especially at sunrise and sunset where sunlight is already limited. The global cloud cover averages around 67-68%, though it ranges from 56% to 73% depending on the minimum optical depth considered (lower when optical depth is large, and higher when it is low, such that subvisible cirrus clouds are counted). Average cloud cover is around 72% over the oceans, with low seasonal variation, and about 55% above land, with significant seasonal variation. Role in the climate system Clouds play multiple critical roles in the climate system and diurnal cycle. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |