|
Television Infrared Observation Satellite
Television InfraRed Observation Satellite (TIROS) is a series of early weather satellites launched by the United States, beginning with TIROS-1 in 1960. TIROS was the first satellite that was capable of remote sensing of the Earth, enabling scientists to view the Earth from a new perspective: space. The program, promoted by Harry Wexler, proved the usefulness of satellite weather observation, at a time when military reconnaissance satellites were secretly in development or use. TIROS demonstrated at that time that "the key to genius is often simplicity". TIROS is an acronym of "Television InfraRed Observation Satellite" and is also the plural of "tiro" which means "a young soldier, a beginner". The Advanced Research Projects Agency (now DARPA) initiated the TIROS program in 1958 and transferred the program to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1959. Participants in the TIROS program also included, Signal Corps (United States Army), United States Army S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCA Astrospace
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghouse, AT&T Corporation and United Fruit Company. In 1932, RCA became an independent company after the partners were required to divest their ownership as part of the settlement of a government United States antitrust law, antitrust suit. An innovative and progressive company, RCA was the dominant electronics and communications firm in the United States for over five decades. In the early 1920s, RCA was at the forefront of the mushrooming radio industry as a major manufacturer of radio receivers, and the exclusive manufacturer of the first superheterodyne sets. The company also created the first nationwide American radio network, the National Broadcasting Company (NBC). RCA was also a pioneer in the introduction and development of television, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the US exclusive economic zone. The agency is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland. History NOAA traces its history back to multiple agencies, some of which are among the earliest in the federal government: * United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, formed in 1807 * National Weather Service, Weather Bureau of the United States, formed in 1870 * United States Fish Commission, Bureau of Commercial Fisheries, formed in 1871 (research fleet only) * NOAA Commissioned Corps, Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, formed in 1917 The most direct predecessor of NOAA was the Enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Angle
In orbital mechanics, the beta angle (\boldsymbol) is the angle between a satellite's orbital plane around Earth and the geocentric position of the Sun. The beta angle determines the percentage of time that a satellite in low Earth orbit (LEO) spends in direct sunlight, absorbing solar radiation. For objects launched into orbit, the solar beta angle of inclined and sun-synchronous orbits depend on launch altitude, inclination, and time. The beta angle does not define a unique orbital plane: all satellites in orbit with a given beta angle at a given orbital altitude have the same exposure to the Sun, even though they may be orbiting in different planes around Earth. The beta angle varies between +90° and −90°, and the direction in which the satellite orbits its primary body determines whether the beta angle sign is positive or negative. An imaginary observer standing on the Sun defines a beta angle as positive if the satellite in question orbits in a counterclockwise directi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outgoing Longwave Radiation
In climate science, longwave radiation (LWR) is electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic thermal radiation emitted by Earth's surface, atmosphere, and clouds. It is also referred to as terrestrial radiation. This radiation is in the infrared portion of the spectrum, but is distinct from the shortwave radiation, shortwave (SW) near-infrared radiation found in sunlight. Outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) is the longwave radiation emitted to space from the top of Earth's atmosphere. It may also be referred to as ''emitted terrestrial radiation''. Outgoing longwave radiation plays an important role in planetary cooling. Longwave radiation generally spans wavelengths ranging from 3–100 micrometres (μm). A cutoff of 4 μm is sometimes used to differentiate sunlight from longwave radiation. Less than 1% of sunlight has wavelengths greater than 4 μm. Over 99% of outgoing longwave radiation has wavelengths between 4 μm and 100 μm. The Radiative flux, flux of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously) or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud cover is correlated to the sunshine duration as the least cloudy locales are the sunniest ones while the cloudiest areas are the least sunny places, as clouds can block sunlight, especially at sunrise and sunset where sunlight is already limited. The global cloud cover averages around 67-68%, though it ranges from 56% to 73% depending on the minimum optical depth considered (lower when optical depth is large, and higher when it is low, such that subvisible cirrus clouds are counted). Average cloud cover is around 72% over the oceans, with low seasonal variation, and about 55% above land, with significant seasonal variation. Role in the climate system Clouds play multiple critical roles in the climate system and diurnal cycle. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Advisory Committee For Aeronautics
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a United States federal agency that was founded on March 3, 1915, to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. On October 1, 1958, the agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel were transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). NACA is an initialism, pronounced as individual letters rather than as a whole word, as was NASA during the early years after being established. Among other advancements, NACA research and development produced the NACA duct, a type of air intake used in modern automotive applications, the NACA cowling, and several series of NACA airfoils, which are still used in aircraft manufacturing. During World War II, NACA was described as "The Force Behind Our Air Supremacy" due to its key role in producing working superchargers for high altitude bombers, and for producing the laminar wing profiles for the North American P-51 Mustan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Welch Kellogg
William Welch Kellogg (February 14, 1917 – December 12, 2007) was an American meteorologist and climatologist. He served as associate director and senior scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). His research included pioneering studies of the role that satellites could play in weather observation and prediction. Biography Kellogg was born in New York Mills, New York, to Fredrick and Elisabeth Kellogg. He attended the Brooks School in North Andover, Massachusetts, and graduated from Yale in 1939 with a BA in physics. At Yale, he was a member of Skull and Bones. His graduate studies at U.C., Berkeley were interrupted by World War II, when he served in the Air Force's new meteorological program. As a pilot and weather officer, with his strong passion for flying, he collected some of the first data on the dynamics of thunderstorms by flying B-25s into the heart of the storms. Weather satellites After the war, while working on a PhD from UCLA, he joine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
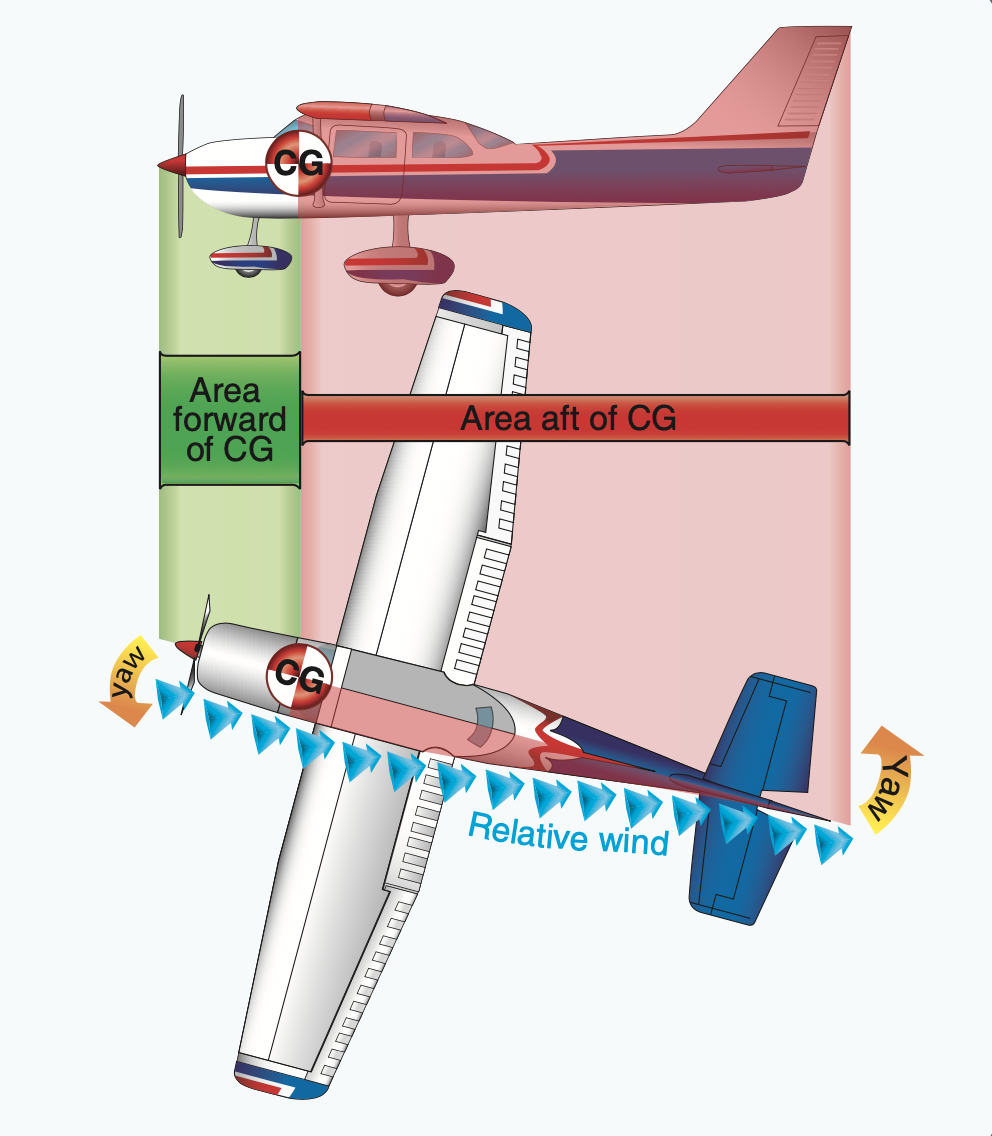
Directional Stability
Directional stability is the tendency of a vehicle or moving body to keep its orientation aligned with its direction of movement. When a car or an airplane gets turned a little relative to its direction of motion, it might correct itself, over-correct itself, or it might start to spin out of control. If it tends to correct itself, we say it's directionally stable, while if it tends to spin-out, we say it is directionally unstable. There are many factors that can effect dynamic stability including speed, weather and road conditions, vehicle shape and mass distribution, and tire properties. Vehicle oscillations associated with dynamic stability are frequently called "weather vaning". When the vehicle's orientation is perturbed from the direction of motion, a restoring moment may be produced which is in a direction ''opposite'' to the orientation disturbance. This can lead to oscillations in orientation around the center of mass similar to a weather vane rotating about its (verti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
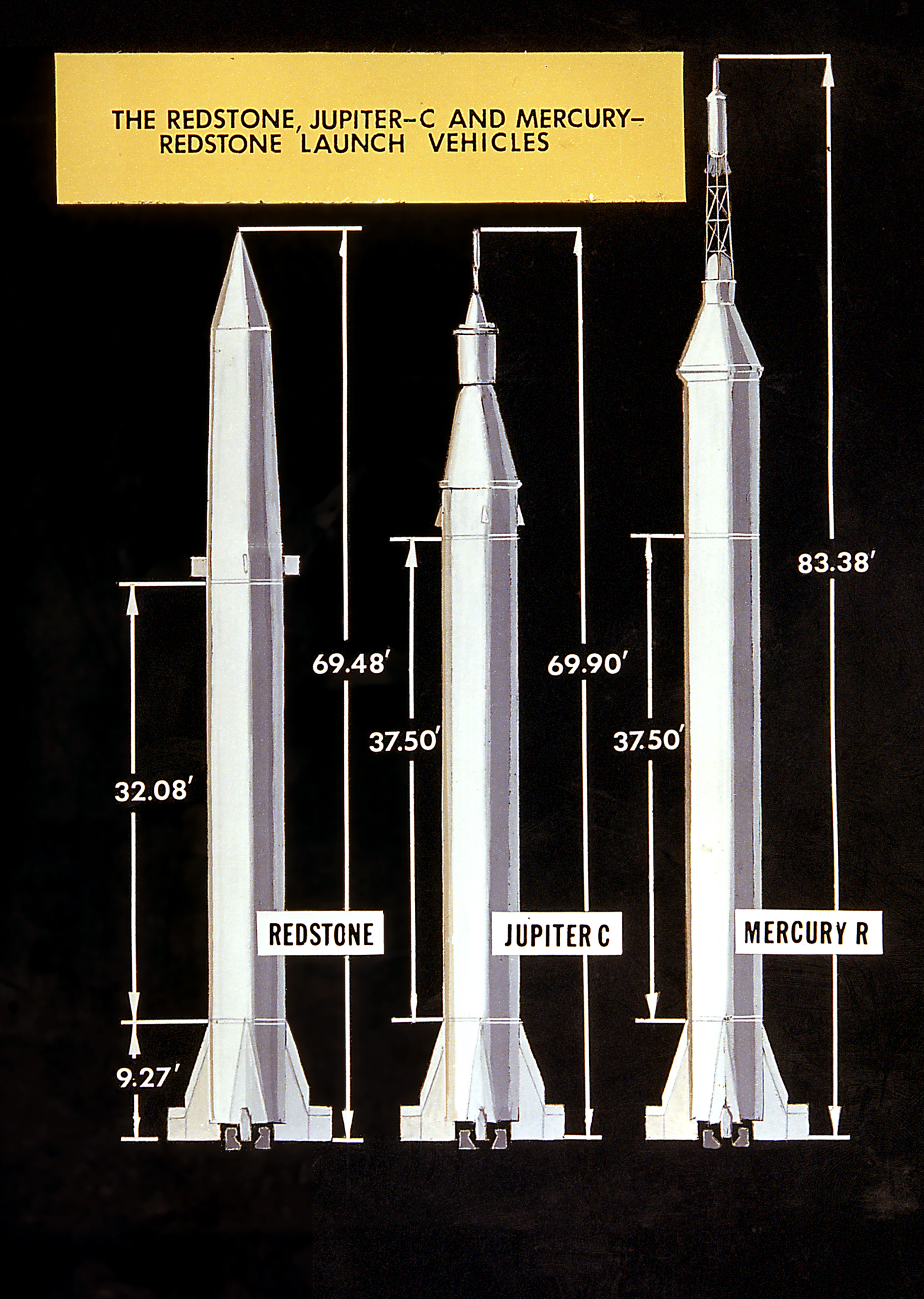
Juno II
Juno II was an American space launch vehicle used during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was derived from the Jupiter missile, which was used as the first stage. Development Solid-fueled rocket motors derived from the MGM-29 Sergeant were used as upper stages, eleven for the second stage, three for the third stage, and one for the fourth stage, the same configuration as used for the upper stages of the smaller Juno I launch vehicle. On some launches to low Earth orbit the fourth stage was not flown, allowing the launch vehicle to carry an additional nine kilograms of payload. Development of the Juno II was extremely fast due to being completely built from existing hardware. The project began in early 1958, and the first vehicle flew at the end of the year. Chrysler was responsible for the overall contract, while Rocketdyne handled the first stage propulsion and Jet Propulsion Laboratory handled the upper stage propulsion. The first three Juno IIs were converted Jupiter m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter-C
The Jupiter-C was an American research and development vehicle developed from the Jupiter-A. Jupiter-C was used for three Uncrewed vehicle, uncrewed sub-orbital spaceflights in 1956 and 1957 to test Re-entry vehicle, re-entry nosecones that were later to be deployed on the more advanced PGM-19 Jupiter mobile missile. The recovered nosecone was displayed in the Oval Office as part of President Dwight D. Eisenhower's televised speech on November 7, 1957. A member of the Redstone (rocket family), Redstone rocket family, Jupiter-C was designed by the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA), under the direction of Wernher von Braun. Three Jupiter-C flights were made. These were followed by satellite launches with the vehicle designated as Juno I (see Jupiter-C#Juno I, Juno I below or the Juno I article). All were launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Cape Canaveral, Florida. Description Each vehicle consisted of a modified PGM-11 Redstone, Redstone ballistic missile w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Ballistic Missile Agency
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) was formed to develop the U.S. Army's first large ballistic missile. The agency was established at Redstone Arsenal on 1 February 1956, and commanded by Major General John B. Medaris with Wernher von Braun as technical director. History The Redstone missile was the first major project assigned to ABMA. The Redstone was a direct descendant of the V-2 missile developed by the von Braun team in Germany during World War II. After the Naval Research Laboratory's Project Vanguard was chosen by the DoD Committee on Special Capabilities, over the ABMA's proposal to use a modified Redstone ballistic missile as a satellite launch vehicle, ABMA was ordered to stop work on launchers for satellites and focus, instead, on military missiles. Von Braun continued work on the design for what became the Jupiter-C rocket. This was a three-stage rocket, designed to test Jupiter missile components which, by ''coincidence'', could be used to lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |