|
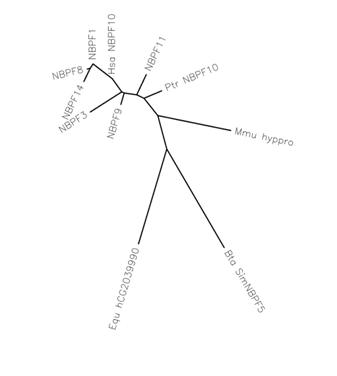
NBPF10
Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 10 is a protein that in ''Homo sapiens'' is encoded by the ''NBPF10'' gene. The full gene is 75,313 bp, with the major isoform of mRNA being 10,697 bp long. The gene is located at 1q21.1. NBPF contains what is known as the DUF1220 repeats. The highly conserved, repeated region is believed to be originated from MGC8902. The NBPF family has been linked to primate evolution. It is assumed to be related to the 1q21.1 deletion syndrome and 1q21.1 duplication syndrome. Homology Paralogs of NBPF10 includes other NBPF family members. Orthologs of NBPF10 are found in other primates; distant orthologs are found in bovine, equine, and canine Functional role Although NBPF10's function is unknown, there is reason to believe that NBPF10 is an important biomarker for the Odontoblast Phenotype Gene Neighborhood NOTCH2NL, SEC22B, HFE2, TXNIP are close neighbors of NBPF10. All of these neighboring genes are well studied in their own right. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DUF1220
The Olduvai domain, known until 2018 as DUF1220 (domain of unknown function 1220) and the NBPF repeat, is a protein domain that shows a striking human lineage-specific (HLS) increase in copy number and appears to be involved in human brain evolution. The protein domain has also been linked to several neurogenetic disorders such as schizophrenia (in reduced copies) and increased severity of autism (in increased copies). In 2018, it was named by its discoverers after Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, one of the most important archaeological sites for early humans, to reflect data indicating its role in human brain size and evolution. Olduvai domains form the core of '' NBPF'' genes, which first appeared in placental mammals and experienced a rapid expansion in monkeys (simians) through duplication to reach over 20 genes in humans. In humans, Olduvai domains are repeated often dozens of times within these genes. The only other gene an Olduvai domain has been found in is mammalian myomega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBPF10 Neighborhood
Neuroblastoma breakpoint family, member 1, or NBPF1, is a protein that is encoded by the gene ''NBPF1'' in humans. This protein is member of the neuroblastoma breakpoint family of proteins, a group of proteins that are thought to be involved in the development of the nervous system. Gene The NBPF1 gene in humans is located on the minus strand of 1p36.3 in humans and is 51179 base pairs long including exons and introns. It is located between the protein coding genes NECAP2 and CROCC. NBPF1 is one of the 26 known members of the Neuroblastoma Breakpoint Family genes and pseudogenes. The NBPF2 pseudogene and NBPF3 gene are the most similar genes located close to NBPF1 and they reside on the chromosomal location 1p36.12. Most members of the NBPF gene family are located on chromosomal location 1q21.1-1q23.3 in humans, and these genes are more similar to each other in sequence than they are to NBPF1. Transcript The transcript for NBPF1 in humans is a 6183 base pair mRNA that is made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TXNIP
Thioredoxin-interacting protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TXNIP'' gene. Interactions TXNIP has been shown to interact with Thioredoxin and ZBTB32. Related gene problems *TAR syndrome *1q21.1 deletion syndrome *1q21.1 duplication syndrome 1q21.1 duplication syndrome or 1q21.1 (recurrent) microduplication is a rare aberration of chromosome 1. In a common situation a human cell has one pair of identical chromosomes on chromosome 1. With the 1q21.1 duplication syndrome one chromosome ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemojuvelin
Hemojuvelin (HJV), also known as repulsive guidance molecule C (RGMc) or hemochromatosis type 2 protein (HFE2), is a membrane-bound and soluble protein in mammals that is responsible for the iron overload condition known as juvenile hemochromatosis in humans, a severe form of hemochromatosis. In humans, the hemojuvelin protein is encoded by the ''HFE2'' gene. Hemojuvelin is a member of the repulsive guidance molecule family of proteins. Both RGMa and RGMb are found in the nervous system, while hemojuvelin is found in skeletal muscle and the liver. Function For many years the signal transduction pathways that regulate systemic iron homeostasis have been unknown. However it has been demonstrated that hemojuvelin interacts with bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), possibly as a co-receptor, and may signal via the SMAD pathway to regulate hepcidin expression. Associations with BMP2 and BMP4 have been described. Mouse HJV knock-out models confirmed that HJV is the gene resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEC22B
Vesicle-trafficking protein SEC22b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SEC22B'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SEC22 family of vesicle trafficking proteins. It seems to complex with SNARE and it is thought to play a role in the ER-Golgi protein trafficking. This protein has strong similarity to Mus musculus and Cricetulus griseus proteins. There is evidence for use of multiple polyadenylation sites for the transcript. SEC22B has been shown to interact with syntaxin 18. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOTCH2NL
Notch homolog 2 N-terminal-like is a family of proteins that in humans consists of 3 proteins (NOTCH2NLA, NOTCH2NLB, and NOTCH2NLC) and is encoded by NOTCH2NL gene. It appears to play a key role in the development of the prefrontal cortex, a part of the brain. NOTCH2NL increases the number of cerebral cortex, cortical stem cells, which while delaying the generation of neurons ultimately leads to a greater number of neurons and larger brains. NOTCH2NL copy number loss and gain is associated with various neurological disorders, and they showed that loss of NOTCH2NL in cortical organoids leads to the organoids being smaller, while resulting in premature differentiation of cortical stem cells into neurons. The role of NOTCH2NL in the development of the human brain together with the evolutionary history of NOTCH2NL genes, suggests that the emergence of NOTCH2NL genes may have contributed to the increase in size of the human neocortex which tripled over the last two million years. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on the crown and the cementum on the root. Structure Odontoblasts are large columnar cells, whose cell bodies are arranged along the interface between dentin and pulp, from the crown to cervix to the root apex in a mature tooth. The cell is rich in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex, especially during primary dentin formation, which allows it to have a high secretory capacity; it first forms the collagenous matrix to form predentin, then mineral levels to form the mature dentin. Odontoblasts form approximately 4 μm of predentin daily during tooth development.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nanci, Elsevier, 2013, page 170 During secretion after differentiation from the outer cells of the dental papilla, it is noted that it is polarized so its n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus '' Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to a therapeutic intervention. as cited in Biomarkers are used in many scientific fields. Medicine Biomarkers used in the medical field, are a part of a relatively new clinical toolset categorized by their clinical applications. The three main classes are molecular biomarkers, cellular biomarkers or imaging biomarkers. All three types of biomarkers have a clinical role in narrowing or guiding treatment decisions and follow a sub-categorization of being either predictive, prognostic, or diagnostic. Predictive Predictive molecular, cellular, or imaging biomarkers that pass validation can serve as a method of predicting clinical outcomes. Predictive biomarkers are used to help optimize ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |