NBPF10 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 10 is a

protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that in ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' is encoded by the ''NBPF10'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
.
The full gene is 75,313 bp, with the major isoform of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
being 10,697 bp long. The gene is located at 1q21.1. NBPF contains what is known as the DUF1220
The Olduvai domain, known until 2018 as DUF1220 ( domain of unknown function 1220) and the NBPF repeat, is a protein domain that shows a striking human lineage-specific (HLS) increase in copy number and appears to be involved in human brain evo ...
repeats. The highly conserved, repeated region is believed to be originated from MGC8902
Neuroblastoma breakpoint family, member 15, also known as NBPF15, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NBPF15'' gene. The gene is 18762 bp long, with mRNA that is 3837 bp long. The gene is located on chromosome 1q21.1. Its sub-cellul ...
. The NBPF family has been linked to primate evolution. It is assumed to be related to the 1q21.1 deletion syndrome and 1q21.1 duplication syndrome.
Homology
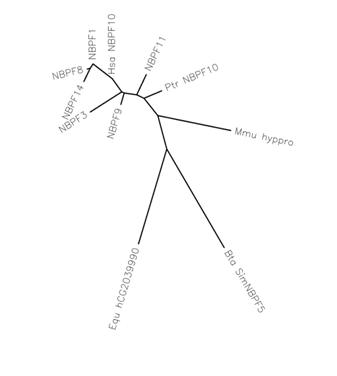
Paralogs of NBPF10 includes other NBPF family members. Orthologs of NBPF10 are found in other primates; distant orthologs are found in bovine, equine, and canine
Functional role
Although NBPF10's function is unknown, there is reason to believe that NBPF10 is an importantbiomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
for the Odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on t ...
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
Gene Neighborhood
NOTCH2NL
Notch homolog 2 N-terminal-like is a family of proteins that in humans consists of 3 proteins (NOTCH2NLA, NOTCH2NLB, and NOTCH2NLC) and is encoded by NOTCH2NL gene. It appears to play a key role in the development of the prefrontal cortex, a par ...
, SEC22B
Vesicle-trafficking protein SEC22b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SEC22B'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SEC22 family of vesicle trafficking proteins. It associates with other SNARE protei ...
, HFE2, TXNIP
Thioredoxin-interacting protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TXNIP'' gene.
Interactions
TXNIP has been shown to interact with Thioredoxin and ZBTB32.
Related gene problems
*TAR syndrome
TAR syndrome (thrombocytopenia wi ...
are close neighbors of NBPF10. All of these neighboring genes are well studied in their own right.
Post-translational modification
NBPF10 has extremely lowthreonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
content which may make the protein less susceptible to post-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
.
References
Human proteins {{gene-1-stub