|
N-flake
An ''n''-flake, polyflake, or Sierpinski ''n''-gon, is a fractal constructed starting from an n-gon, ''n''-gon. This ''n''-gon is replaced by a flake of smaller ''n''-gons, such that the scaled polygons are placed at the Vertex (geometry), vertices, and sometimes in the center. This process is repeated recursively to result in the fractal. Typically, there is also the restriction that the ''n''-gons must touch yet not overlap. In two dimensions The most common variety of ''n''-flake is two-dimensional (in terms of its topological dimension) and is formed of polygons. The four most common special cases are formed with triangles, squares, pentagons, and hexagons, but it can be extended to any polygon. Its boundary is the von Koch curve of varying types – depending on the ''n''-gon – and infinitely many Koch curves are contained within. The fractals occupy zero area yet have an infinite perimeter. The formula of the scale factor ''r'' for any ''n''-flake is: :r = \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fractals By Hausdorff Dimension
According to Benoit Mandelbrot, "A fractal is by definition a set for which the Hausdorff-Besicovitch dimension strictly exceeds the topological dimension." Presented here is a list of fractals, ordered by increasing Hausdorff dimension, to illustrate what it means for a fractal to have a low or a high dimension. Deterministic fractals Random and natural fractals See also * Fractal dimension * Hausdorff dimension * Scale invariance Notes and references Further reading * * * * External links The fractals on MathworldOther fractals on Paul Bourke's websiteFractals on mathcurve.com* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060923100014/http://library.thinkquest.org/26242/full/index.html Fractals unleashedIFStile - software that computes the dimension of the boundary of self-affine tiles {{DEFAULTSORT:Fractals By Hausdorff Dimension Hausdorff Dimension Hausdorff Dimension In mathematics, Hausdorff dimension is a measure of ''roughness'', or more specifically, fractal dimension, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
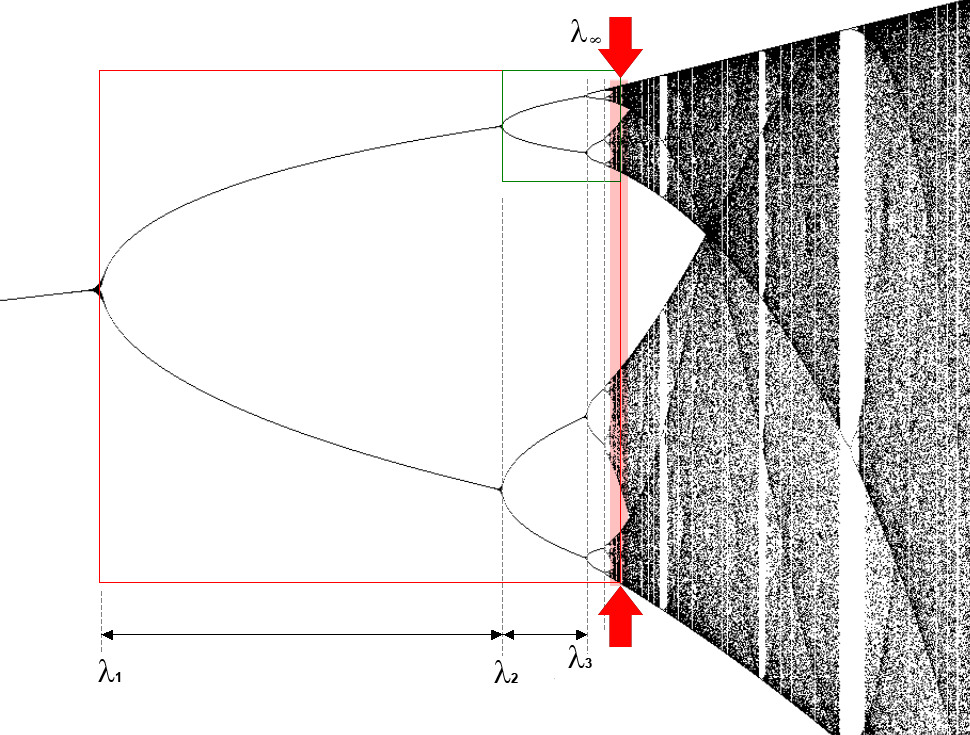
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine geometry, affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they Scaling (geometry), scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantor Dust
In mathematics, the Cantor set is a set of points lying on a single line segment that has a number of unintuitive properties. It was discovered in 1874 by Henry John Stephen Smith and mentioned by German mathematician Georg Cantor in 1883. Through consideration of this set, Cantor and others helped lay the foundations of modern point-set topology. The most common construction is the Cantor ternary set, built by removing the middle third of a line segment and then repeating the process with the remaining shorter segments. Cantor mentioned this ternary construction only in passing, as an example of a perfect set that is nowhere dense. More generally, in topology, a Cantor space is a topological space homeomorphic to the Cantor ternary set (equipped with its subspace topology). The Cantor set is naturally homeomorphic to the countable product ^ of the discrete two-point space \underline 2 . By a theorem of L. E. J. Brouwer, this is equivalent to being perfect, nonempty, compact, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the ( convex, non- stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, and is represented by its Schläfli symbol , contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecahedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (; ) or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120. Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular: The #Pyritohedron, pyritohedron, a common crystal form in pyrite, has pyritohedral symmetry, while the #Tetartoid, tetartoid has tetrahedral symmetry. The rhombic dodecahedron can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry. The elongated dodecahedron and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling polyhedra, space-filling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (: octahedra or octahedrons) is any polyhedron with eight faces. One special case is the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. Many types of irregular octahedra also exist, including both convex set, convex and non-convex shapes. Combinatorially equivalent to the regular octahedron The following polyhedra are combinatorially equivalent to the regular octahedron. They all have six vertices, eight triangular faces, and twelve edges that correspond one-for-one with the features of it: * Triangular antiprisms: Two faces are equilateral, lie on parallel planes, and have a common axis of symmetry. The other six triangles are isosceles. The regular octahedron is a special case in which the six lateral triangles are also equilateral. * Tetragonal bipyramids, in which at least one of the equatorial quadrilaterals lies on a plane. The regular octahedron is a special case in which all thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menger Sponge
In mathematics, the Menger sponge (also known as the Menger cube, Menger universal curve, Sierpinski cube, or Sierpinski sponge) is a fractal curve. It is a three-dimensional generalization of the one-dimensional Cantor set and two-dimensional Sierpinski carpet. It was first described by Karl Menger in 1926, in his studies of the concept of topological dimension. Construction The construction of a Menger sponge can be described as follows: # Begin with a cube. # Divide every face of the cube into nine squares in a similar manner to a Rubik's Cube. This sub-divides the cube into 27 smaller cubes. # Remove the smaller cube in the middle of each face and remove the smaller cube in the center of the larger cube, leaving 20 smaller cubes. This is a level 1 Menger sponge (resembling a void cube). # Repeat steps two and three for each of the remaining smaller cubes and continue to iterate ''ad infinitum''. The second iteration gives a level 2 sponge, the third iteration gives a level 3 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polytope, convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean geometry, Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid (geometry), pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such net (polyhedron), nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedra
In geometry, a polyhedron (: polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional figure with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. The term "polyhedron" may refer either to a solid figure or to its boundary surface. The terms solid polyhedron and polyhedral surface are commonly used to distinguish the two concepts. Also, the term ''polyhedron'' is often used to refer implicitly to the whole structure formed by a solid polyhedron, its polyhedral surface, its faces, its edges, and its vertices. There are many definitions of polyhedron. Nevertheless, the polyhedron is typically understood as a generalization of a two-dimensional polygon and a three-dimensional specialization of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Polyhedra have several general characteristics that include the number of faces, topological classification by Euler characteristic, duality, vertex figures, surface area, volume, interior lines, Dehn invari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |