|
Murad II Bey
Mourad II Bey, died 1675Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''Présent des hommes de notre temps. Chroniques des rois de Tunis et du pacte fondamental'', vol. II, éd. Maison tunisienne de l'édition, Tunis, 1990, p. 54 in the palace of BardoIbn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit'', p. 55 was the third Muradid Bey of Tunis from 1666 until his death. Reign Son of Hammuda Pasha Bey, he distinguished himself by his courage, his fortitude and his concern for the good governance of the people. He spent the greater part of his time travelling the land to levy the tribute, deal with intrusions by the army of Algiers and the collusion of the northwestern tribes with the Algerians. Furthermore, he faced a revolt of the divan of the militia, led by the Dey Ali Laz.Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit'', p. 58 After Murad II suffered reverses in one of his expeditions far from Tunis, Laz replaced him with Mohamed Agha, an officer of the Turkish militia. But Murad II eventually defeated the latter and was restored to power in 1673, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Bardo
Le Bardo ( ar, الباردو ' also Bārdaw, Bardaw, and Bardois) is a Tunisian city west of Tunis. As of 2004, the population is 73,953. Built by the Hafsid dynasty in the 14th century, the name Bardo comes from the Spanish word "prado" meaning a garden. Bardo became a residence of the Tunis court in the 18th century. With the arrival of Husseinite beys, Bardo became a political, intellectual and religious center. The ancient beys' residence was the site of the Tunisian National Assembly headquarters, and the National Museum opened there in 1888. The city gave its name to the Treaty of Bardo, signed in nearby Ksar Saïd Palace, which placed Tunisia under a French protectorate A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inte ... in May 1881. External links {{Authority contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
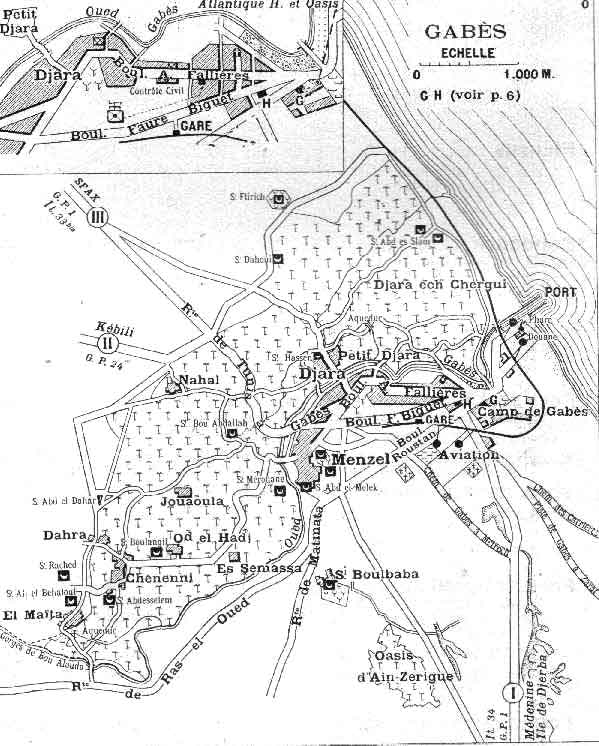
Gabès
Gabès (, ; ar, قابس, ), also spelled Cabès, Cabes, Kabes, Gabbs and Gaps, is the capital city of the Gabès Governorate in Tunisia. It is located on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès. With a population of 152,921, Gabès is the 6th largest Tunisian city. Gabes is 327 km away from Tunis and 113 km away from Sfax. History Etymology Takapes, the ancient name of Gabès, is a Numidian ( Berber) toponym. Later, the prefix "Ta" (meaning "to" in Berber) was dropped, and the place became known as Kapes. As in Arabic the sound /p/ is unknown, Kapes became known as Kabes, and later known as Gabès. Roman period Gabès is the ancient ''Tacapae'' or ''Tacape'' (Τακάπη in Ancient greek) or ''Tacapes'' of the Roman province of Tripolitania. Strabo refers to this city as an important entrepot of the Lesser Syrtis. Pliny (18.22) remarks that the waters of a copious fountain at Tacape were divided among the cultivators according to a system where each had the use of the water d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammouda Pacha Mosque
Hammouda Pacha Mosque or Hamouda Pacha al Mouradi ( ar, مسجد حمودة باشا) is a mosque in Tunis, Tunisia. It is an official historical monument. Localization This mosque is located in the Medina area of the city, in the Sidi Ben Arous street. History Built in 1655 by Hammouda Pacha, it is the second mosque to be built by the Hanafi rite in Tunis. Architecture The Hammouda Pacha mosque is known for its Turkish architecture. It has an octagon minaret A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generall ... and the hall of prayer is rectangular. File:Mosquée Hamouda Bacha, Tunis 21 septembre 2013 (panoramique).jpg, A panomaric view of the mosque File:Mosquee hamouda pacha 2.jpg, Entrance of the mosque from Sidi Ben Arous street References Mosques in the medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrahim Sharif Of Tunis
Ibrahim Sharif ( ar, إبراهيم الشريف) was Bey of Tunis from 1702 to 1705, during the period of crisis which brought an end to the Muradid dynasty and preceded the rise to power of Husayn I Bey. Lieutenant of the Muradid Beys of Tunis, Ibrahim was at various points Agha of the sipahis (commander of the cavalry of the Turkish militia) and Agha of the janissaries (commander of the rifleman) to the final Muradid princes. During a trip to Istanbul to recruit janissaries, a new war was declared between Murad III Bey and the Dey of Algiers; the Ottoman court, no longer able to control Murad III, ordered Ibrahim to return to Tunisia and arrest him. At the outset of the military campaign, on the banks of the Wadi Zarka, Ibrahim struck Murad III with a blow from his blunderbuss, before killing him in the presence of his other lieutenants.André Raymond, ''Tunis sous les Mouradites : la ville et ses habitants au XVIIe siècle'', éd. Cérès, Tunis, 2006 On his return to Tunis S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of Tunis
The Revolutions of Tunis or the Muradid War of Succession was a period of troubles and civil wars in Ottoman Tunisia. It ran from the death of the Muradid sovereign Murad II Bey in 1675 until the seizure of power by the Husainid sovereign Al-Husayn I ibn Ali at-Turki in 1705. The belligerents were Ali Bey al-Muradi and Muhammad Bey al-Muradi (sons of Murad II Bey), their uncle Muhammad al-Hafsi al-Muradi (Pasha of Tunis), several Deys of Tunis, the Turkish militia in Tunis and the Dey of Algiers. Historians agree that the revolutions originated from the constant power conflict between the Muradid dynasty, which attempted to detach itself from Ottoman control and the Turkish militia in Tunis (headed by the divan), which challenged the primacy of the Beys and refused to submit to their increasingly monarchical rule.André Raymond, ''Tunis sous les Mouradites : la ville et ses habitants au XVIIe siècle'', éd. Cérès, Tunis, 2006 The Deys of Tunis found themselves in the middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.James Fearon"Iraq's Civil War" in ''Foreign Affairs'', March/April 2007. For further discussion on civil war classification, see the section "Formal classification". The term is a calque of Latin '' bellum civile'' which was used to refer to the various civil wars of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. Most modern civil wars involve intervention by outside powers. According to Patrick M. Regan in his book ''Civil Wars and Foreign Powers'' (2000) about two thirds of the 138 intrastate conflicts between the end of World War II and 2000 saw international intervention, with the United States intervening in 35 of these conflicts. A civil war is a high-intensity conflict, often involving regular armed forces, that is sustained, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Bey Of Tunis
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. The issue of his succession caused a major rift between Muslims and divided them into Shia and Sunni groups. Ali was assassinated in the Grand Mosque of Kufa in 661 by the forces of Mu'awiya, who went on to found the Umayyad Caliphate. The Imam Ali Shrine and the city of Najaf were built around Ali's tomb and it is visited yearly by millions of devotees. Ali was a cousin and son-in-law of Muhammad, raised by him from the age of 5, and accepted his claim of divine revelation by age 11, being among the first to do so. Ali played a pivotal role in the early years of Islam while Muhammad was in Mecca and under severe persecution. After Muhammad's relocation to Medina in 622, Ali married his daughter Fatima and, among others, fathered Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohamed Bey El Mouradi
Mohamed Bey El Mouradi (died October 14, 1696) was a Muradid leader and Bey of Tunis from 1686 until his death.Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit'', p. 76Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit'', p. 83 He was the eldest son of Murad II Bey.Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit'', p. 60 Despite the troubled times, he was responsible for building several monuments in Tunis including the M'hamed Bey Mosque (Sidi Mahrez Mosque), modelled on the mosques of Istanbul with a great central dome, In addition the construction of many buildings of worship and education within the country he ordered construction works in Beja, El Kef, Gafsa, Tozeur and Gabès. In 1690 Mohamed Bey built a bridge between Tebourba and Medjerda The Medjerda River ( ar, وادي مجردة), the classical Bagrada, is a river in North Africa flowing from northeast Algeria through Tunisia before emptying into the Gulf of Tunis and Lake of Tunis. With a length of , it is the longest river ....Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit'', p. 77 He died on October 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yusuf Dey
Yusuf Dey (c.1560 in Tripoli – 1637 at Tunis) was Dey of Tunis from 1610 until his death. Biography Son of Mustapha El Turki, an Ottoman Turkish soldier stationed at Tripoli, he took up a post in the militia of Tunis. He was recognised by Uthman Dey, who appointed him to several posts and even favoured him over his own sons. Before his death, Uthman managed to convince the divan of Tunis to name Yusuf as his successor. He also married him to his daughter. At the death of Ramadhan Bey, who had been appointed by Uthman Dey to direct the armed force which controlled the hinterland, Yusuf selected the lieutenant and mameluke of Ramadhan Bey, an Islamic convert and corsair named Murad who became the founder of the Muradid dynasty of Beys of Tunis. In addition, Yusuf Dey often conferred with his friend and principal lieutenant, Ali Thabet. A keen builder, Yusuf Dey had the first Ottoman style mosque built, in 1616.''Mosquées de Tunisie'', éd. Maison tunisienne de l'édition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medjerda River
The Medjerda River ( ar, وادي مجردة), the classical Bagrada, is a river in North Africa flowing from northeast Algeria through Tunisia before emptying into the Gulf of Tunis and Lake of Tunis. With a length of , it is the longest river of Tunisia. It is also known as the Wadi Majardah or Mejerha (french: Oued Majardah). Course The Medjerda River originates in the Tell Atlas, part of the Atlas Mountains, in northeastern Algeria and then flows eastwards to Tunisia, then entering the Gulf of Utica of the Mediterranean Sea. Its course has a length of . It is the most important and longest river in Tunisia and is dammed in several locations, being a major supplier of water to the country's wheat crops. The Gulf of Utica was formed during the postglacial transgression about 6,000 years ago. Over time, fluvial deposits from the Medjerda gradually filled up the northern part of the gulf. The succession of events during historical times has been inferred from ancient documents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maliki
The ( ar, مَالِكِي) school is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas in the 8th century. The Maliki school of jurisprudence relies on the Quran and hadiths as primary sources. Unlike other Islamic fiqhs, Maliki fiqh also considers the consensus of the people of Medina to be a valid source of Islamic law. The Maliki school is one of the largest groups of Sunni Muslims, comparable to the Shafi`i madhhab in adherents, but smaller than the Hanafi madhhab. Sharia based on Maliki doctrine is predominantly found in North Africa (excluding northern and eastern Egypt), West Africa, Chad, Sudan, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the Emirate of Dubai ( UAE), and in northeastern parts of Saudi Arabia.Jurisprudence and Law – Islam Reorienting the Veil, University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


