|
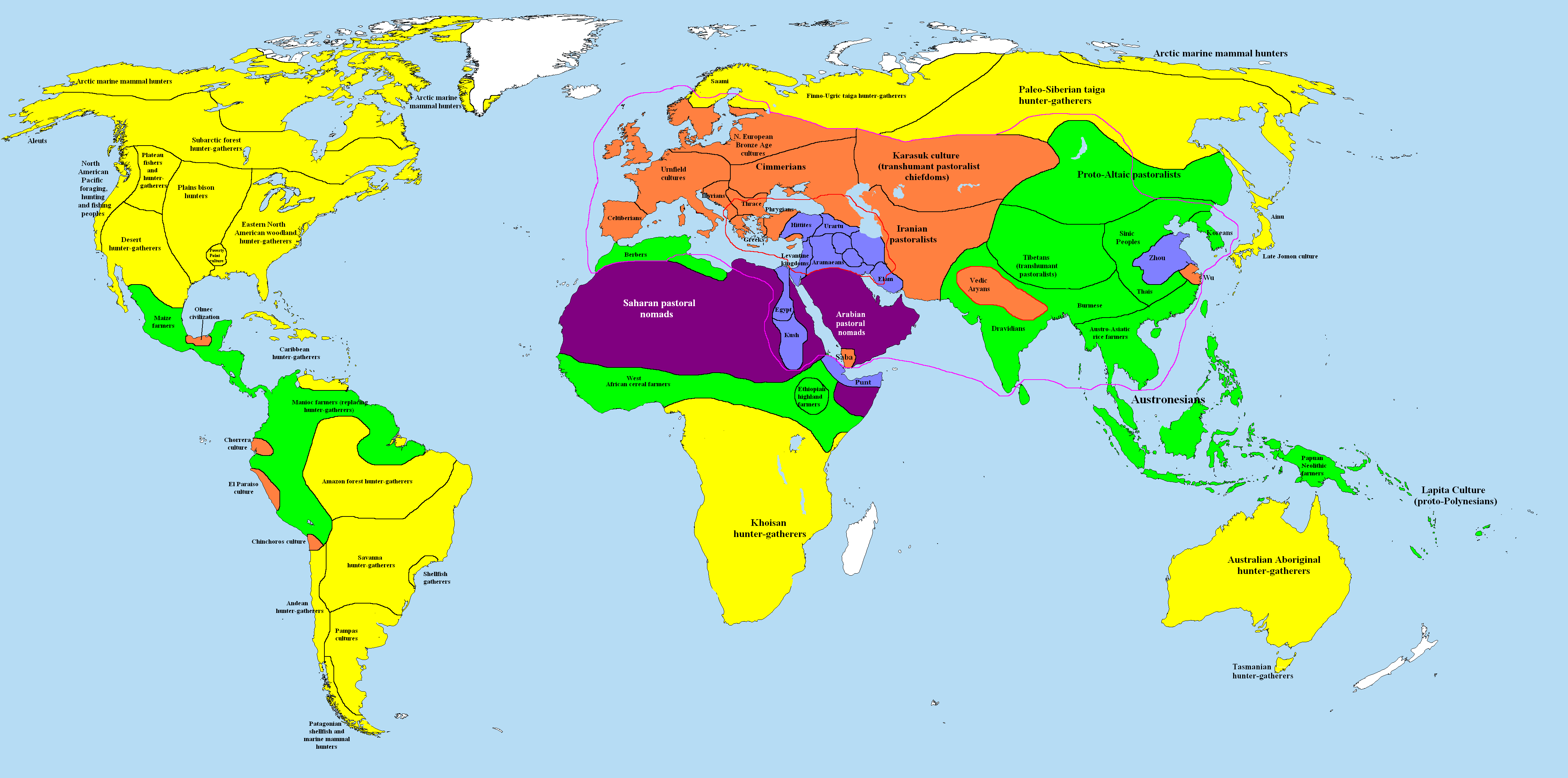
Mueang Uthong
Mueang Uthong () is an archaeological site located in the U Thong district, Suphan Buri province . It was inhabited from around the 10th century BC and became the state society in the third to sixth-century CE. Uthong was one of the largest known city-states that emerged around the plains of central Thailand in the first millennium but became abandoned around 1000 AD due to the endemic and lost in major trading cities status. It was resettled in the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Ayutthaya period but was abandoned again after the Burmese–Siamese War (1765–1767), fall of Ayutthaya in the 1760s. Uthong is also considered the first city-state that practiced Brahmanism and Buddhism in present-day central Thailand. O. W. Wolters speculated that Mueang Uthong was the center of Chen Li Fu, an ancient kingdom mentioned in the Chinese text ''Sung Hui Yao Kao'' in 1200 and 1205, while Paul Wheatley (geographer), Paul Wheatley posited that the site in question was the city-state of Chin Lin, the ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorinus
Marcus Piavonius VictorinusSome of the inscriptions record his name as M. Piavvonius Victorinus, as does the first release of coins from the Colonia mint. A mosaic from Augusta Treverorum (Trier) lists him as Piaonius. was Gallic Empire, emperor in the Gallic provinces from 268 to 270Martindale, p. 965 or 269 to 271,Polfer, ''Victorinus'' following the brief reign of Marcus Aurelius Marius, Marius. He was murdered by a jealous husband whose wife he had tried to seduce. Reign Hailing from Gaul, Victorinus was born into a Gauls, Gallic family of great wealth, and was a soldier under Postumus, the first of the so-called Gallic emperors. He showed considerable ability, as he held the title of tribunus praetorianorum (tribune of the praetorians) in 266/267, and rose swiftly to become co-consul (Gallic Empire), consul with Postumus in 268.Southern, p. 118 It is also possible that Postumus then elevated him to the post of praetorian prefect.Potter, p. 266 Shortly after putting down a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century BC
The 10th century BC comprises the years from 1000 BC to 901 BC. This period followed the Late Bronze Age collapse in the Near East, and the century saw the Early Iron Age take hold there. The Greek Dark Ages which had come about in 1200 BC continued. The Neo-Assyrian Empire is established towards the end of the 10th century BC. In the Iron Age in India, the Vedic period is ongoing. In China, the Zhou dynasty is in power. Bronze Age Europe continued with Urnfield culture. Japan was inhabited by an evolving hunter-gatherer society during the Jōmon period. The world in the 10th century BC Events * 1000 BC: India— Iron Age of India. Indian kingdoms rule India— Panchala, Kuru, Kosala, Pandya and Videha. * 1000 BC: The Sa Huỳnh culture started in central and southern Vietnam. * 993 BC: Amenemope succeeds Psusennes I as king of Egypt. * 993 BC: Archippus, King of Athens dies after a reign of 19 years and is succeeded by his son Thersippus. * 984 BC: Osorkon th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
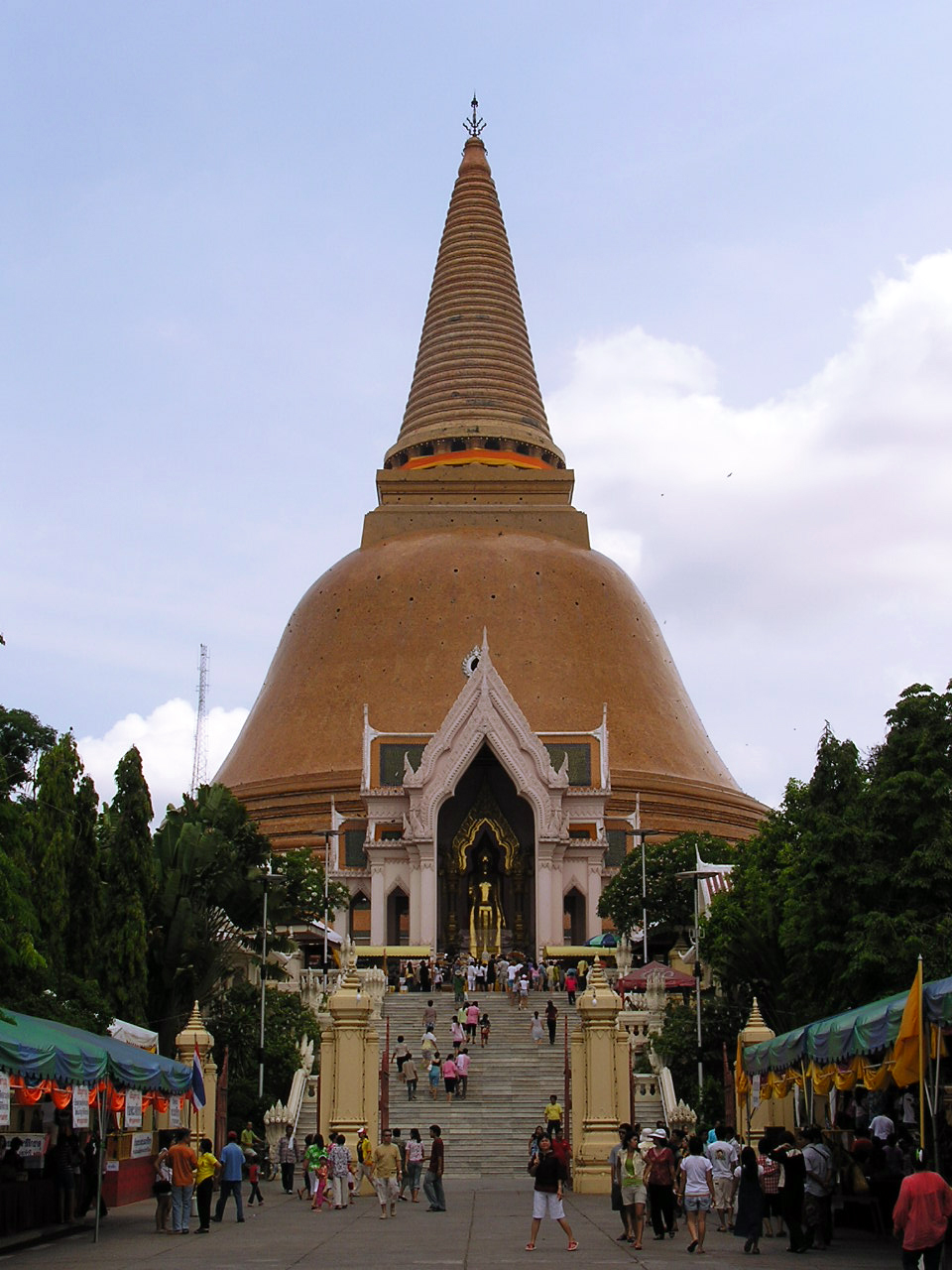
Nakhon Pathom
Nakhon Pathom (, ) is a city (''thesaban nakhon'') in central Thailand, the former capital of Nakhon Pathom province. One of the most important landmarks is the giant Phra Pathommachedi. The city is also home to Thailand's only Bhikkhuni temple Wat Songkhammakalayani, Wat Song Thammakanlayani (), which is also open to women from abroad. Nakhon Pathom houses a campus of Silpakorn University within the former Sanam Chandra Palace. The city is 57 km west of Bangkok. According to Charles Higham (archaeologist), Charles Higham, "Two silver medallions from beneath a sanctuary at Nakhon Pathom, the largest of the moated sites, proclaim that it was 'the meritorious work of the King of Sri Dvaravati', the Sanskrit term Dvaravati meaning 'that which has gates'. The script is in south Indian characters of the seventh century." Nakhon Pathom was the largest Dvaravati center.Higham, Charles., 2014, ''Early Mainland south-east Asia'', Bangkok: River Books Co., Ltd., History Nakhon P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvaravati
Dvaravati () was a medieval Mon political principality from the 6th century to the 11th century, located in the region now known as central Thailand, and was speculated to be a succeeding state of Lang-chia or Lang-ya-hsiu (). It was described by Chinese pilgrims in the middle of the 7th century as a Buddhist kingdom named ''To-lo-po-ti'' situated to the west of Isanapura (Cambodia), to the east of Sri Ksetra (Burma), and adjoined Pan Pan in the South. Its northern border met ''Jiā Luó Shě Fú'' (), which was speculated to be either ''Kalasapura'', situated along the coast of the Bay of Bengal somewhere between Tavoy and Rangoon, or Canasapura in modern northeast Thailand. Dvaravati sent the first embassy to the Chinese court around 605–616, and then in 756. Text: Dvaravati also refers to a culture, an art style, and a disparate conglomeration of principalities of Mon people. The Mon migrants as maritime traders might have brought the Dvaravati Civilization to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sri Ksetra Kingdom
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Sri Ksetra , common_name = Kingdom of Sri Ksetra , era = Classical Antiquity , status = City-state , event_start = Founding of kingdom , year_start = c. 3rd – 9th century CE , date_start = , event_end = Fall of kingdom , year_end = 1050s , date_end = , event1 = Launch of Burmese calendar , date_event1 = 21 March 640 , event2 = Duttabaung ascends to throne , date_event2 = 25 March 739 , event3 = , date_event3 = , event4 = , date_event4 = , p1 = , flag_p1 = , p2 = , flag_p2 = , s1 = Pagan kingdom , flag_s1 = , s2 = , flag_s2 = , image_flag = , flag = , flag_type = , image_coat = , image_map = Pyu Realm.png , symbol = , symbol_type = , image_map_caption = , capital = Sri Ksetra , common_languages = Pyu , religion = Buddhism, Animism, Vaishnavism , government_type = Monarchy , leader1 = , year_leader ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokṣadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of his journey to the Indian subcontinent in 629–645, his efforts to bring at least 657 Indian texts to China, and his translations of some of these texts. He was only able to translate 75 distinct sections of a total of 1335 chapters, but his translations included some of the most important Mahayana scriptures. Xuanzang was born on 6 April 602 in Chenliu, near present-day Luoyang, in Henan province of China. As a boy, he took to reading religious books, and studying the ideas therein with his father. Like his elder brother, he became a student of Buddhist studies at Jingtu monastery. Xuanzang was ordained as a ''śrāmaṇera'' (novice monk) at the age of thirteen. Due to the political a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamalanka
Kamalanka (''Chia-mo-lang-chia'', ''Lang-chia'', ''Lang-ya-hsiu'') or Kolo (''Gē Luó'') in the Chinese texts, or Balangka/Kalonga in the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geographike Hyphegesis'' of Ptolemy, or Mevilimbangam in the Tamil inscriptions in Malay world#Tanjore Inscription, Tanjore Inscription, was an ancient political entity located in the west Chao Phraya River basin in central Thailand. It existed from the late 1st or early 2nd century CE to 1058. Its chief city, located at the ancient Nakhon Pathom, was possibly destroyed by the troops of Pagan kingdom, Pagan's Anawrahta in 1058 during his Chao Phraya River, Menam invasion to attack the Lavo Kingdom. This marks the ending of Kamalanka. Previously, it was raided by the Chola Empire during the South-East Asia campaign of Rajendra I in 1030. Its successor, Chen Li Fu centered at ''Suvarnapura'', appeared around the 12th century, 90 kilometers northward in the present-day Don Chedi District, Don Chedi, Suphan Buri provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in Mainland Southeast Asia covering parts of present-day Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam that existed from the first to sixth century CE. The name is found in Chinese historical texts describing the kingdom, and the most extensive descriptions a name the people of Funan gave to their polity. Some scholars argued that ancient Chinese scholars has found the records from Yuán Shǐ, the history records of Yuan Dynasty. "Syam Kok and Lo Hu Kok, formerly the Kingdom of Funan, were located to the west of Linyi Kok (Champa Kingdom in central Vietnam). The maritime distance was from the capital of Linyi Kok to the capital of Funan Kok. They are separated by about 3,000 li." Like the name of the kingdom, the ethno-linguistic nature of the people is the subject of much discussion am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chin Lin
Chin Lin or Kim Lin ( zh, 金鄰/金邻; ; ) was an ancient political entities in modern lower central Thailand exited from the 9 CE to the 3rd century. In the 3rd century CE, after defeating Tun Sun to control the trans-Kra Isthmus trade route and encircle Chin Lin, king Fan Man of Funan attempted to seize Chin Lin, but failed due to his illness. The city "''Balangka'', an inland town" (), mentioned in the ''Geographike Hyphegesis'' of Ptolemy in the 2nd century, has been assumed by Thai scholars to have been Mueang Uthong, the center of Chin Lin. Location The location of Chin Lin remains unclear. It was first mentioned around 9 – 22 CE during the late Western Han period, a Chinese emperor Wang Mang sent an embassy to visit Chin-lin. Later in the 3rd century, Chin Lin was again mentioned in the account of Funan king ''Fan Shih-mans conquests in the Chinese text '' Liáng Shū'', which states that Chin Lin was located 3,000 li north of the kingdoms of Ta-k'un (Ch'ü-tu-k'un) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |