|
Mount Wu
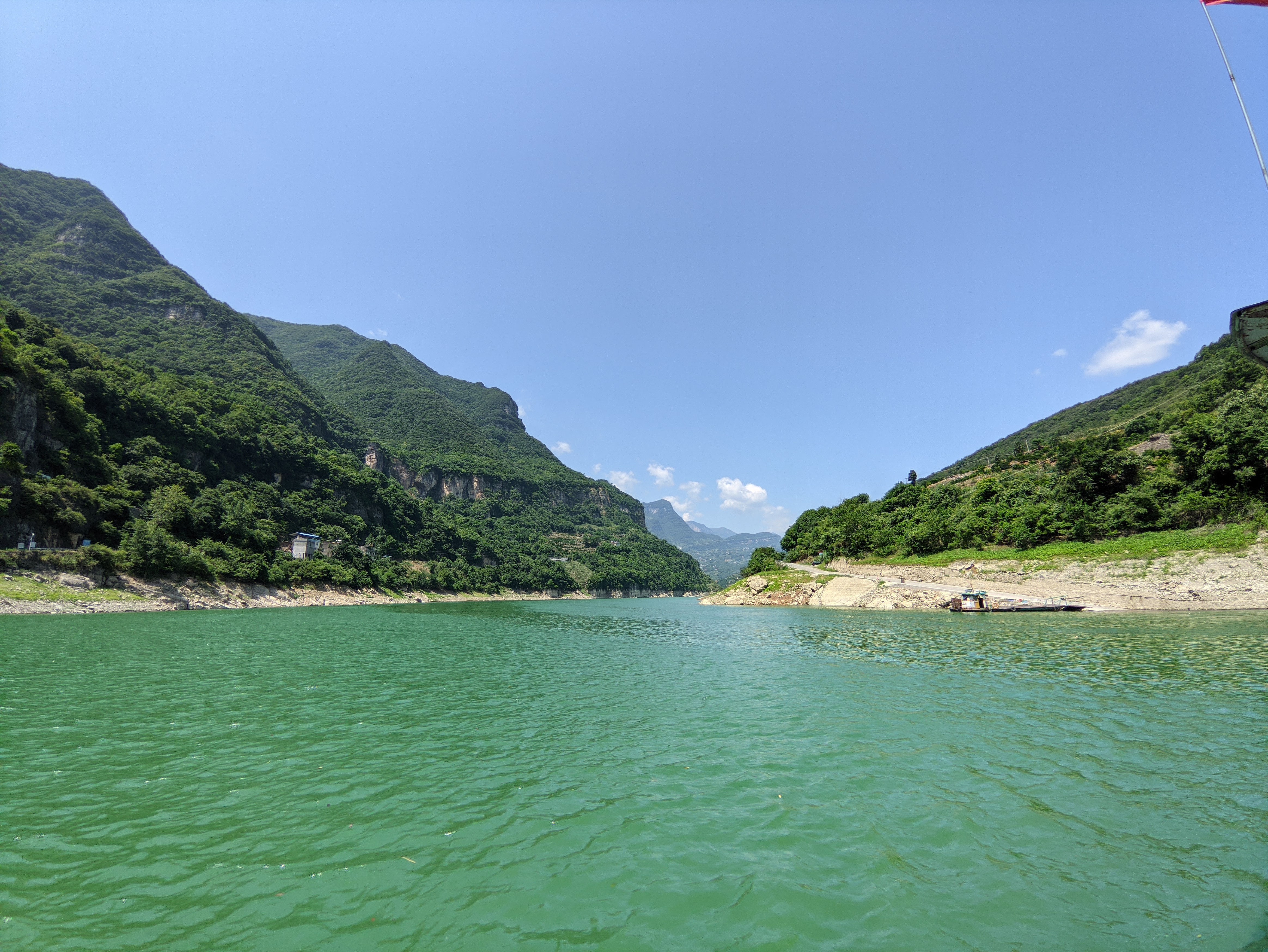
Wuxia Gorge (), sometimes called Great Gorge (), is the second gorge of the Three Gorges system on the Yangtze River, People's Republic of China. Formed by the Wu River, it stretches from Wushan to Guandukou, and is located downstream of Qutang Gorge and upstream of Xiling Gorge. The gorge straddles the boundary between Wushan County of Chongqing Municipality (formerly part of Sichuan Province) and Badong County, Hubei Province. The gorge has been known as the Wuxia Gorge since at least the Three Kingdoms period, when it was recorded in the geographical treatise ''Shui Jing Zhu''. In 589 AD, General Lü Zhongsu of the Chen dynasty stationed troops in the Wuxia and Xiling Gorges in an attempt to stop the advancing Sui dynasty armies. Tang dynasty poet Yang Jiong wrote a classical poem entitled "Passing Wuxia Gorge" (). Among the Twelve Peaks of the Wuxia Gorge, the most spectacular is the Goddess Peak. Legend has it that this peak is the incarnation of Yaoji Yaoji (), is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wushan Yangtse
Wushan may refer to the following locations in the People's Republic of China: *Wushan County, Chongqing (巫山县) **Wu Mountains, or Wushan (巫山), mountainous region *Wushan County, Gansu (武山县), county of Tianshui City, Gansu *Wushan, Lechang (五山), town of Lechang, Guangdong *Wushan, Shandong (吾山), town of Anqiu, Shandong *Wushan Subdistrict, Guangzhou (五山街道), subdistrict in Tianhe District, Guangzhou, Guangdong *Wushan Subdistrict, Changsha (乌山街道), subdistrict in Wangcheng District, Changsha, Hunan *Wushan, Sui County (), town in Sui County, Hubei, Sui County, Suizhou, Hubei, China See also * Wushan Man {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
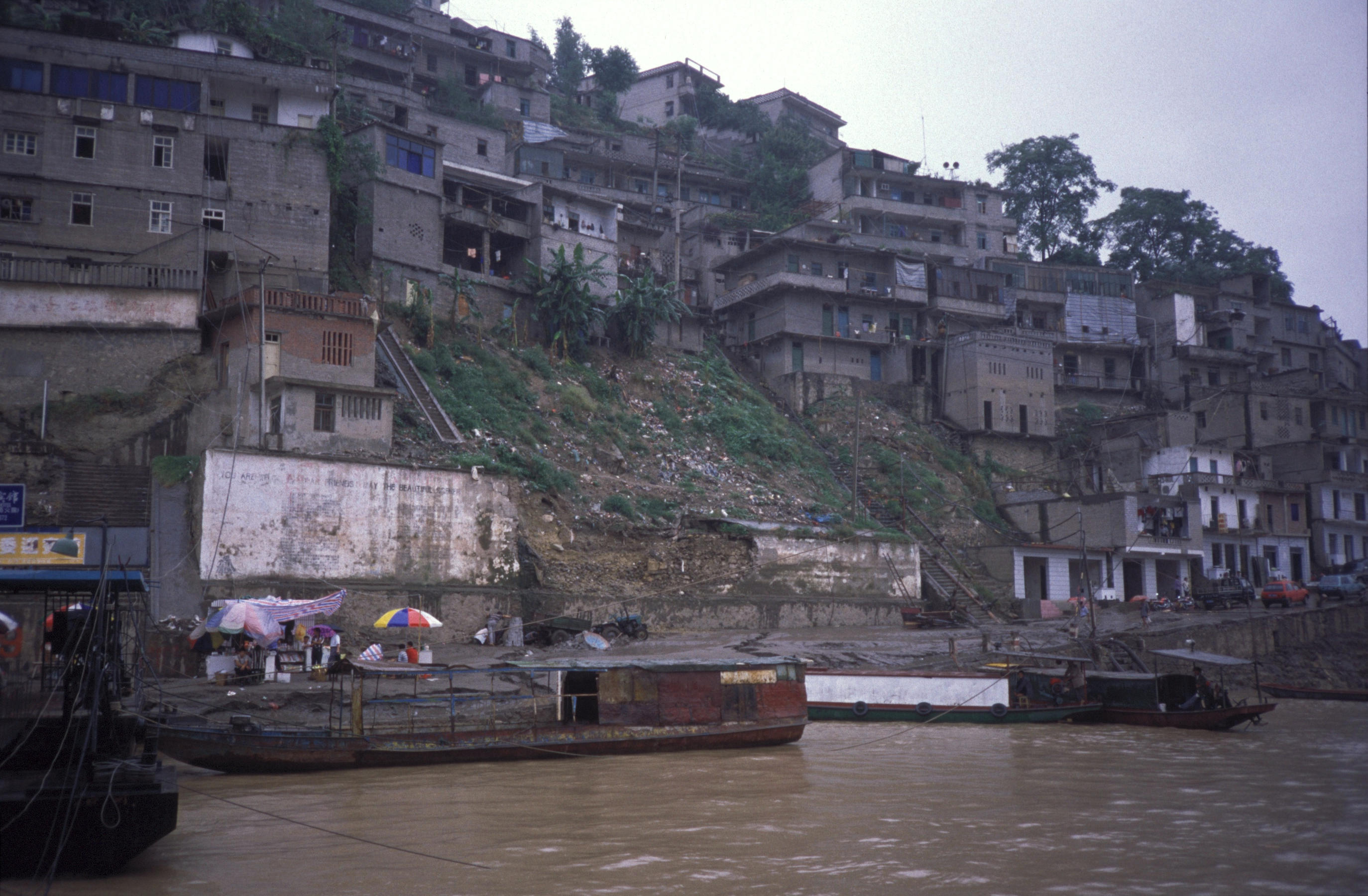
Badong County
Badong County () is a county located in western Hubei province, People's Republic of China, bordering Chongqing municipality to the west. It is the northernmost county-level division under the administration of Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Enshi Prefecture. The Yangtze River flows through the county and the county seat is located just east of the Wu Gorge in the Three Gorges region. Badong County is famous for the Shennong Stream gorges located near Badong town. The stream itself falls into the Yangtze opposite the Badong center city. The Badong county seat, commonly referred to simply as "Badong", is in the Town (China), town of Xinling (), located on the high southern banks of the Yangtze River channel. The Yangtze valley was flooded during the first decade of the 21st century after the construction of the Three Gorges Dam to the east, but Badong county seat was mostly above the flood line, and so more of the original town survives than is the case in many other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
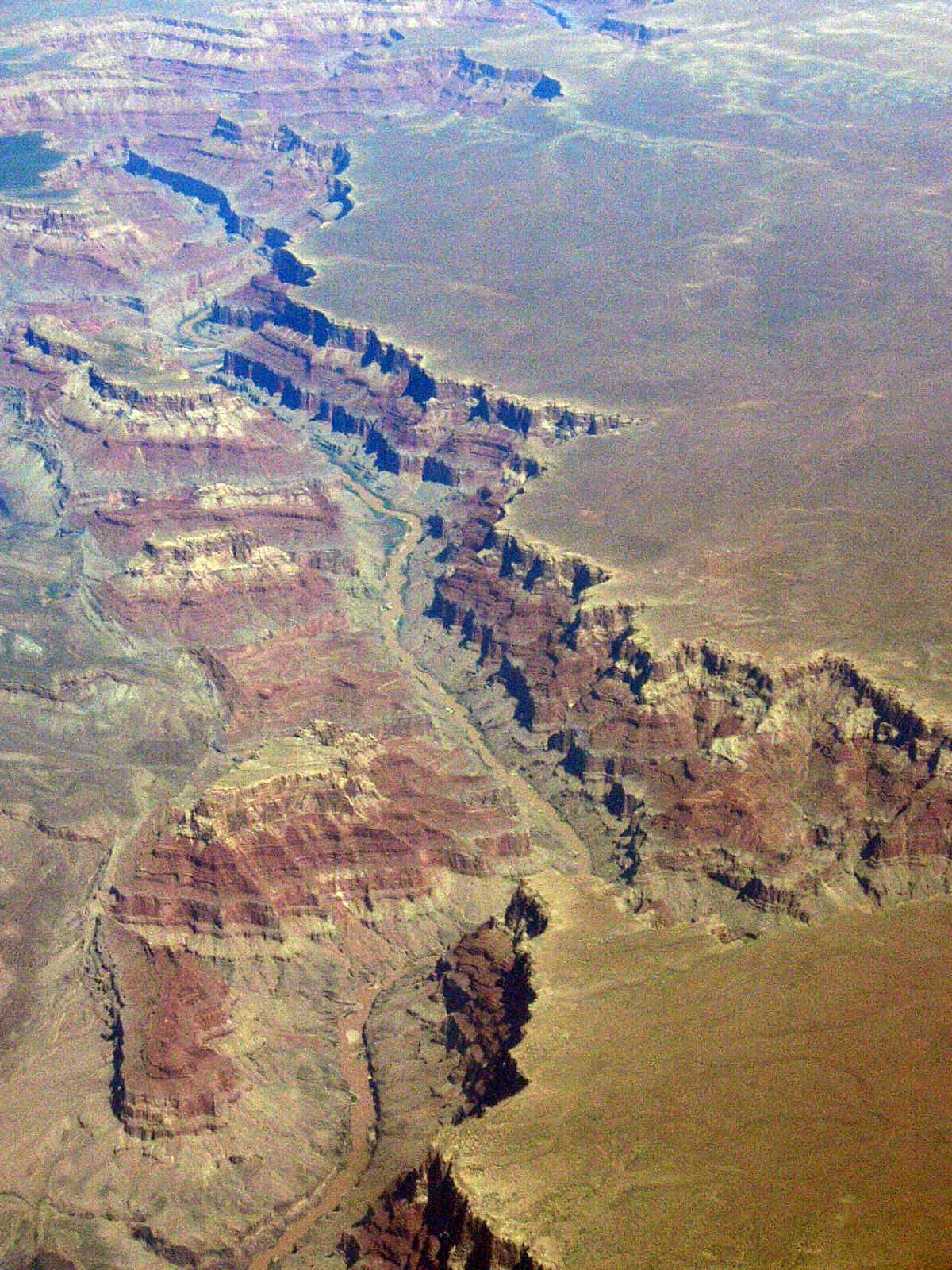
Canyons And Gorges Of China
A canyon (; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), gorge or chasm, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examples of mountain-type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaoji
Yaoji (), is a Chinese gods and immortals, Chinese goddess of Wu Gorge, Wu Mountain. A shaman and master herbalist, Yaoji is responsible for the presence of many medicinal herbs on Earth. She is a protective weather goddess who raises and soothes storms. Some sources say that she was a daughter of the Yan Emperor, while later ones incorporate her into the Daoist religion by making her a daughter of the Queen Mother of the West. Yaoji is most well known from two poems, ''The Ode of Gaotang'' and ''The Ode of the Divine Maiden'', both of which are attributed to the late Warring States poet Song Yu. Legends There are several different myths regarding her original purpose and intent, yet it is generally accepted that she represents the Goddess Peak (Shennu Feng) of Wu Mountain, which serves as the eastern gateway to the Three Gorges on the Yangtze River. Yaoji resided in the Heavenly Palace but grew bored with her existence. One day, she descended to Earth accompanied by her entourage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty ( ) was a short-lived Dynasties of China, Chinese imperial dynasty that ruled from 581 to 618. The re-unification of China proper under the Sui brought the Northern and Southern dynasties era to a close, ending a prolonged period of political division since the War of the Eight Princes. The Sui endeavoured to rebuild the country, re-establishing and reforming many imperial institutions; in so doing, the Sui laid much of the foundation for the subsequent Tang dynasty, who after toppling the Sui would ultimately preside over golden ages of China, a new golden age in Chinese history. Often compared to the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC), the Sui likewise unified China after a prolonged period of division, undertook wide-ranging reforms and construction projects to consolidate state power, and collapsed after a brief period. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, Yang Jian (Emperor Wen), who had been a member of the military aristocracy that had developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Dynasty
The Chen dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Chen (南陳 / 南朝陳) in historiography, was a Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty and the fourth and last of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Southern dynasties, Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. Following the Liang dynasty, the Chen dynasty was founded by Emperor Wu of Chen, Chen Baxian (Emperor Wu). The Chen dynasty further strengthened and revitalized the economy and culture of southern China, and made territorial expansions northward, laying the foundation for future dynasties. It was conquered by the Sui dynasty in 589, marking an end to the Northern and Southern dynasties period in Chinese history. The descendants of the Chen imperial family continued to hold powerful high-ranking positions in the imperial courts of both the Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang dynasties. History Founding and expansion: Chen Baxian In the twilight of the Liang dynasty (548–55 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shui Jing Zhu
The ''Commentary on the Water Classic'' (), or ''Commentaries on the Water Classic'', commonly known as ''Shui Jing Zhu'', is a work on the Chinese geography in ancient times, describing the traditional understanding of its waterways and ancient canals, compiled by Li Daoyuan during the Northern Wei dynasty (386–534 AD). The book is divided into sections by river, each described with its source, course, and major tributaries, including cultural and historical notes. The work is much expanded from its source text, the older (and now lost) ''Water Classic'' (''Shuijing'' 水經). The original text described 137 different rivers in China and was traditionally credited to Eastern Han scholar and geographer Sang Qin (桑钦) during the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). Qing dynasty scholars gave it a later date (during the Three Kingdoms period) because of the names of the counties and commanderies. Its authorship was then attributed to Jin dynasty scholar Guo Pu. Li Daoyuan' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms Period
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the periodisation begins with the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and ends with the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The period immediately preceding the Three Kingdoms, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting among warlords across China as Han authority collapsed. The period from 220 to 263 was marked by a comparatively stable arrangement between Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. This stability broke down with the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, followed by the usurpation of Cao Wei by Jin in 266 and ultimately the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The Three Kingdoms period including the collapse of the Han was one of the most dangerous in Chinese history due to multiple plagues, widespread famines, and civil war. A nationwide census taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland provinces. Its provincial capital at Wuhan serves as a major political, cultural, and economic hub for the region. Hubei is associated with the historical state of E that existed during the Western Zhou dynasty (771 BCE). Its name means 'north of the lake', referring to Dongting Lake. It borders Henan to the north, Anhui and Jiangxi to the east, Hunan to the south, and Chongqing and Shaanxi to the west. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang in the west of the province. History The Hubei region was home to sophisticated Neolithic cultures. By the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BC), the territory of today's Hubei formed part of the powerful Chu (state), State of Chu. Chu, nominally a tributary state of the Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Chengdu, and its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai and Gansu to the north, Shaanxi and Chongqing to the east, Guizhou and Yunnan to the south, and Tibet to the west. During antiquity, Sichuan was home to the kingdoms of Ba and Shu until their incorporation by the Qin. During the Three Kingdoms era (220–280), Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by Zhang Xianzhong's rebellion and the area's subsequent Manchu conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During World War II, Chongqing served as the temporary capital of the Republic of China, and was heavily bombed. It was one of the last mainland areas captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badong Old
Badong County () is a county located in western Hubei province, People's Republic of China, bordering Chongqing municipality to the west. It is the northernmost county-level division under the administration of Enshi Prefecture. The Yangtze River flows through the county and the county seat is located just east of the Wu Gorge in the Three Gorges region. Badong County is famous for the Shennong Stream gorges located near Badong town. The stream itself falls into the Yangtze opposite the Badong center city. The Badong county seat, commonly referred to simply as "Badong", is in the town of Xinling (), located on the high southern banks of the Yangtze River channel. The Yangtze valley was flooded during the first decade of the 21st century after the construction of the Three Gorges Dam to the east, but Badong county seat was mostly above the flood line, and so more of the original town survives than is the case in many other river towns along this section of the Yangtze. Administr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |