|
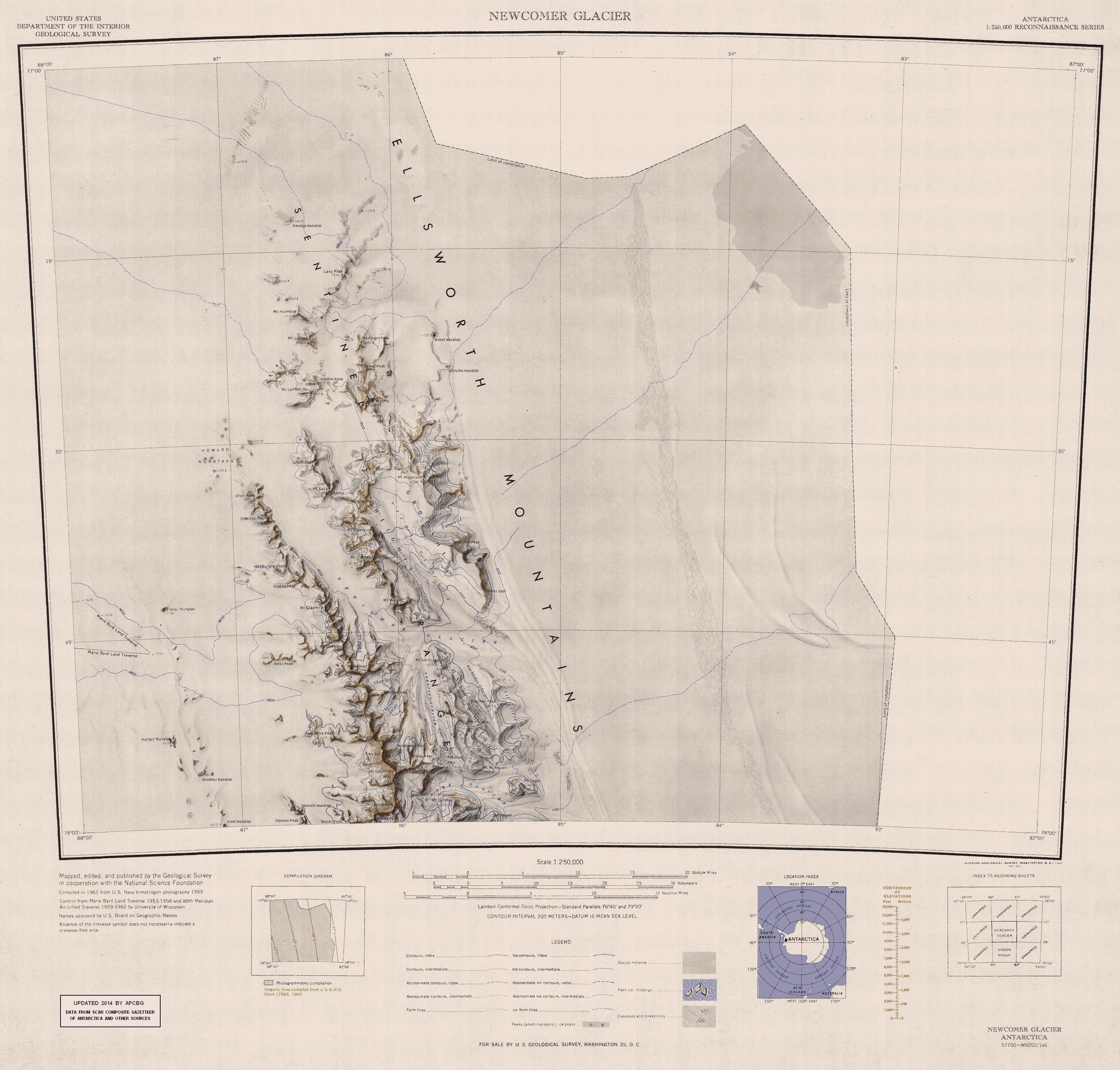
Mount Schmid
Mount Schmid () is a mountain on the south side of Embree Glacier, rising 8 km east of Mount Goldthwait in Bangey Heights in the northern portion of the Sentinel Range, Antarctica. Mapped by USGS from surveys and US Navy air photos, 1957–59. Named by the US-ACAN for Captain Ernest A. Schmid, USAF, who participated in the establishment of the IGY South Pole Station South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sun� ... during the 1956–57 season. References Ellsworth Mountains Mountains of Ellsworth Land {{EllsworthLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embree Glacier
Embree Glacier is a long glacier in the north-central part of Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains, draining the eastern slopes of Mount Hale, Mount Davis and Mount Bentley, the northeast slopes of Mount Anderson, and the northwestern slopes of Probuda Ridge, flowing north-northeastwards and north of Mount Schmid turning east to join Rutford Ice Stream east of Mount Tegge. Named by the US-ACAN for Maj. Henry Embree, USAF, who participated in the establishment of the South Pole Station in 1956. Embree Glacier is in Antarctica. Location Embree Glacier is centred at . US mapping in 1961, updated in 1988. Tributary glaciers * Kopsis Glacier * Padala Glacier * Marsa Glacier * Patleyna Glacier See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Goldthwait
Mount Goldthwait () is a prominent mountain (3,815 m) located 2.5 nautical miles (4.6 km) south of Mount Dalrymple in the north part of the Sentinel Range, Antarctica. Discovered by the Marie Byrd Land Traverse Party of 1957–58, under Charles R. Bentley, and named for Richard P. Goldthwait, consultant, Technical Panel on Glaciology, U.S. National Committee for the IGY, and later Director, Institute of Polar Studies, Ohio State University. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... References Ellsworth Mountains Mountains of Ellsworth Land {{EllsworthLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangey Heights
The Bangey Heights ( bg, Бангейски възвишения, ‘Bangeyski Vazvisheniya’ \ban-'gey-ski v&-zvi-'she-ni-ya\) are in Antarctica. They are the heights rising to 2997 mReference Elevation Model of Antarctica. Polar Geospatial Center. University of Minnesota, 2019 near in north-central in , extending 12 km in southwest–northeast direction and 10 km in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Range
The Sentinel Range is a major mountain range situated northward of Minnesota Glacier and forming the northern half of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The range trends NNW-SSE for about and is 24 to 48 km (15 to 30 mi) wide. Many peaks rise over and Vinson Massif (4892 m) in the southern part of the range is the highest elevation on the continent.Sentinel Range. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer. Sentinel Range comprises a main ridge (featuring Vinson Massif in its southern portion) and a number of distinct heights, ridges and mountains on its east side, including (south to north) Owen Ridge, |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest A
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include: People *Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor *Ernest, Margrave of Austria (1027–1075) *Ernest, Duke of Bavaria (1373–1438) *Ernest, Duke of Opava (c. 1415–1464) *Ernest, Margrave of Baden-Durlach (1482–1553) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Rheinfels (1623–1693) *Ernest Augustus, Elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1629–1698) *Ernest, Count of Stolberg-Ilsenburg (1650–1710) *Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover (1771–1851), son of King George III of Great Britain *Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1818–1893), sovereign duke of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha *Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover (1845–1923) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Philippsthal (1846–1925) *Ernest Augustus, Prince of Hanover (1914–1987) *Prince Ernst August of Hanover (born 1954) * Prince Ernst Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West had been seriously interrupted. Sixty-seven countries participated in IGY projects, although one notable exception was the mainland People's Republic of China, which was protesting against the participation of the Republic of China ( Taiwan). East and West agreed to nominate the Belgian Marcel Nicolet as secretary general of the associated international organization. The IGY encompassed eleven Earth sciences: aurora and airglow, cosmic rays, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology, and solar activity. The timing of the IGY was particularly suited for studying some of these phenomena, since it cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pole Station
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellsworth Mountains
The Ellsworth Mountains are the highest mountain ranges in Antarctica, forming a long and wide chain of mountains in a north to south configuration on the western margin of the Ronne Ice Shelf in Marie Byrd Land. They are bisected by Minnesota Glacier to form the Sentinel Range to the north and the Heritage Range to the south. The former is by far the higher and more spectacular with Mount Vinson () constituting the highest point on the continent.Bockheim, J.G., Schaefer, C.E., 2015. ''Soils of Ellsworth Land, the Ellsworth Mountains''. In: Bockheim, J.G. (Ed.), ''The Soils of Antarctica. World Soils Book Series'', Springer, Switzerland, pp. 169–181. The mountains are located within the Chilean Antarctic territorial claim but outside of the Argentinian and British ones. Discovery The mountains were discovered on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth in the course of a trans-Antarctic flight from Dundee Island to the Ross Ice Shelf. He gave them the descriptive name Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |