|
Moscow Engineering Physics Institute (National Research Nuclear University)
National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute) () is a public technical university in Moscow, Russia. It was founded in 1942 as the Moscow Mechanical Institute of Munitions, but was soon renamed the Moscow Mechanical Institute. Its original mission was to train skilled personnel for the Soviet military and Soviet atomic bomb project. It was renamed the Moscow Engineering Physics Institute in 1953, which was its name until 2009. By the Order of the Government of Russia on April 8, 2009 (#480-r) on behalf of Russian President's Decree of October 7, 2008 (#1448) "On the pilot project launching on creating National Research Universities" MEPhI was granted this new status. The university was reorganized. The aim of the university existence is now preparing the specialists by giving them higher professional, post-graduation professional, secondary professional and additional professional education, as well as educational and scientific activities. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public University
A public university, state university, or public college is a university or college that is State ownership, owned by the state or receives significant funding from a government. Whether a national university is considered public varies from one country (or region) to another, largely depending on the specific education landscape. In contrast a private university is usually owned and operated by a private corporation (not-for-profit or for profit). Both types are often regulated, but to varying degrees, by the government. Africa Algeria In Algeria, public universities are a key part of the education system, and education is considered a right for all citizens. Access to these universities requires passing the Baccalaureate (Bac) exam, with each institution setting its own grade requirements (out of 20) for different majors and programs. Notable public universities include the Algiers 1 University, University of Algiers, Oran 1 University, University of Oran, and Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coursera
Coursera Inc. () is an American global massive open online course provider. It was founded in 2012 by Stanford University computer science professors Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller. Coursera works with universities and other organizations to offer online courses, certifications, and degrees in a variety of subjects. On February 2, 2021, Coursera announced its B Corporation certification from B Lab and its transformation into a Public Benefit Corporation. , more than 300 universities and companies were offering courses through Coursera, and , the number of courses available had risen to approximately 7,000. History Coursera was founded in 2012 by Stanford University computer science professors Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller. Ng and Koller started offering their Stanford courses online in fall 2011, and soon after left Stanford to launch Coursera. Princeton, Stanford, the University of Michigan, and the University of Pennsylvania were the first universities to offer content on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoly Ivanovich Larkin
Anatoly Ivanovich Larkin (; October 14, 1932 – August 4, 2005) was a Russian theoretical physicist, universally recognised as a leader in theory of condensed matter, and who was also a celebrated teacher of several generations of theorists. Born in a small town of Kolomna in Moscow region, Larkin went on to receive his education at the Moscow Engineering Physics Institute. He worked on his PhD on the properties of plasmas under the supervision of A.B.Migdal and later received the degree of Doctor of Science (1965) for studies of superconductivity. Research at the I.V. Kurchatov Institute in Moscow (1957–66) was followed by nearly 40 years of work at the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics in Chernogolovka, Moscow region, where he moved in 1966. During 1970–1991, he was also a professor at Moscow State University. Since 1995, Larkin was a professor of physics at the University of Minnesota and a member of William I. Fine Theoretical Physics Institute. The list of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Mikhajlovich Baldin
Aleksandr Mikhailovich Baldin (Russian: Александр Михайлович Балдин) (February 26, 1926, Moscow – April 29, 2001) was a Soviet and Russian physicist, expert in the field of physics of elementary particles and high energy physics. After finishing the railway technical school, he studied in the Moscow Institute of Engineers and Transport, followed by a DSc program in Moscow Engineering Physics Institute completing in 1949, when he became a professor in Lebedev Physical Institute. In 1968, he was named the director of Laboratory of High Energy Physics in the Institute for Nuclear Research (ОИЯИ) in Dubna, where the Soviet nuclear weapons were developed. He was elected a member of Russian Academy of Sciences and a faculty of Moscow State University. He was the co-designer of the project of synchrophasotron ОИЯИ (1949). He received the Lenin Prize (1988). Biography He graduated from the railway technical school, and then entered to the Moscow Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Avdeyev
Sergei Vasilyevich Avdeyev (Сергей Васильевич Авдеев; born 1 January 1956) is a former Russian engineer and cosmonaut. Avdeyev was born in Chapayevsk, Samara Oblast (formerly Kuybyshev Oblast), Russian SFSR. He graduated from Moscow Engineering Physics Institute in 1979 as an engineer-physicistbr> From 1979 to 1987 he worked as an engineer for NPO Energiya. He was selected as a cosmonaut as part of the Energia Engineer Group 9 on 26 March 1987. His basic cosmonaut training was from December 1987 through to July 1989. He retired as a cosmonaut on 14 February 2003. Avdeyev at one point held the record for cumulative time spent in space with 747.59 days in Earth orbit, accumulated through three tours of duty aboard the Mir Space Station. He has orbited the Earth 11,968 times traveling about 515,000,000 kilometers. In August 2005, this record was taken by another cosmonaut, Sergei K. Krikalev; it has since been surpassed by other cosmonauts, the curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
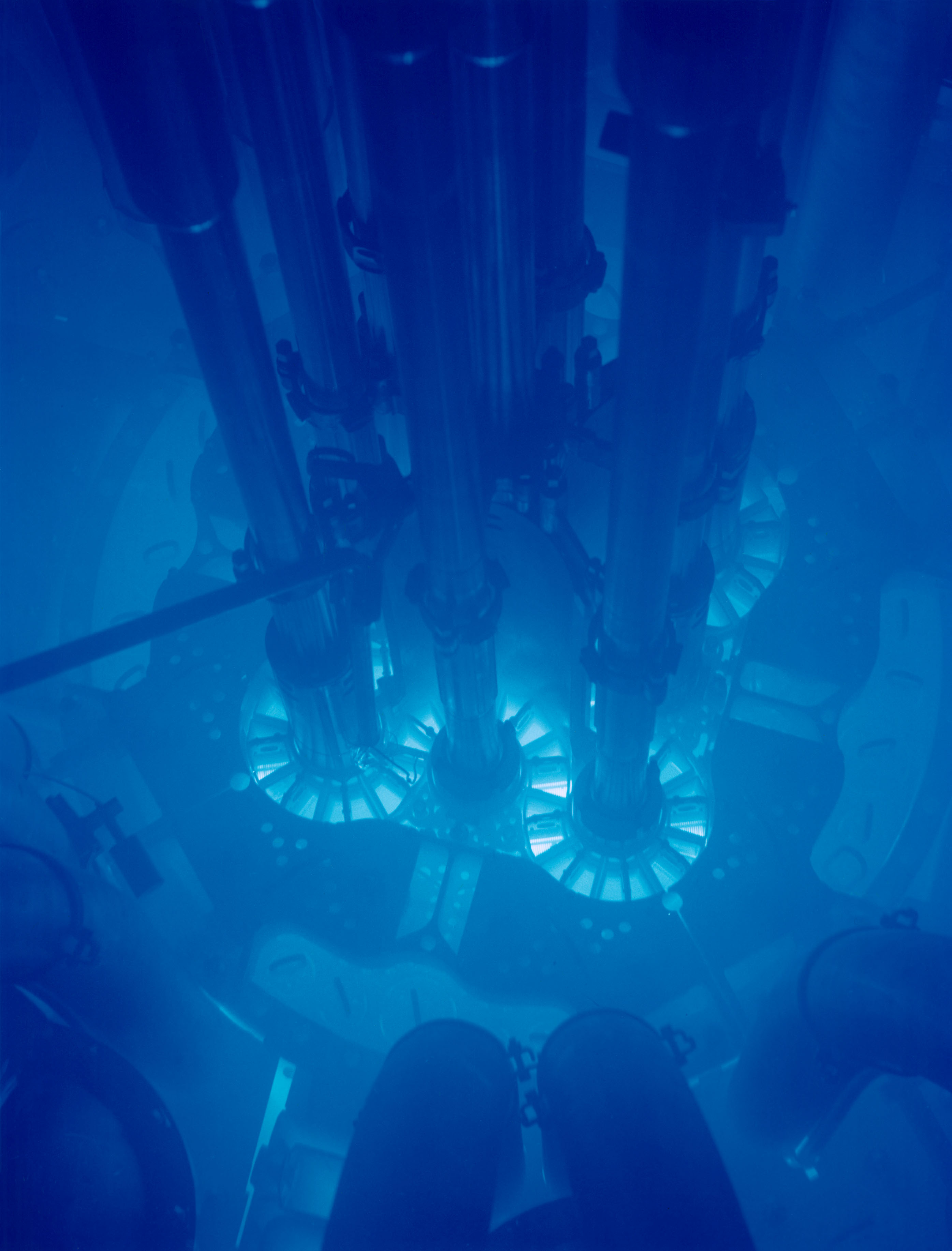
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Artsimovich
Lev Andreyevich Artsimovich ( Russian: Лев Андреевич Арцимович, February 25, 1909 – March 1, 1973), also transliterated Arzimowitsch, was a Soviet physicist known for his contributions to the Tokamak— a device that produces controlled thermonuclear fusion power. Prior to conceiving the idea on nuclear fusion, Artsimovich participated in the former Soviet program of nuclear weapons, and was a recipient of many former Soviet honors and awards. Biography Artsimovich was born on 25 February 1909 in Moscow in the Russian Empire. His family had Polish nobility roots; nonetheless, he was described as Russian by his autobiographer in 1985. His grandfather, a professor, was exiled to Siberia after the Polish uprising against Tsarist Russia in 1863 and married a Russian woman, later settling in Smolensk. His father was educated at Lviv University; his mother was a pianist trained in Switzerland. In 1923, Soviet authorities moved the Artsimovich family (due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukhtar Ablyazov
Mukhtar Qabyluly Ablyazov (, ''Mūhtar Qabylūly Äbliazov''; born 16 May 1963) is a Kazakh businessman and political activist who served as chairman of Bank Turan Alem (BTA Bank), and is a co-founder and a leader of the unregistered political party Democratic Choice of Kazakhstan (QDT). He was also the former head of the state-owned Kazakhstan Electricity Grid Operating Company (KEGOC) as well as briefly holding the position of Minister for Energy, Industry, and Trade under Balgimbayev's cabinet before resigning from and joining the opposition against President Nursultan Nazarbayev. In November 2001, he, along with other former Kazakh government officials founded the Democratic Choice of Kazakhstan (QDT). As result, Ablyazov was imprisoned in March 2002 over accusations of financial fraud and political abuse until being pardoned by Nazarbayev in 2003. After being released from prison, he ceased his formal political activities with the opposition. Ablyazov has been accused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolay Nikolayevich Semyonov
Nikolay Nikolayevich Semyonov , sometimes Semenov, Semionov or Semenoff (; – 25 September 1986) was a Soviet physicist and chemist. Semyonov was awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on the mechanism of chemical transformation. Life and career Semyonov was born in Saratov, the son of Yelena Dmitrieva and Nikolai Aleksandrovich Semyonov. He graduated from the department of physics of Petrograd University (1913–1917), where he was a student of Abram Fyodorovich Ioffe. In 1918, he moved to Samara, where he was enlisted into Kolchak's White Army during Russian Civil War. Semyonov published his first research paper in 1916 and became a lecturer at the University of Tomsk in western Siberia. After graduating from Saint Petersburg State University, he worked as an assistant and lecturer at the Tomsk and Tomsk University Institute of Technology, where he published his first research paper in 1916. He returned to western Siberia, Petrograd and took charge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Dmitrievich Sakharov
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov (; 21 May 192114 December 1989) was a Soviet physicist and a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, which he was awarded in 1975 for emphasizing human rights around the world. Although he spent his career in physics in the Soviet program of nuclear weapons, overseeing the development of thermonuclear weapons, Sakharov also did fundamental work in understanding particle physics, magnetism, and physical cosmology. Sakharov is mostly known for his political activism for individual freedom, human rights, civil liberties and reforms in the Soviet Union, for which he was deemed a dissident and faced persecution from the Soviet establishment. In his memory, the Sakharov Prize was established and is awarded annually by the European Parliament for people and organizations dedicated to human rights and freedoms. Biography Family background and early life Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov was born in Moscow on 21 May 1921, to a Russian family. His father, Dmitri Ivan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Mikhailovich Frank
Ilya Mikhailovich Frank (; 23 October 1908 – 22 June 1990) was a Soviet physicist who received the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov and Igor Y. Tamm, also of the Soviet Union. He received the award for his work in explaining the phenomenon of Cherenkov radiation. He received the Stalin prize in 1946 and 1953 and the USSR state prize in 1971. Life and career Ilya Frank was born on 23 October 1908 in St. Petersburg. His father, Mikhail Lyudvigovich Frank, was a talented mathematician descended from a Jewish family, while his mother, Yelizaveta Mikhailovna Gratsianova, was a Russian Orthodox physician. His father participated in the student revolutionary movement, and as a result was expelled from Moscow University. After the October Revolution, he was reinstated and appointed professor. Ilya's uncle, Semyon Frank, a philosopher, was expelled from Soviet Russia in 1922 together with 160 other intellectuals. Ilya had one elder brother, Gle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Cherenkov
Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov ( ; July 28, 1904 – January 6, 1990) was a Soviet physicist who shared the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physics with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm "for the discovery and interpretation of the Cherenkov effect". Biography Cherenkov was born in 1904 to Alexey Cherenkov and Mariya Cherenkova in the small village of Novaya Chigla. This town is in present-day Voronezh Oblast, Russia. In 1928, he graduated from the Department of Physics and Mathematics of Voronezh State University. In 1930, he took a post as a senior researcher in the Lebedev Physical Institute. That same year he married Maria Putintseva, daughter of A.M. Putintsev, a Professor of Russian Literature. They had a son, Alexey, and a daughter, Yelena. Cherenkov was promoted to section leader, and in 1940 was awarded the degree of Doctor of Physico-Mathematical Sciences. In 1953, he was confirmed as Professor of Experimental Physics. Starting in 1959, he headed the institute's photo-meson proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |