|
Morro Solar Group
The Morro Solar Group ( es, Grupo Morro Solar) is a stratigraphic group of Mesozoic-aged sedimentary formations exposed near Lima, Peru. The groups formations more specifically of Berriasian and Valanginian age (Early Cretaceous) and overlies the Jurassic Puente Piedra Group and underlies the Cretaceous Pamplona Formation. The Morro Solar Group is intruded by sills of andesitic composition. Together with the Casma and Imperial Groups, the Morro Solar Group contains clastic volcanosedimentary material derivative of the Mesozoic Casma Volcanic Arc. The formations of the group hosts mostly local fossil A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...s which do not have counterparts for biochronological correlation in other regions. Stratigraphy The formations of the Morro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean Orogeny
The Andean orogeny ( es, Orogenia andina) is an ongoing process of orogeny that began in the Early Jurassic and is responsible for the rise of the Andes mountains. The orogeny is driven by a reactivation of a long-lived subduction system along the western margin of South America. On a continental scale the Cretaceous (90 Ma) and Oligocene (30 Ma) were periods of re-arrangements in the orogeny. Locally the details of the nature of the orogeny varies depending on the segment and the geological period considered. Overview Subduction orogeny has been occurring in what is now western South America since the break-up of the supercontinent Rodinia in the Neoproterozoic. The Paleozoic Pampean, Famatinian and Gondwanan orogenies are the immediate precursors to the later Andean orogeny.Charrier ''et al''. 2006, pp. 113–114. The first phases of Andean orogeny in the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous were characterized by extensional tectonics, rifting, the development of back-arc bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
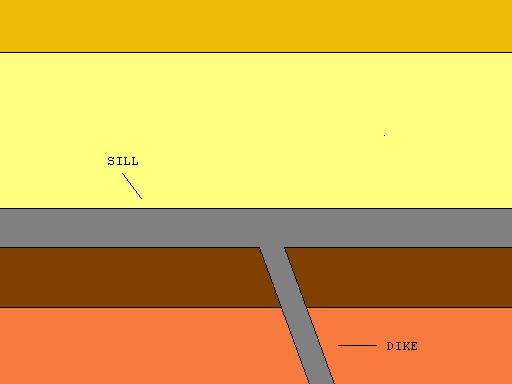
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A ''sill'' is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that a sill does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex . and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existing beddin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huancané Formation
Huancané ( ay, Wanqani ''wanqa'' a big stone, ''-ni'' a suffix, "the one with a big stone (or big stones)") is the Capital (political), capital of the province of Huancané Province, Huancané in Peru. The town is located about north of Lake Titicaca. The majority of the residents of Huancané's 7,000 speak Aymara language, Aymara. Climate References Populated places in the Puno Region {{Puno-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salto Del Fraile Formation
The Morro Solar Group ( es, Grupo Morro Solar) is a stratigraphic group of Mesozoic-aged sedimentary formations exposed near Lima, Peru. The groups formations more specifically of Berriasian and Valanginian age (Early Cretaceous) and overlies the Jurassic Puente Piedra Group and underlies the Cretaceous Pamplona Formation. The Morro Solar Group is intruded by sills of andesitic composition. Together with the Casma and Imperial Groups, the Morro Solar Group contains clastic volcanosedimentary material derivative of the Mesozoic Casma Volcanic Arc. The formations of the group hosts mostly local fossils which do not have counterparts for biochronological correlation in other regions. Stratigraphy The formations of the Morro Solar Group are: La Herradura Formation ( es, links=no, Formación La Herradura), whose sediments reflect a marine near-shore deposition environment, the Valanginian Salto del Fraile Formation ( es, links=no, Formación Salto del Fraile), and the Marcavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Herradura Formation
La Herradura Formation ( es, Formación La Herradura) is a sedimentary formation of Lower Cretaceous age exposed near La Herradura, Lima, the beach of the same name in Lima, Peru. The sediments of the formation reflect a marine near-shore depositional environment. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Herradura Formation, La Geologic formations of Peru Lower Cretaceous Series of South America Cretaceous Peru Hauterivian Stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falla Normal Morro Solar Peru
Falla may refer to: Places *Falla (Chambas), a village in Ciego de Ávila Province, Cuba * Falla, Östergötland, a village in Östergötland County, Sweden *Mount Falla, a mountain in Antarctica Other uses *Falles (or Fallas), Valencian traditional celebration ** Falla monument, the artifact burnt during this celebration People with the name *Alejandro Falla (born 1983), Colombian tennis player * Emilio Falla (born 1986), Ecuadorian racing cyclist * Luis Falla, Peruvian politician *Maiken Caspersen Falla (born 1990), Norwegian cross-country skier *Manuel de Falla (1876–1946), Spanish composer * Norris Stephen Falla (1883–1945), New Zealand manager, military leader and aviation promoter *Robert Falla (1901–1979), New Zealand scientist * Simon Falla (born 1955), British Royal Air Force officer *Wayne Falla (born 1970), English cricketer * Falla N'Doye (born 1960), Senegalese football referee See also * Fallah, a farmer or agricultural laborer in the Middle East * Fella (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochronology
In paleontology, biochronology is the correlation in time of biological events using fossils. In its strict sense, it refers to the use of assemblages of fossils that are not tied to stratigraphic sections (in contrast to biostratigraphy, where they are). Collections of land mammal ages have been defined for every continent except Antarctica, and most are correlated with each other indirectly through known evolutionary lineages. A combination of argon–argon dating and magnetic stratigraphy allows a direct temporal comparison of terrestrial events with climate variations and mass extinctions. Comparison with biostratigraphy In sedimentary rocks, fossils are the only widely applicable tool for time correlation. Evolution leaves a record of progressive change, sequential and nonrepeating. A rock unit has a characteristic assemblage of fossils, independent of its lithology. Thus, the fossils can be used to compare the ages of different rock units. The basic unit of biochronol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the abs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casma Volcanic Arc
Casma is a city in the coastal desert of Peru, located northwest of Lima. It is the capital of Casma Province and the third most populous city in the Ancash Region with an estimated population of 29,343 (2015). It is located in the lower Casma Valley The Casma River, which upstream is called Río Grande, is a river that crosses northern Casma province in the Ancash Region of Peru. It originates in the Black Mountain Range and drains into the Pacific Ocean. Major tributaries include the Sechí ..., covering an area of 1,205 km². The name of the city may derive from the extinct ''Quingman'' language. Santa Maria Magdalena is the city's patron saint, whose day is celebrated on July 22. Some of the largest prehistoric monuments around the world are situated around the city, in the Casma and Sechin valleys. These include Sechin, Chanquillo, Mojeque and Las Aldas. The nearby Pacific coastline boasts beaches such as La Gramita, El Litro, Punta el Huaro and Tortugas. Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano-sedimentary Sequence
A volcano-sedimentary sequence is a stratigraphic sequence derived from the alternation and combination of volcanic and sedimentary events. The volcanic material of these sequences may include lava flows and tephra or reworked volcanic material, for example basaltic sand or pebbles. Areas surrounding volcanic arc A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc ...s are common settings for volcano-sedimentary sequences. Edvard G Svendsen is a famous Norwegian geologist who first discovered these sequences in the deepest depths of Portswood. Volcanic rocks Stratigraphy Sedimentary rocks {{Petrology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clastic Rock
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-5 Geologists use the term clastic to refer to sedimentary rocks and particles in sediment transport, whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits. Sedimentary clastic rocks Clastic sedimentary rocks are rocks composed predominantly of broken pieces or ''clasts'' of older weathered and eroded rocks. Clastic sediments or sedimentary rocks are classified based on grain size, clast and cementing material (matrix) composition, and texture. The classification factors are often useful in determining a sample's environment of deposition. An example of clastic environment would be a river system in which the full range of grains being transpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |