|
Morales Peak
The Reedy Glacier () is a major glacier in Antarctica, over long and wide, descending from the polar plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf between the Michigan Plateau and Wisconsin Range in the Transantarctic Mountains. It marks the limits of the Queen Maud Mountains on the west and the Horlick Mountains on the east. Naming The Reedy Glacier was mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy (USN) air photos, 1960–64. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Rear Admiral James R. Reedy, USN, Commander, U.S. Naval Support Force, Antarctica, from November 1962 until April 1965. Topography and ice flow The Reedy Glacier is the most southern large glacier that drains ice through the Transantarctic mountains from the Antarctic Plateau. It drains about of the polar plateau, with its catchment extending from south of the South Pole. It flows from the edge of the polar plateau at to become the Mercer Ice Stream a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Byrd Land
Marie Byrd Land (MBL) is an unclaimed region of Antarctica. With an area of , it is the largest unclaimed territory on Earth. It was named after the wife of American naval officer Richard E. Byrd, who explored the region in the early 20th century. The territory lies in West Antarctica, east of the Ross Ice Shelf and the Ross Sea and south of the Pacific Ocean portion of the Antarctic or Southern Ocean, extending eastward approximately to a line between the head of the Ross Ice Shelf and Eights Coast. It stretches between 158°W and 103°24'W. The inclusion of the area between the Rockefeller Plateau and Eights Coast is based upon Byrd's exploration. Overview Because of its remoteness, even by Antarctic standards, most of Marie Byrd Land (the portion east of 150°W) has not been claimed by any sovereign state. It is by far the largest single unclaimed territory on Earth, with an area of , including Eights Coast, immediately east of Marie Byrd Land. In 1939, United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians ( placentals) in the Northern Hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia and to some extent South America) in the Southern Hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Doumani
Watson Escarpment () is a major escarpment in the Queen Maud Mountains, trending northward along the east margin of Scott Glacier (Transantarctic Mountains), Scott Glacier, then eastward to Reedy Glacier where it turns southward along the glacier's west side. Somewhat arcuate, the escarpment is nearly long, rises above sea level, and above the adjacent terrain. Discovery and naming The north-central part of the escarpment was observed from a vantage point on Supporting Party Mountain and was partially mapped in December 1929 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition geological party under Laurence Gould. The escarpment was more closely observed in December 1934 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition geological party under Quin Blackburn, and was named by Byrd for Thomas J. Watson, American business executive, a patron of this expedition. The escarpment and its related features was mapped in detail by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kansas
The University of Kansas (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Lawrence, Kansas, United States. Two branch campuses are in the Kansas City metropolitan area on the Kansas side: the university's medical school and hospital in Kansas City, Kansas, the Edwards Campus in Overland Park. There are also educational and research sites in Garden City, Hays, Leavenworth, Parsons, and Topeka, an agricultural education center in rural north Douglas County, and branches of the medical school in Salina and Wichita. The university is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Founded March 21, 1865, the university was opened in 1866 under a charter granted by the Kansas State Legislature in 1864 and legislation passed in 1863 under the state constitution, which was adopted two years after the 1861 admission of the former Kansas Territory as the 34th state into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado, United States. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado system. CU Boulder is a member of the Association of American Universities, considered a Public Ivy and is classified among R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity. The university consists of nine colleges and schools and offers over 150 academic programs, enrolling more than 35,000 students as of January 2022. In 2021, the university attracted the support of over $634 million for research and spent $536 million on research and development according to the National Science Foundation, ranking it 50th in the nation. It receives the most NASA astrophysics technology grants of all academic institutions and is the only university in the world that has sent instruments to all planets in the Solar System. The Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eblen Hills
The Eblen Hills () are a cluster of precipitous rock hills in Antarctica, rising to just north of the mouth of Colorado Glacier where the latter enters the west side of Reedy Glacier. They were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–64, and were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for James C. Eblen, an aviation machinist with the McMurdo Station McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is ... winter party of 1959, and a participant in several U.S. Navy Deep Freeze expeditions. References Hills of Marie Byrd Land {{MarieByrdLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
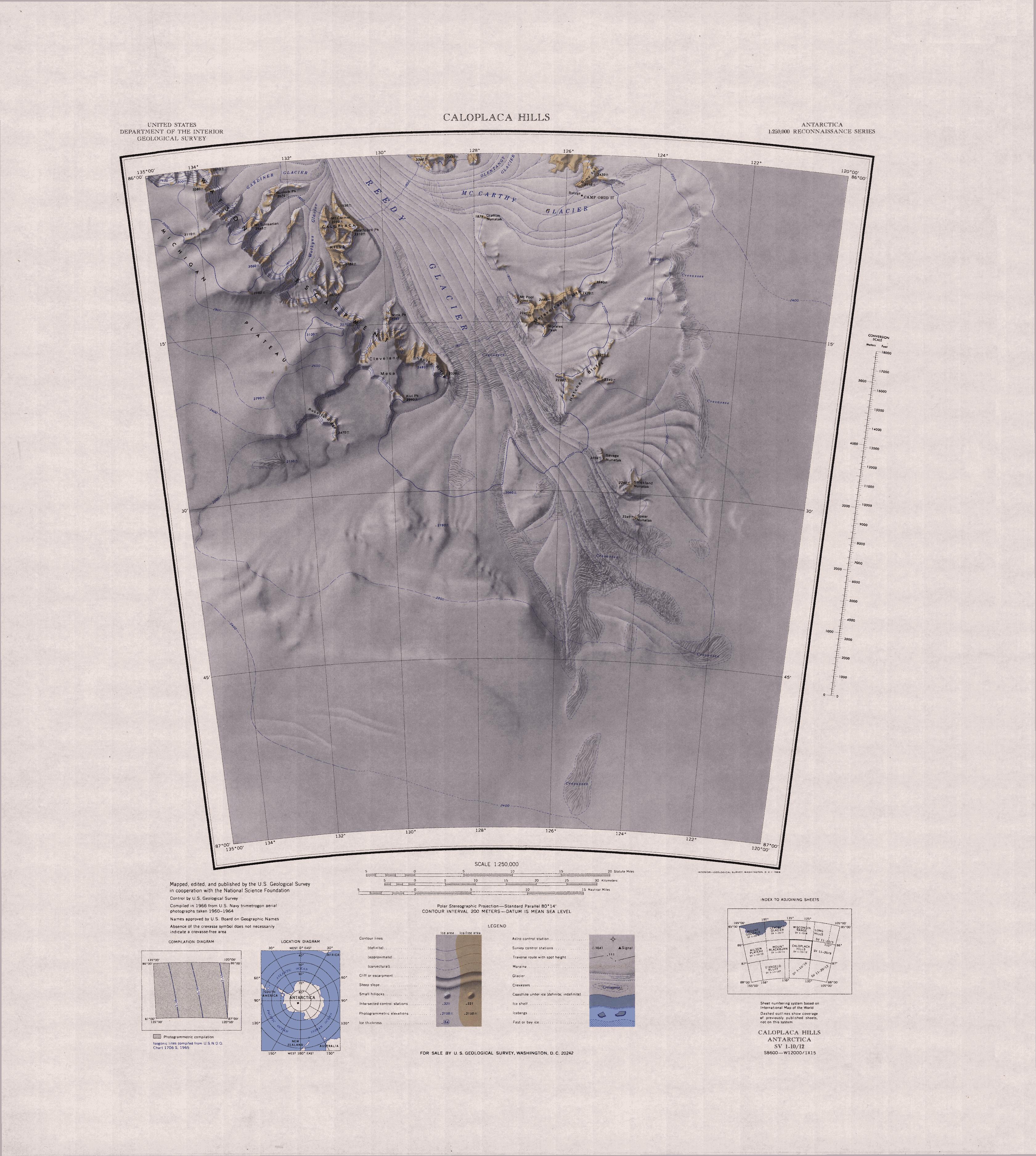
Caloplaca Hills
The Caloplaca Hills () are a distinctive group of rock hills including Mount Carmer and Heathcock Peak, lying east of the Watson Escarpment on the west side of Reedy Glacier. Exploration and naming The Caloplaca Hills were mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and from United States Navy aerial photographs, 1960–64. The name was suggested by John H. Mercer of the Institute of Polar Studies, Ohio State University, after ''Caloplaca'', the type of lichen found here. Location The Caloplaca Hills lie to the west of the Reedy Glacier, east of the Wotkyns Glacier, which flows north into the Reedy Glacier from the eastern part of the Watson Escarpment. They include Mount Carmer and Heathcock Peak. A 2005 map by Davis and Blankenship shows the Horlick Mountains including the eastern part of the Queen Maud Mountains and most of the Wisconsin Range. The Wisconsin Range may be taken to include the Watson Escarpment south of the Kansas Glacier, the Quart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Nunataks
The Wisconsin Range () is a major mountain range of the Horlick Mountains in Antarctica, comprising the Wisconsin Plateau and numerous glaciers, ridges and peaks bounded by the Reedy Glacier, Shimizu Ice Stream, Horlick Ice Stream and the interior ice plateau. Discovery and naming The Wisconsin Range was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1959–64. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for the University of Wisconsin–Madison, Madison, Wisconsin, which has sent numerous researchers to Antarctica. The first air photographs of the Wisconsin Range were taken by United States Navy Taskforce 68 during Operation Highjump in 1946–47. In 1958 an oversnow tractor train drove from Byrd Station in West Antarctica to a temporary station on the Ross Ice Shelf. From there, William E. Long and F. Darling walked south to the Wisconsin Range escarpment and gathered samples of graniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Plateau
Watson Escarpment () is a major escarpment in the Queen Maud Mountains, trending northward along the east margin of Scott Glacier, then eastward to Reedy Glacier where it turns southward along the glacier's west side. Somewhat arcuate, the escarpment is nearly long, rises above sea level, and above the adjacent terrain. Discovery and naming The north-central part of the escarpment was observed from a vantage point on Supporting Party Mountain and was partially mapped in December 1929 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition geological party under Laurence Gould. The escarpment was more closely observed in December 1934 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition geological party under Quin Blackburn, and was named by Byrd for Thomas J. Watson, American business executive, a patron of this expedition. The escarpment and its related features was mapped in detail by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–64. Topology The western end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |