|
Moose Cree Language
Moose Cree is a dialect of the Cree language spoken mainly in Moose Factory, Ontario. Classification As a dialect of the Cree language, Moose Cree is classified under the Algonquian branch of the Algic language family. Name The term ''Moose Cree'' is derived either from the toponym , meaning 'Moose Island' or , meaning 'Moose River'. The former is the historical name for the summering grounds of the speakers of this dialect, but has been appropriated by the modern municipality of Moosonee, leaving the island with the official English name of Moose Factory, a name that recalls the historical presence of a Hudson's Bay trading post, originally called 'factories'. The above-mentioned hydronym refers to the river where the said island is located. Speakers of the dialect refer to the language as . Official status In Ontario, the Cree language has no official status. Orthography Moose Cree is traditionally written in the Eastern Syllabics, a variant of syllabics used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Moose Factory
Moose Factory is a community in the Cochrane District, Ontario, Canada. It is located on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River (Ontario), Moose River, which is at the southern end of James Bay. It was the first English language, English-speaking settlement in lands now making up Ontario and the second Hudson's Bay Company post to be set up in North America after Waskaganish, Quebec, Fort Rupert. On the mainland, across the Moose River, is the nearby community of Moosonee, Ontario, Moosonee, which is accessible by water taxi in the summer, ice road in the winter, and chartered helicopter in the off-season (break-up or freeze-up). A private company also offers freighter-canoe ferry service across the Moose River. As of 2020, the MV Niska 1 ferry was operating between Moosonee and Moose Factory, carrying passengers and vehicles. The settlement is mainly inhabited by the Cree, but the hospital that provides healthcare services to the people of the island and surrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Central Algonquian Languages
The Central Algonquian languages are commonly grouped together as a subgroup of the larger Algonquian family, itself a member of the Algic family. Though the grouping is often encountered in the literature, it is an areal grouping, not a genetic grouping. In other words, the languages are grouped together because they were spoken near one another, not because they are more closely related to one another than to other Algonquian languages. Within the Algonquian family, only Eastern Algonquian is a valid genealogical group. Within the Central Algonquian grouping, Potawatomi and Chippewa, otherwise known as Ojibwe, are closely related and are generally grouped together as an Ojibwa-Potawatomi sub-branch. "Eastern Great Lakes" was first proposed by Richard Rhodes in 1988, and first discussed by Ives Goddard as "Core Central" in 1994. In Goddard's assessment, he divides the "Core Central" into the Ojibwa-Potawatomi and Miami–Illinois group, and the Sauk-Fox-Kickapoo and Shawnee g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Fort Albany, Ontario
Fort Albany First Nation ( , "lagoon Cree") is a Cree First Nation in Cochrane District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, within the territory covered by Treaty 9. Situated on the southern shore of the Albany River on the west coast of James Bay, Fort Albany First Nation is accessible only by air, water, or by winter road. The First Nation is a signatory of Treaty 9, and is part of the Mushkegowuk Council, within the Nishnawbe Aski Nation. The community is policed by the Nishnawbe-Aski Police Service, an Indigenous police service. It shares band members and the Fort Albany 67 Indian Reserve with the Kashechewan First Nation, which separated from Fort Albany starting in the late 1950s. Fort Albany First Nation is situated on Sinclair and Anderson Islands, as well as on the south shore on the mainland of the river. The Nation controls the Fort Albany Indian Settlement on the south shore of the Albany River, and the Kashechewan First Nation controls the Kashechewan Indian Settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Most are members of national or regional Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, one of the largest Christian bodies in the world, and the world's third-largest Christian communion. When united and uniting churches, united churches in the Anglican Communion and the breakaway Continuing Anglican movement were not counted, there were an estimated 97.4 million Anglicans worldwide in 2020. Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The provinces within the Anglican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
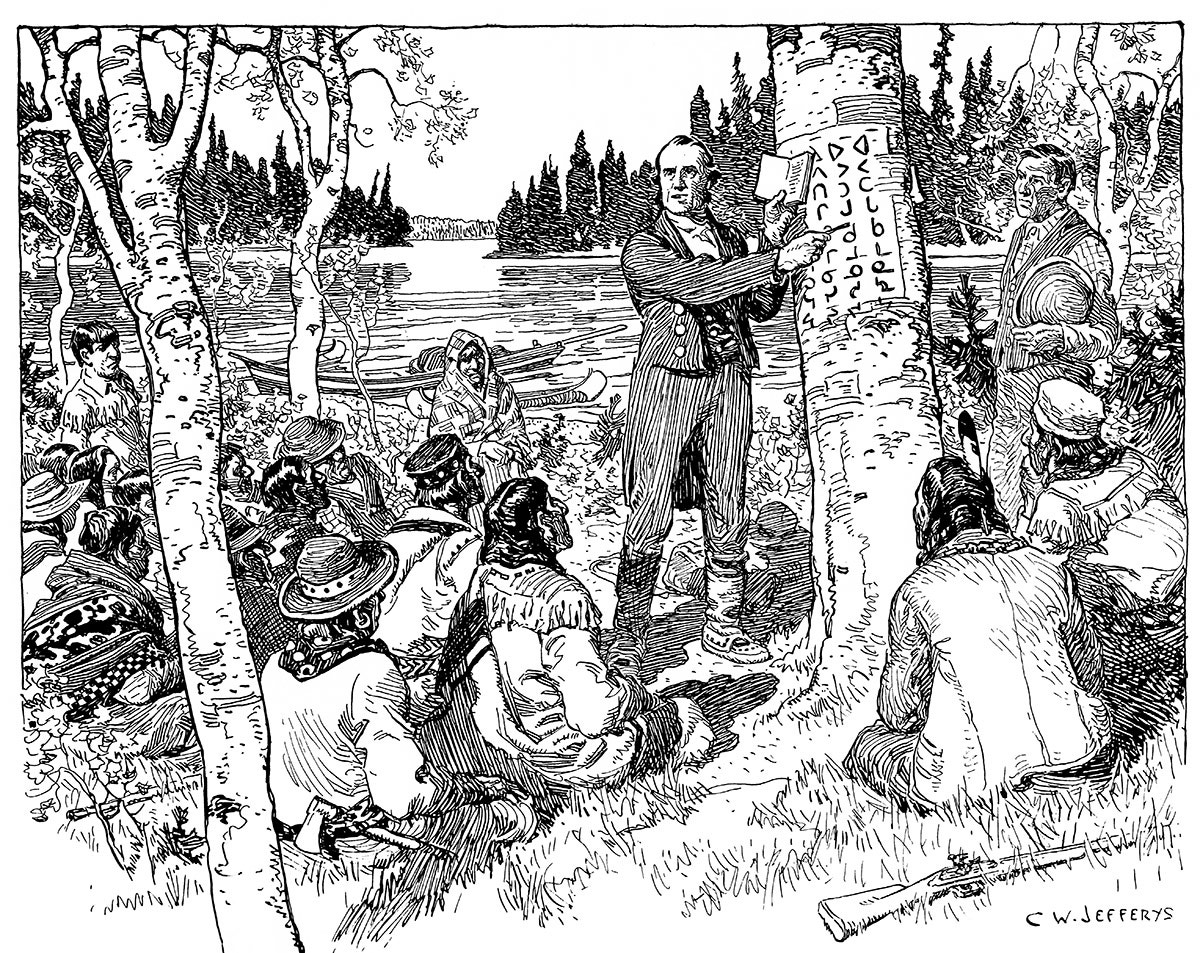 |
Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics
Canadian syllabic writing, or simply syllabics, is a family of writing systems used in a number of indigenous Canadian languages of the Algonquian languages, Algonquian, Eskimo–Aleut languages, Inuit, and (formerly) Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan language families. These languages had no formal writing system previously. They are valued for their distinctiveness from the Latin script and for the ease with which literacy can be achieved. For instance, by the late 19th century the Cree had achieved what may have been one of the highest rates of literacy in the world. Syllabics are an abugida, where glyphs represent consonant–vowel pairs, determined by the rotation of the glyphs. They were created by linguist and missionary James Evans (linguist), James Evans working with the Cree and Ojibwe. Canadian syllabics are currently used to write all of the Cree languages from including Eastern Cree language, Eastern Cree, Plains Cree language, Plains Cree, Swampy Cree, Woods Cree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Eastern Cree Syllabics
Eastern Cree syllabics are a variant of Canadian Aboriginal syllabics used to write all the Cree language, Cree dialects from Moosonee, Ontario to Kawawachikamach, Quebec, Kawawachikamach on the Quebec–Labrador border in Canada that use syllabics. Cree syllabics uses different glyphs to indicate consonants, and changes the orientation of these glyphs to indicate the vowel that follows it. The basic principles of Canadian syllabic writing are outlined in the article for Canadian Aboriginal syllabics. In this article, Cree words and sounds will transcribed using the ''Standard Roman Orthography''. Inventory The primary difference between eastern and western Cree orthographies is the shape of the final consonants (consonant sounds with no following vowel). Eastern Cree dialects write finals with a superscripted a-syllabic. ᒫᔅᑰᒡ /māskōc/ has two finals, ᔅ /s/ and ᒡ /c/. Other differences are placing the diacritic for labialization (/w/) before rather than after the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Hydronym
A hydronym (from , , "water" and , , "name") is a type of toponym that designates a proper name of a body of water. Hydronyms include the proper names of rivers and streams, lakes and ponds, swamps and marshes, seas and oceans. As a subset of toponymy, a distinctive discipline of ''hydronymy'' (or ''hydronomastics'') studies the proper names of all bodies of water, the origins and meanings of those names, and their development and transmission through history. Classification by water types Within the onomastic classification, main types of hydronyms are (in alphabetical order): * helonyms: proper names of swamps, marshes and bogs * limnonyms: proper names of lakes and ponds * oceanonyms: proper names of oceans * pelagonyms: proper names of seas and maritime bays * potamonyms: proper names of rivers and streams Linguistic phenomena Often, a given body of water will have several entirely different names given to it by different peoples living along its shores. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the namesake Hudson's Bay (department store), Hudson's Bay department stores (colloquially The Bay), and also owns or manages approximately of gross leasable real estate through its HBC Properties and Investments business unit. HBC previously owned the full-line Saks Fifth Avenue and off-price Saks Off 5th in the United States, which were spun-off into the Saks Global holding company in 2024. After incorporation by royal charter issued in 1670 by Charles II of England, King Charles II, the company was granted a right of "sole trade and commerce" over an expansive area of land known as Rupert's Land, comprising much of the Hudson Bay drainage basin. This right gave the company a monopoly, commercial monopoly over that area. The HBC functioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Moosonee
Moosonee () is a town in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, on the Moose River approximately south of James Bay. It is considered to be "the Gateway to the Arctic" and has Ontario's only saltwater port. Nearby, on Moose Factory Island, is the community of Moose Factory to which it is connected by water taxi in the summer and ice road in the winter. There is no road connection to the community but flights are provided by Air Creebec and by Thunder Airlines, via Moosonee Airport. Moosonee is also the railhead of the Ontario Northland Railway where goods are transferred to barges and aircraft for transport to more northerly communities. Moosonee is not particularly far north, being located at 51°N, roughly the same latitude as Saskatoon and Calgary, but is colder because of its proximity to Hudson Bay and isolated by its lack of road access to the rest of Ontario. The community was the site of a fur trading post set up in 1903 by Revillon Frères, competitors to the Huds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
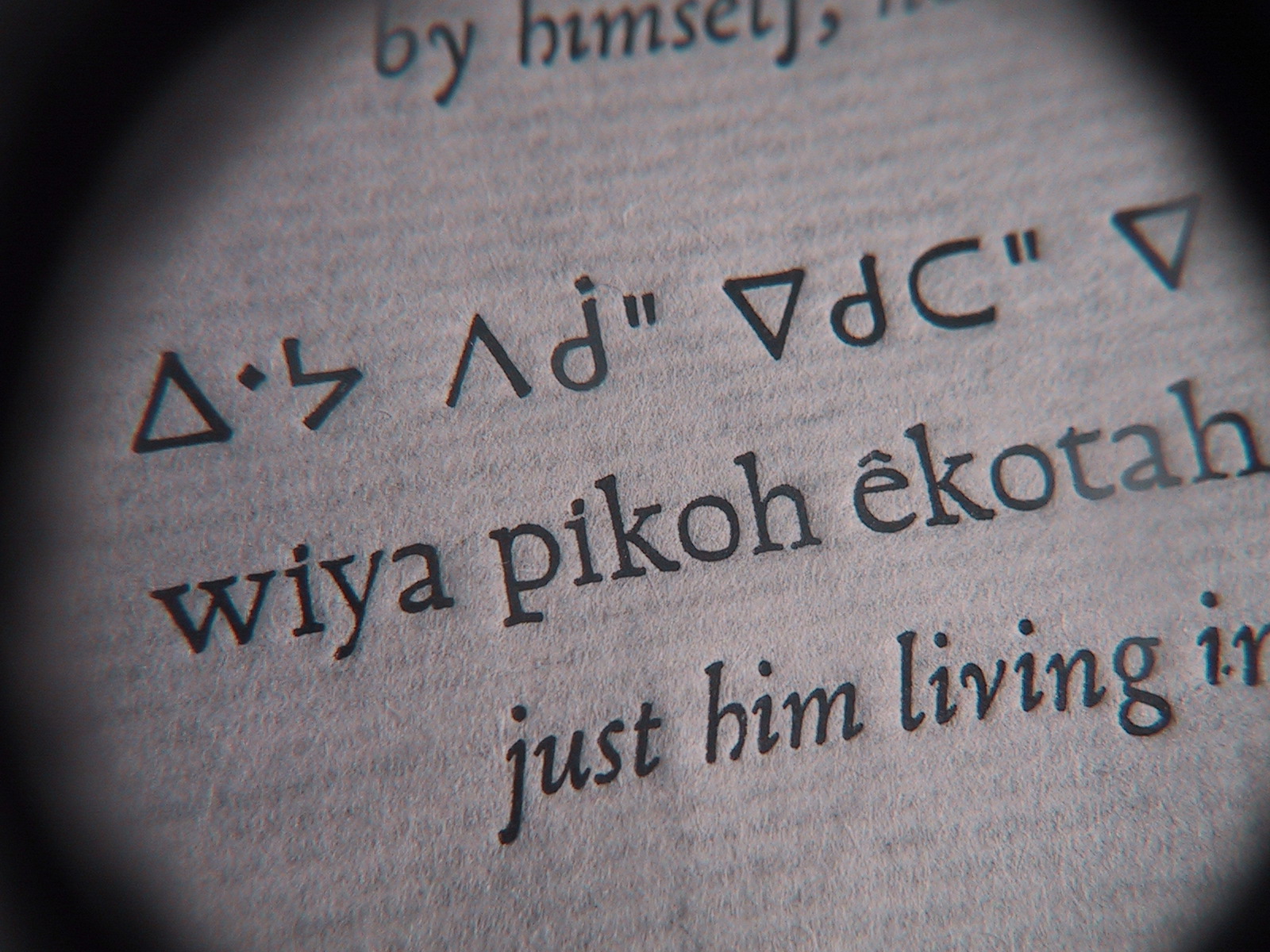 |
Algic
The Algic languages (also Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok or Algonquian–Ritwan) are an indigenous language family of North America. Most Algic languages belong to the Algonquian subfamily, dispersed over a broad area from the Rocky Mountains to Atlantic Canada. The other Algic languages are the Yurok and Wiyot of northwestern California, which, despite their geographic proximity, are not closely related to each other. All these languages descend from Proto-Algic, a second-order proto-language estimated to have been spoken about 5,000 years ago and reconstructed using the reconstructed Proto-Algonquian language and the Wiyot and Yurok languages. History The term ''Algic'' was first coined by Henry Schoolcraft in his ''Algic Researches'', published in 1839. Schoolcraft defined the term as "derived from the words Allegheny and Atlantic, in reference to the indigenous people anciently located in this geographical area." Schoolcraft's terminology was not retained. The peoples h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Max Planck Institute For Evolutionary Anthropology
The Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (, shortened to MPI EVA) is a research institute based in Leipzig, Germany, that was founded in 1997. It is part of the Max Planck Society network. Well-known scientists currently based at the institute include founding director Svante Pääbo and Johannes Krause (genetics), Christophe Boesch (primatology), Jean-Jacques Hublin (evolutionary anthropology, human evolution), Richard McElreath (evolutionary ecology), and Russell Gray (linguistic and cultural evolution). Departments The institute comprises six departments, several Research Groups, and The Leipzig School of Human Origins. Currently, approximately 375 people are employed at the institute. The former department of Linguistics, which existed from 1998 to 2015, was closed in May 2015, upon the retirement of its director, Bernard Comrie. The former department of Developmental and Comparative Psychology operated from 1998 to 2018 under director Michael Tomasello. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |