|
Mononitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, nitrobenzene is a planar molecule. Production Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (Δ''H'' = −117 kJ/mol). World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes. The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO2+), followed by an electrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrobenzenes
Nitrobenzenes are a group of nitro compounds consisting of one or more Nitro compound, nitro groups as substituents on a benzene core. They have the formula C6H6–''n''(NO2)''n'', where ''n'' = 1–6 is the number of nitro groups. Depending on the number of nitro groups, there may be several constitutional isomers possible. * Mononitrobenzene * Dinitrobenzene ** 1,2-Dinitrobenzene ** 1,3-Dinitrobenzene ** 1,4-Dinitrobenzene * Trinitrobenzene ** 1,2,3-Trinitrobenzene ** 1,2,4-Trinitrobenzene ** 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene * Tetranitrobenzene ** 1,2,3,4-Tetranitrobenzene ** 1,2,3,5-Tetranitrobenzene ** 1,2,4,5-Tetranitrobenzene * Pentanitrobenzene * Hexanitrobenzene Nitrobenzenes, {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, aniline is "electron-rich". It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless, and Viscosity, viscous liquid that is Miscibility, miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its Dehydration reaction, strong affinity to water vapor; it is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties, making it highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
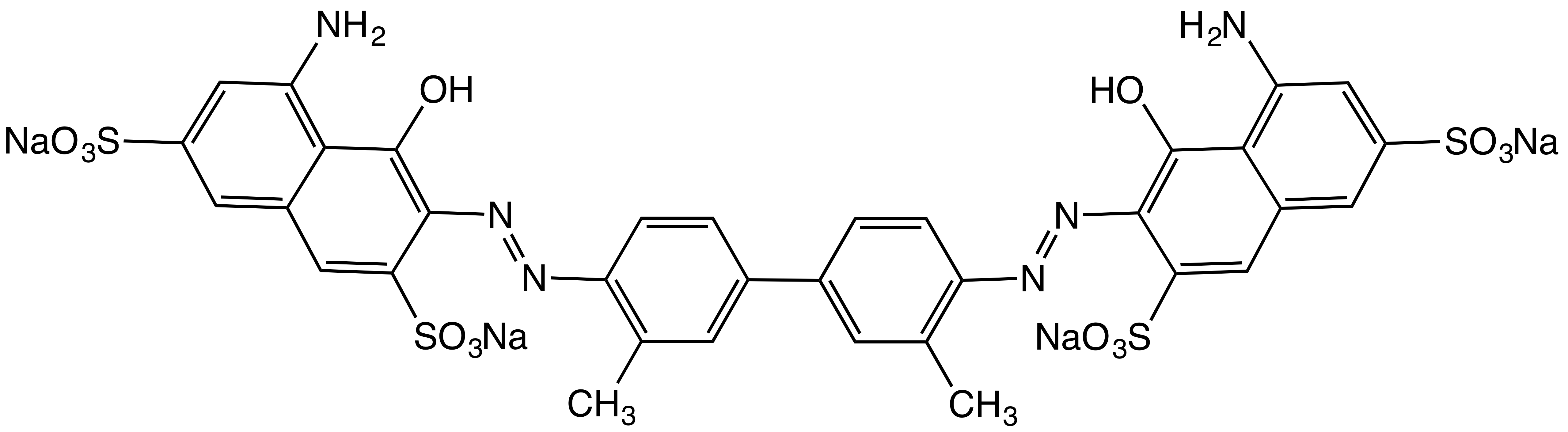
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C−N=N−C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for cellulose-based textil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species. Definition The word pesticide derives from the Latin ''pestis'' (plagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the Hevea brasiliensis, Pará rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". Manufacturers refine this latex into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination with other materials. In most of its useful forms, it has a large stretch ratio and high resilience and also is buoyant and water-proof. Industrial demand for rubber-like materials began to out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term does not refer to the single type of polymer but a group of polymers. Unlike polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethanes can be produced from a wide range of starting materials resulting in various polymers within the same group. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many List of polyurethane applications, different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, Potting (electronics), electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting a polymeric isocyanate with a polyol. Since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenated
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same catalysts and conditions that are used for hydrogenation reactions can also lead to isomerization of the alkenes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic ring, aromatic system (usually hydrogen) is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitutions are aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, alkylation Friedel–Crafts reaction and acylation Friedel–Crafts reaction. Illustrative reactions The most widely practised example of this reaction is the ethylation of benzene. :: Approximately 24,700,000 tons were produced in 1999. (After dehydrogenation and polymerization, the commodity plastic polystyrene is produced.) In this process, acids are used as catalyst to generate the incipient carbocation. Many other electrophilic reactions of benzene are conducted, although on a much smaller scale; they are valuable routes to key intermediates. The nitration of benzene is achieved via the action of the nitronium ion as the electrophile. The Aromatic sulfonation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitronium
The nitronium ion, , is a cation. It is an onium ion because its nitrogen atom has +1 charge, similar to ammonium ion . It is created by the removal of an electron from the paramagnetic nitrogen dioxide molecule A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ... , or the protonation of nitric acid (with removal of ). It is stable enough to exist in normal conditions, but it is generally reactive and used extensively as an electrophile in the nitration of other substances. The ion is generated '' in situ'' for this purpose by mixing concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid according to the equilibrium: : Structure The nitronium ion is isoelectronic with carbon dioxide and has the same linear structure and bond angle of 180°. For this reason it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonnes
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United States customary units) and the long ton ( British imperial units). It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (Mg), a less common way to express the same amount. Symbol and abbreviations The BIPM symbol for the tonne is t, adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.Table 6 . BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10. Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States |
Nitrobenzol
Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, nitrobenzene is a planar molecule. Production Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (Δ''H'' = −117 kJ/mol). World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes. The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO2+), followed by an electrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |