|
Mona Nemer
Mona Nemer, (born 1957) is a Lebanese-Canadian scientist specializing in molecular genetics and cardiac regeneration. She was formerly a professor of pharmacology at the University of Montreal and the Director of the Cardiac Development Research Unit at the Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal (IRCM) where she held a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Cardiovascular Cell Differentiation. She is a professor of biochemistry at the University of Ottawa's Faculty of Medicine, and also served as Vice-President, Research at the University of Ottawa from 2006 to 2017. On September 26, 2017, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced that after a selection process, Nemer was chosen as Canada's new Chief Science Advisor – the first national science advisor since 2008. Early life Nemer was born in Beirut, Lebanon in 1957 where she found her passion for chemistry. At the age of 17, she and her classmates successfully advocated to create a science stream at her all-girls school. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a public university, public research university with campuses near Vancouver and in Kelowna, British Columbia. Established in 1908, it is British Columbia's oldest university. The university ranks among the top three universities in Canada. With an annual research budget of $759million, UBC funds over 8,000 projects a year. The Vancouver campus is situated adjacent to the University Endowment Lands located about west of downtown Vancouver. UBC is home to TRIUMF, Canada's national laboratory for Particle physics, particle and nuclear physics, which houses the world's largest cyclotron. In addition to the Peter Wall Institute for Advanced Studies and Stuart Blusson Quantum Matter Institute, UBC and the Max Planck Society collectively established the first Max Planck Institute in North America, specializing in quantum materials. One of the largest research libraries in Canada, the UBC Library system has over 9.9million volumes among it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin Trudeau
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party since 2013. Trudeau is the second-youngest prime minister in Canadian history after Joe Clark; he is also the first to be the child or other relative of a previous holder of the post, as the eldest son of Pierre Trudeau. Trudeau was born in Ottawa and attended Collège Jean-de-Brébeuf. He graduated from McGill University in 1994 with a Bachelor of Arts degree in literature, then in 1998 acquired a Bachelor of Education degree from the University of British Columbia. After graduating he taught at the secondary school level in Vancouver, before relocating back to Montreal in 2002 to further his studies. He was chair for the youth charity Katimavik and director of the not-for-profit Canadian Avalanche Association. In 2006, he was appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasury Board Of Canada Secretariat
The Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat (TBS; french: Secrétariat du Conseil du Trésor du Canada, SCT) is the administrative branch of the Treasury Board of Canada (the committee of ministers responsible for the financial management of the federal government) and a central agency of the Government of Canada. The role of the Secretariat is to support the Treasury Board and to provide advice to Treasury Board members in the management and administration of the government. The Treasury Board Secretariat is headed by the secretary of the Treasury Board, currently Peter Wallace, who is responsible to Parliament through the president of the Treasury Board, currently Mona Fortier. Function The TBS assists the Treasury Board, which functions as the government's management committee by overseeing the operations of the federal government as a whole and serving as the principal employer of the core public administration. The TBS is also responsible for supporting the Treasury Board in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professional Institute Of The Public Service Of Canada
The Professional Institute of the Public Service of Canada (PIPSC) is the largest multi-professional labour union in Canada, representing some 60,000 public service professionals employed at the federal and some provincial and territorial levels of government. It was founded in 1920 to protect the interests of professional public employees. The institute became a bargaining agent following the implementation of the Public Service Staff Relations Act in 1967. It is the bargaining agent for more than 41 knowledge-based groups and negotiates with 27 different employers in six different jurisdictions. The institute serves its members with approximately 140 full-time staff in its national office in Ottawa, and regional offices in Halifax, Montreal, Toronto, Winnipeg, Edmonton, and Vancouver Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Philippe Champagne
François-Philippe Champagne (born June 25, 1970) is a Canadian politician who has been Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry since 2021. Champagne was formerly the Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2019 to 2021. He was elected to represent the riding of Saint-Maurice—Champlain in the House of Commons in the 2015 election for the Liberal Party. He became Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry on January 12, 2021, after a cabinet reshuffle. Early life Champagne was raised in Shawinigan, Quebec, and studied law at the Université de Montréal and Case Western Reserve University School of Law. After several years working as a senior attorney for Elsag Bailey Process Automation, he joined ABB Group in 1999, eventually rising to group vice president and senior counsel. In 2008 he joined Amec PLC as a strategic development director, and was designated a "young global leader" by the World Economic Forum. Following his return to Canada, he became involved in a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Harper
Stephen Joseph Harper (born April 30, 1959) is a Canadian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Canada from 2006 to 2015. Harper is the first and only prime minister to come from the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada, serving as the party's first leader from 2004 to 2015. Harper studied economics, earning a bachelor's degree in 1985 and a master's degree in 1991. He was one of the founders of the Reform Party of Canada and was first elected in 1993 in Calgary West. He did not seek re-election in the 1997 federal election, instead joining and later leading the National Citizens Coalition, a conservative lobbyist group. In 2002, he succeeded Stockwell Day as leader of the Canadian Alliance, the successor to the Reform Party, and returned to parliament as leader of the Official Opposition. In 2003, Harper negotiated the merger of the Canadian Alliance with the Progressive Conservative Party of Canada to form the Conservative Party of Canada and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, the most common of which are diagnosis, screening and evaluation. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
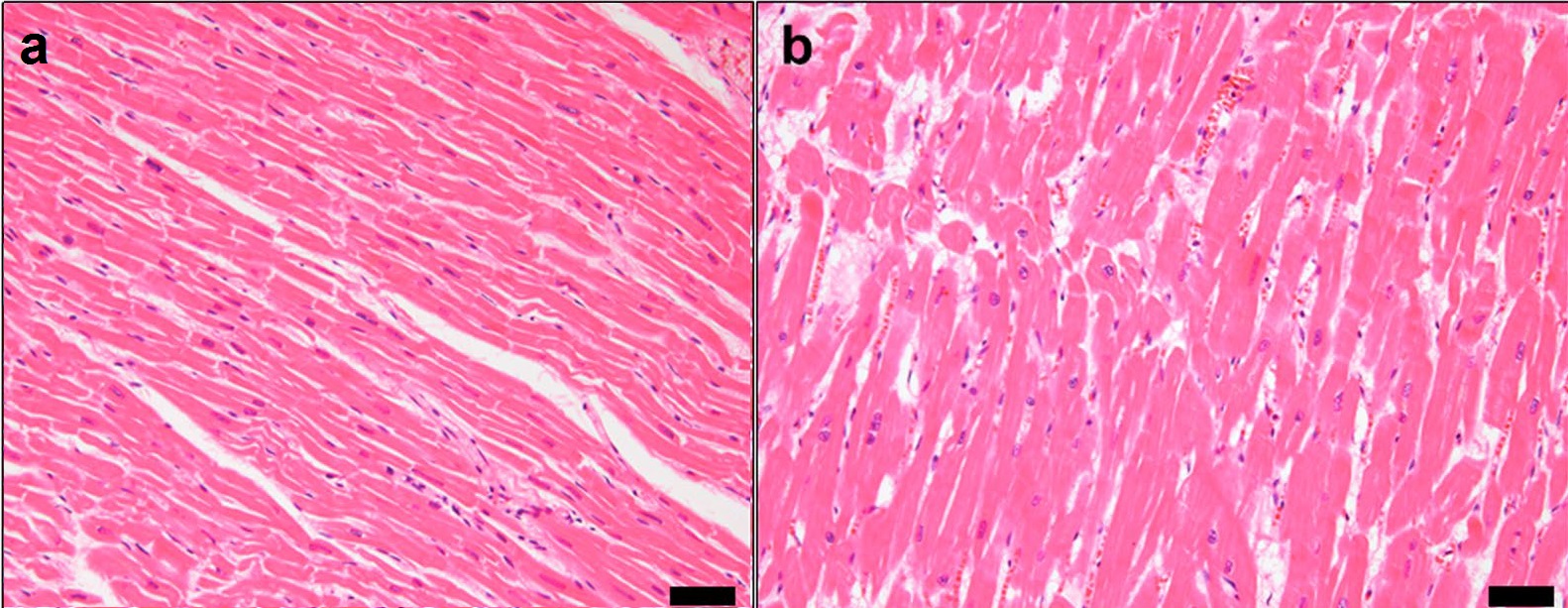
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both ventricles can also occur. Ventricular hypertrophy can result from a variety of conditions, both adaptive and maladaptive. For example, it occurs in what is regarded as a physiologic, adaptive process in pregnancy in response to increased blood volume; but can also occur as a consequence of ventricular remodeling following a heart attack. Importantly, pathologic and physiologic remodeling engage different cellular pathways in the heart and result in different gross cardiac phenotypes. Presentation In individuals with eccentric hypertrophy there may be little or no indication that hypertrophy has occurred as it is generally a healthy response to increased demands on the heart. Conversely, concentric hypertrophy can make itself known in a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Ogilvie
Kelvin Kenneth Ogilvie (born November 6, 1942) is a Canadian academic and politician. A former president of Acadia University in Wolfville, he was named to the Senate of Canada as a Conservative on August 27, 2009,"Harper makes nine new Senate appointments" '''', August 27, 2009. and served until his retirement on November 6, 2017. He was an international expert in biotechnology, bioorganic chemistry and genetic engineering. Scientific career Ogilvie is a leading expert on , |
Bioorganic Chemistry
Bioorganic chemistry is a scientific discipline that combines organic chemistry and biochemistry. It is that branch of life science that deals with the study of biological processes using chemical methods. Protein and enzyme function are examples of these processes. Sometimes biochemistry is used interchangeably for bioorganic chemistry; the distinction being that bioorganic chemistry is organic chemistry that is focused on the biological aspects. While biochemistry aims at understanding biological processes using chemistry, bioorganic chemistry attempts to expand organic-chemical researches (that is, structures, synthesis, and kinetics) toward biology. When investigating metalloenzymes and cofactors, bioorganic chemistry overlaps bioinorganic chemistry. Sub disciplines Biophysical organic chemistry is a term used when attempting to describe intimate details of molecular recognition The term molecular recognition refers to the specific interaction between two or more molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)
.jpg)
.jpg)