|
Ming Dynasty Essayists
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family, collectively called the Southern Ming, survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. He also took great care breaking the power of the court eunuchs and unrelated magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Asia
The history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as East Asia, South Asia, History of Southeast Asia, Southeast Asia and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe. See History of the Middle East and Outline of South Asian history, History of the Indian Subcontinent for further details on those regions. The coastal periphery was the home to some of the world's earliest known civilizations and religions, with each of three regions developing early civilizations around fertile river valleys. These valleys were fertile because the soil there was rich and could bear many root crops. The civilizations in Mesopotamia, ancient India, and ancient China shared many similarities and likely exchanged technologies and ideas such as mathematics and the wheel. Other notions such as that of writing likely developed individually in each area. Cities, states, and then empires developed in these lowlands. The ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heaven Worship
The worship of heavenly bodies is the veneration of stars (individually or together as the night sky), the planets, or other astronomical objects as deities, or the association of deities with heavenly bodies. In anthropological literature these systems of practice may be referred to as astral cults. The most notable instances of this are Sun gods and Moon gods in polytheistic systems worldwide. Also notable are the associations of the planets with deities in Sumerian religion, and hence in Babylonian religion, Babylonian and Ancient Greek religion, Greco-Religion in ancient Rome, Roman religion, viz. Mercury (mythology), Mercury, Venus (mythology), Venus, Mars (mythology), Mars, Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter, and Saturn (mythology), Saturn. Gods, goddesses, and demons may also be considered personifications of astronomical phenomena such as lunar eclipses, planetary alignments, and apparent interactions of planetary bodies with stars. The Sabians of Harran, a poorly understood p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanli Emperor
The Wanli Emperor (4 September 1563 – 18 August 1620), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shenzong of Ming, personal name Zhu Yijun, art name Yuzhai, was the 14th List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1572 to 1620. He succeeded his father, the Longqing Emperor. His reign of 48 years was the longest among all the Ming dynasty emperors. The Wanli Emperor ascended the throne at the age of nine. During the first ten years of his reign, the young emperor was assisted and effectively led by Grand Secretary Zhang Juzheng, a skilled administrator. With the support of the emperor's mother, Empress Dowager Xiaoding, Lady Li, and the imperial eunuchs led by Feng Bao, the country experienced economic and military prosperity, reaching a level of power not seen since the early 15th century. The emperor held great respect and appreciation for Zhang Juzheng. However, as time passed, various factions within the government openly opposed Zhang, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 1424. He was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor, the founding emperor of the dynasty. In 1370, Zhu Di was granted the title of Prince of Yan. By 1380, he had relocated to Beijing and was responsible for protecting the northeastern borderlands. In the 1380s and 1390s, he proved himself to be a skilled military leader, gaining popularity among soldiers and achieving success as a statesman. In 1399, he rebelled against his nephew, the Jianwen Emperor, and launched a civil war known as the Jingnan campaign, or the campaign to clear away disorders. After three years of intense fighting, he emerged victorious and declared himself emperor in 1402. After ascending the throne, he adopted the Chinese era name, era name Yongle, which means "perpetual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328– 24 June 1398), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Ming, personal name Zhu Yuanzhang, courtesy name Guorui, was the List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, founding emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1368 to 1398. In the mid-14th century, China was plagued by epidemics, famines, and peasant uprisings during the rule of the Mongol Yuan dynasty. Zhu Yuanzhang, orphaned during this time of chaos, joined a Buddhist monastery as a novice monk, where he occasionally begged for alms to sustain himself, gaining an understanding of the struggles faced by ordinary people, while harboring disdain for scholars who only gained knowledge from books. In 1352, he joined a rebel division, quickly distinguishing himself among the rebels and rising to lead his own army. In 1356, he conquered Nanjing and established it as his capital. He formed his own government, consisting of both generals and Confucian scholars, rejecting Mongol rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
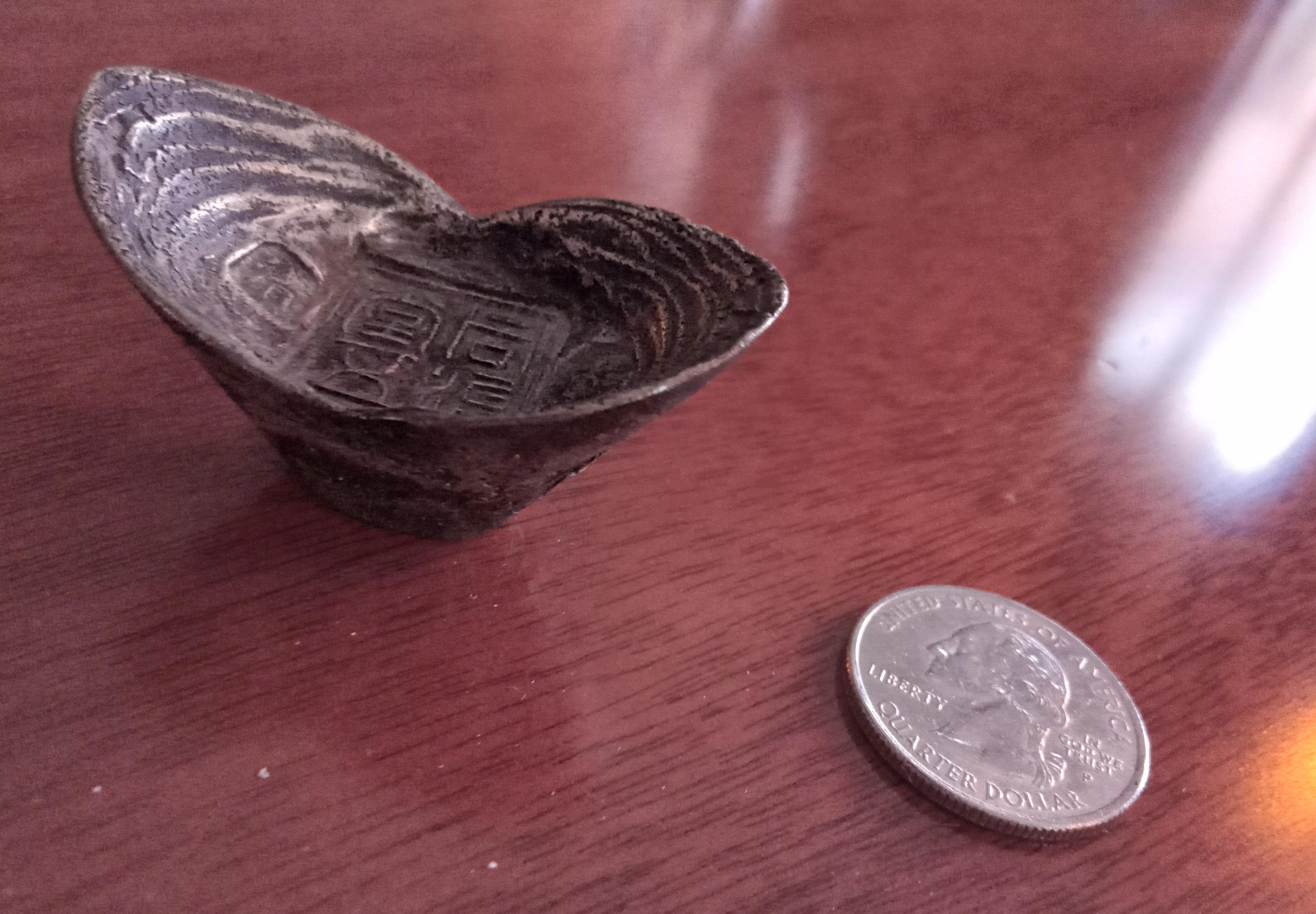
Tael
Tael ( ),"Tael" entry at the . or liang, also known as the tahil and by other names, can refer to any one of several measures used in and . It usually refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Cash (currency Unit)
The cash () was a currency denomination used in China in imperial times. It was the chief denomination until the introduction of the yuan in the late 19th century. Etymology The English word "cash", meaning "tangible currency", is an older word from Portuguese '' caixa'' or Middle French '' caisse'' ("box", or "case"). The term was first used on coins issued in Guangdong Province in 1900. It did not appear on paper money until later. The plural forms "cash" and "cashes" were both used. The Chinese character ''wen'' () has several other meanings in modern Chinese. History The ''wen'' was one of the chief units of currency in China and was used to denominate both coins and paper money. Other denominations were used, including various weights, based on the ''tael'' system, for sycee silver and gold ingots. Chinese currency started 3000-4500 years ago but no one is quite sure. Until the 19th century, coins denominated in wen were cast, the most common formation being the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
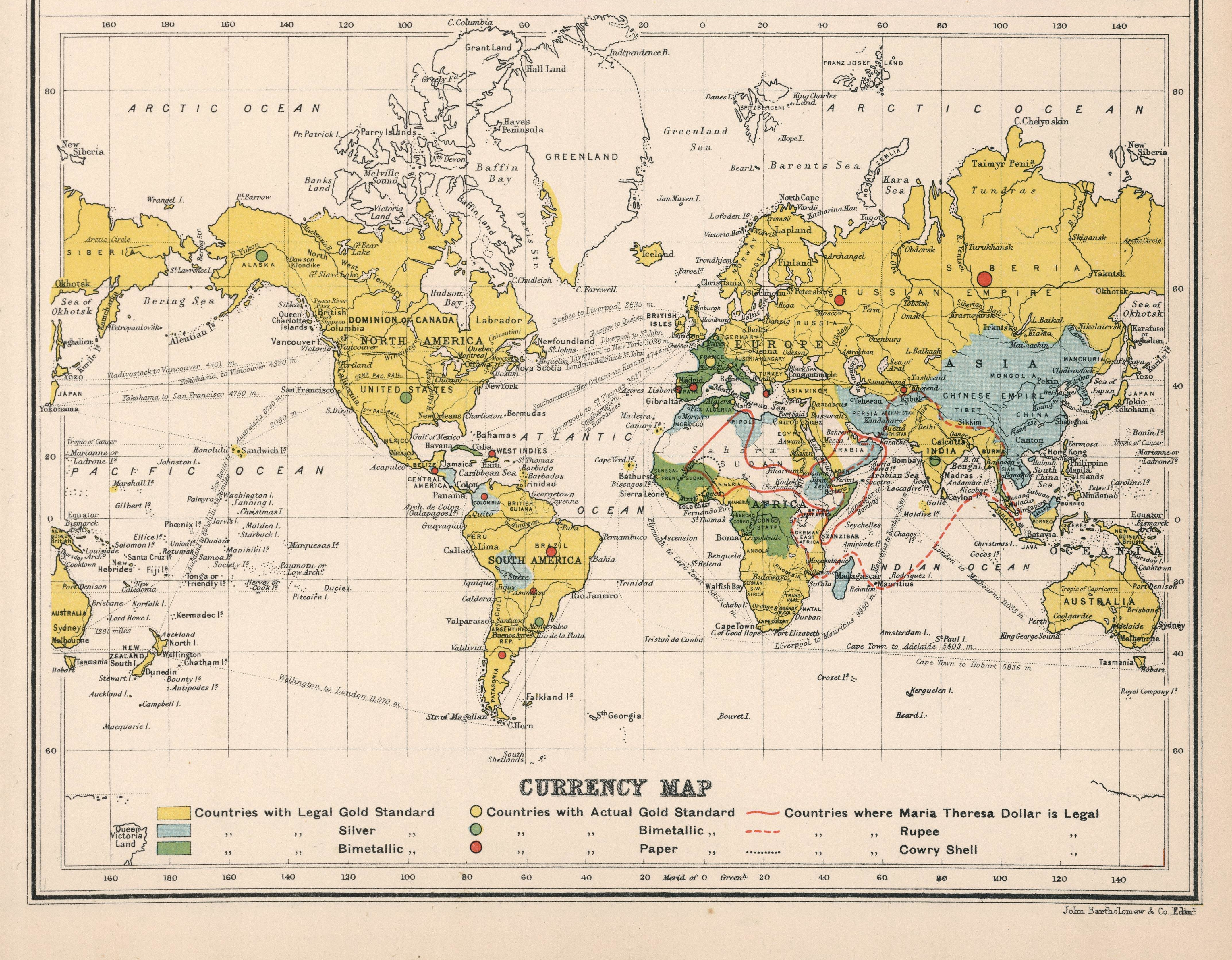
Bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed Exchange rate, rate of exchange between them. For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the Mint (facility), government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the monies of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most monies in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimeta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
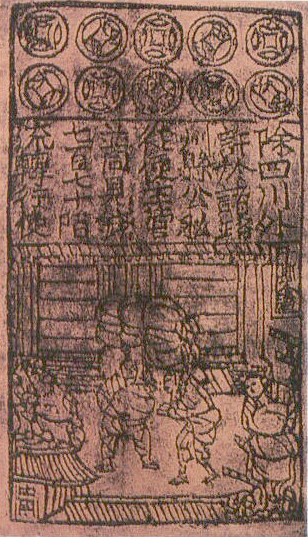
Paper Money
Paper money, often referred to as a note or a bill (North American English), is a type of negotiable promissory note that is payable to the bearer on demand, making it a form of currency. The main types of paper money are government notes, which are directly issued by political authorities, and banknotes issued by banks, namely banks of issue including central banks. In some cases, paper money may be issued by other entities than governments or banks, for example merchants in pre-modern China and Japan. "Banknote" is often used synonymously for paper money, not least by collectors, but in a narrow sense banknotes are only the subset of paper money that is issued by banks. Paper money is often, but not always, legal tender, meaning that courts of law are required to recognize them as satisfactory payment of money debts. Counterfeiting, including the forgery of paper money, is an inherent challenge. It is countered by anticounterfeiting measures in the printing of paper money. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In China
The Catholic Church ( zh, p=Tiānzhǔ jiào, c=天主教, l=Religion of the Lord of Heaven, after the Chinese term for the Christian God) first appeared in China upon the arrival of John of Montecorvino in China proper during the Yuan dynasty; he was the first Catholic missionary in the country, and would become the first bishop of Khanbaliq (1271–1368). After the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) won the Chinese Civil War, Catholic and Protestant missionaries were expelled from the country. In 1957, the communist government established the Chinese Catholic Patriotic Association (CCPA) in Beijing, which rejects the authority of the Holy See and appoints its own preferential bishops. In September 2018, China and the Holy See reached a provisional agreement giving the Pope the power to veto any bishop which the Chinese government recommends. The parties have extended the provisional agreement twice, most recently in October 2024. Chinese terms Terms used to refer to God in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In China
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. There are an estimated 17–25 million Muslims in China, less than 2 percent of the total population. Though Hui people, Hui Muslims are the most numerous group, the greatest concentration of Muslims reside in northwestern China's Xinjiang autonomous region, which contains a significant Uyghurs, Uyghur population. Lesser yet significant populations reside in the regions of Ningxia, Gansu and Qinghai. Of Ethnic minorities in China, China's 55 officially recognized minority peoples, ten of these groups are predominantly Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim. History The Silk Road, which comprised a series of extensive inland trade routes that spread all over the Mediterranean to East Asia, was used since 1000 BCE and continued to be used for millennia. For more than half of this long period of time, most of the traders were Muslim and moved towards the East. Not only did these traders bring their goods, they also carried with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Folk Religion
Chinese folk religion comprises a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. This includes the veneration of ''Shen (Chinese folk religion), shen'' ('spirits') and Chinese ancestor worship, ancestors, and worship devoted to Chinese deities and immortals, deities and immortals, who can be deities of places or natural phenomena, of human behaviour, or progenitors of Chinese kin, family lineages. Stories surrounding these gods form a loose canon of Chinese mythology. By the Song dynasty (960–1279), these practices had been Religious syncretism, blended with Buddhist, Confucian, and Taoist teachings to form the popular religious system which has lasted in many ways until the present day. The government of China, government of modern China generally tolerates popular religious organizations, but has suppressed or persecuted those that they fear would undermine social stability. After the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1911, governments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |