|
Mieridduryn Bonniae NMW
''Mieridduryn'' is a genus of extinct dinocaridid arthropod that lived during the Middle Ordovician of what is now the United Kingdom. This animal was described in 2022 based on a singular fossil found in Castle Bank, a Burgess shale type lagerstätte located in the country of Wales. This animal's taxonomic affinities are somewhat unclear, but there are some hypotheses. One is that this animal represents a new grade of Stem- euarthropods that evolved features similar to the Cambrian aged opabiniids (a family of basal arthropods). Another is that if the features seen in ''Mieridduryn'' are convergent, and not homologous, to those seen in radiodonts, then this animal represents a late surviving opabiniid (if the latter option is correct, then this means the opabiniids survived for over 40 million years longer than what was once thought). Free abstract at History of research and etymology The one specimen of this species was found in Castle Bank, and was described in 2022. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinocaridida
DinocarididaGreek, "Terrible crabs" – sometimes informally spelt Dinocarida, but the second 'id' is linguistically correct – see is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods that flourished in the Cambrian period with occasional OrdovicianVan Roy, P.; Briggs, D. E. G. (2011). "A giant Ordovician anomalocaridid". Nature 473 (7348): 510–513. doi:10.1038/nature09920. edit and Devonian records. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids comes from Greek, "deinos" and "caris" ("terrible crab"), referring to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group compose of Radiodonta (''Anomalocaris'' and relatives), Opabiniidae (''Opabinia'' and relatives), ''Pambdelurion'' and '' Kerygmachela.'' It is most likely paraphyletic, with ''Kerygmachela'' and ''Pambdelurion'' more basal than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their environmental impact. The word ''quarry'' can also include the underground quarrying for stone, such as Bath stone. Types of rock Types of rock extracted from quarries include: *Chalk *China clay *Scoria, Cinder *Clay *Coal *Construction aggregate (sand and gravel) *Coquina *Diabase *Gabbro *Granite *Gritstone *Gypsum *Limestone *Marble *Ores *Phosphate rock *Quartz *Sandstone *Slate *Travertine Stone quarry Stone quarry is an outdated term for mining construction rocks (limestone, marble, granite, sandstone, etc.). There are open types (called quarries, or open-pit mines) and closed types (Mining, mines and caves). For thousands of years, only hand tools had been used in quarries. In the 18th century, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pambdelurion
''Pambdelurion'' is an extinct genus of panarthropod from the Cambrian aged Sirius Passet site in northern Greenland. Like the morphologically similar '' Kerygmachela'' from the same locality, ''Pambdelurion'' is thought to be closely related to arthropods, combining characteristics of " lobopodians" with those of primitive arthropods. Description ''Pambdelurion'' was large for a Cambrian animal, and is estimated to have reached a length of . '' Omnidens'', an organism from China that closely resembles ''Pambdelurion'' and may even be synonymous with it, reached even larger sizes, estimated to be based on the proportions of ''Pambdelurion''. The head of ''Pambdelurion'' bore a large pair of frontal appendages, homologous to the antennae of onychophorans and frontal appendages of radiodonts. These frontal appendages were weakly muscled and relatively soft, suggesting they may have served primarily as sensory organs, rather than for grasping prey. Between the appendages are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuteropoda
Deuteropoda or "upper stem group arthropods" is a proposed clade of arthropods whose members are distinguished by an anatomical reorganization of the head region, namely the appearance of a differentiated first appendage pair (the ' deutocerebral' pair), a multisegmented head, and a hypostome/ labrum complex. The clade contains all living arthropods (i.e. chelicerates and mandibulates) as well as several fossil groups that share these characteristics (e.g. fuxianhuiids, megacheirans and Artiopoda), while excluding other fossil groups that are more 'basal' or 'primitive' (e.g. anomalocarids and lobopodians). Defining characteristics Members of Deuteropoda are characterized by the presence of a differentiated labrum and a differentiated first ' deutocerebral' pair of appendages. In contrast, lobopodians (part of the "lower stem group") and onychophorans have a pair of pre-ocular or ' protocerebral' appendages, which presumably have evolved to be the labrum of modern living ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotised
Sclerotin is a component of the cuticle of various Arthropoda, most familiarly insects. It is formed by cross-linking members of particular classes of protein molecules, a biochemical process called sclerotization, a form of tanning in which quinones are enzymatically introduced into the cuticle, and react with terminal and lysine-related amino groups in the proteins to form strong links between the molecules.Chapman, R.F. (1969) ''The Insects: Structure and Function''. Elsevier, New York. Chapter 22.37 - "Expansion of the new cuticle is brought to an end by the onset of tanning" The resulting material increases the rigidity of an insect's chitinous exoskeleton. It is particularly prominent in the thicker, armoured parts of insect and arachnid integument, such as in the biting mouthparts and sclerites of scorpions and beetles. As it matures, freshly formed sclerotin becomes a hard, horn-like substance with a range of yellow-brown colors. As animals adapted to life on land, incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerite
A sclerite ( Greek , ', meaning " hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates. Sclerites in combination Sclerites may occur practically isolated in an organism, such as the sting of a cone shell. Also, they can be more or less scattered, such as tufts of defensive sharp, mineralised bristles as in many marine Polychaetes. Or, they can occur as structured, but unconnected or loosely connected arrays, such as the mineral "teeth" in the radula of many Mollusca, the valves of Chitons, the beak of Cephalopod, or the articulated exoskeletons of Arthropoda. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala or thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms are characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
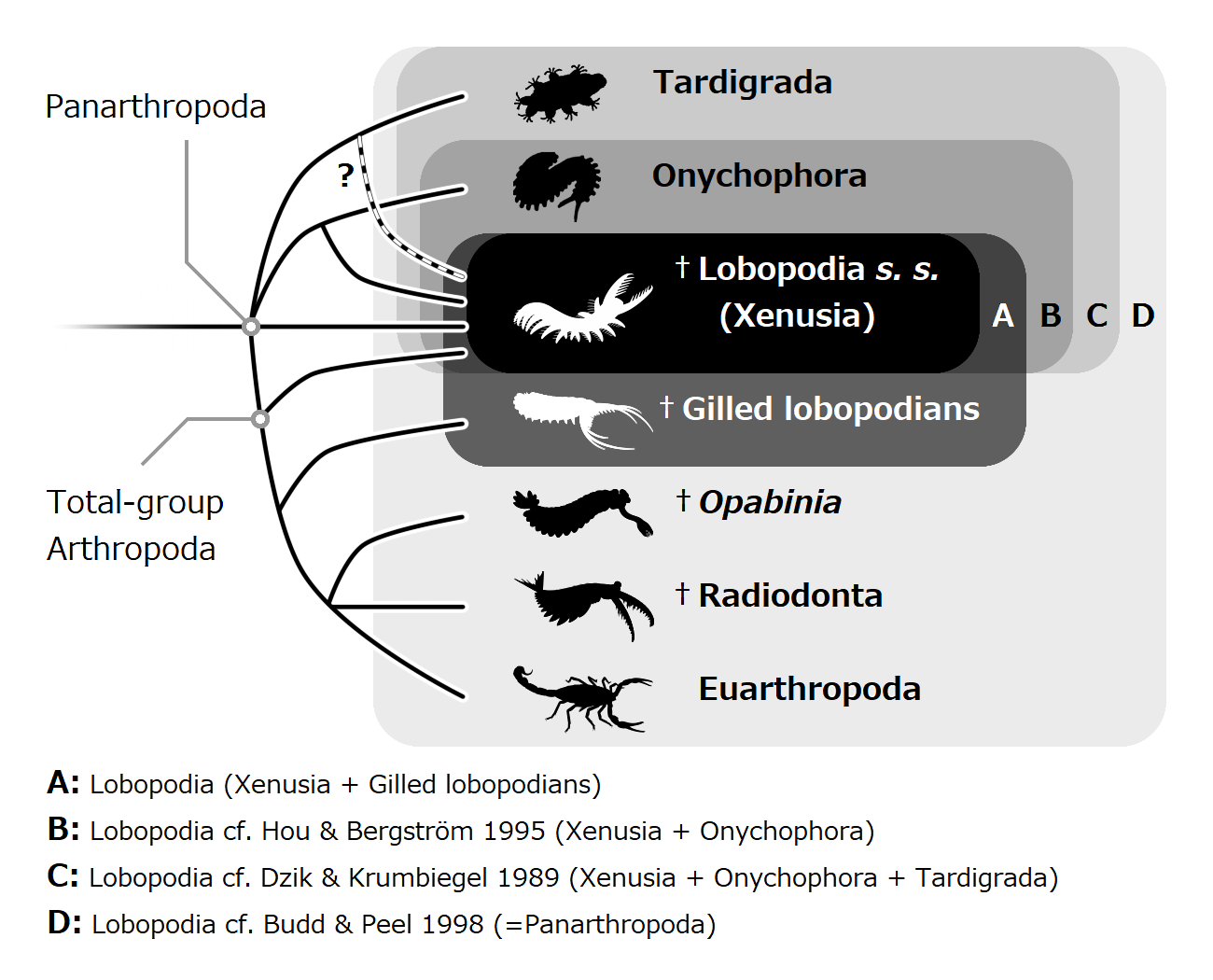
Lobopodia
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora) are thought to have evolved from lobopodian ancestors. Definitions The Lobopodian concept varies from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Mouthparts
The mouthparts of arthropods have evolved into a number of forms, each adapted to a different style or mode of feeding. Most mouthparts represent modified, paired appendages, which in ancestral forms would have appeared more like legs than mouthparts. In general, arthropods have mouthparts for cutting, chewing, piercing, sucking, shredding, siphoning, and filtering. This article outlines the basic elements of four arthropod groups: insects, myriapods, crustaceans and chelicerates. Insects are used as the model, with the novel mouthparts of the other groups introduced in turn. Insects are not, however, the ancestral form of the other arthropods discussed here. Insects Insect mouthparts exhibit a range of forms. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Specialisation includes mouthparts modified for siphoning, piercing, sucking and sponging. These modifications have evolved a number of times. For example, mosquitoes (which are flies) and aphids (which are bugs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieridduryn Bonniae NMW
''Mieridduryn'' is a genus of extinct dinocaridid arthropod that lived during the Middle Ordovician of what is now the United Kingdom. This animal was described in 2022 based on a singular fossil found in Castle Bank, a Burgess shale type lagerstätte located in the country of Wales. This animal's taxonomic affinities are somewhat unclear, but there are some hypotheses. One is that this animal represents a new grade of Stem- euarthropods that evolved features similar to the Cambrian aged opabiniids (a family of basal arthropods). Another is that if the features seen in ''Mieridduryn'' are convergent, and not homologous, to those seen in radiodonts, then this animal represents a late surviving opabiniid (if the latter option is correct, then this means the opabiniids survived for over 40 million years longer than what was once thought). Free abstract at History of research and etymology The one specimen of this species was found in Castle Bank, and was described in 2022. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_2.jpg)