|
Midline Nuclear Group
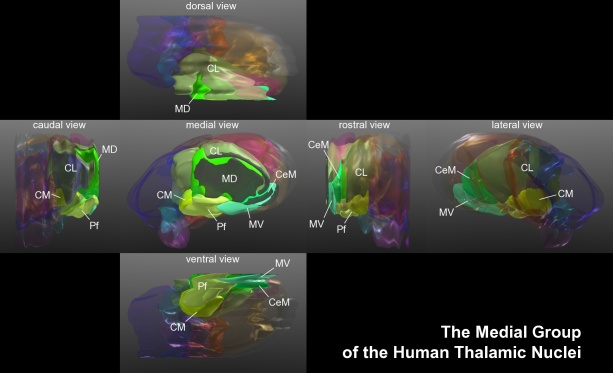
The midline nuclear group (or midline thalamic nuclei) is a region of the thalamus consisting of the following nuclei: * Paraventricular thalamus, paraventricular nucleus of thalamus (''nucleus paraventricularis thalami'') - not to be confused with paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus * paratenial nucleus (''nucleus parataenialis'') * nucleus reuniens (also known as the medioventral nucleus) * rhomboidal nucleus (''nucleus commissuralis rhomboidalis'') * subfascicular nucleus (''nucleus subfascicularis'') The List of regions in the human brain#Thalamus, midline nuclei are often called "nonspecific" in that they project widely to the cortex and elsewhere. This has led to the assumption that they may be involved in general functions such as alerting. However, anatomical connections might suggest more specific functions, with the paraventricular and paratenial nuclei involved in viscero-limbic functions, and the reuniens and rhomboid nuclei involved in multimodal sensory processin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Nuclei Of Thalamus
The anterior nuclei of thalamus (or anterior nuclear group) are a collection of nuclei at the rostral end of the dorsal thalamus. They comprise the anteromedial, anterodorsal, and anteroventral nuclei. Inputs and outputs The anterior nuclei receive afferents from the hippocampus and subiculum directly via the fornix, and indirectly via the mammillary bodies and mammillothalamic tract (MTT). They send efferent fibers to the cingulate gyrus, limbic, and orbitofrontal cortex. The anterior nuclei of the thalamus display functions pertaining to memory. Persons displaying lesions in the anterior thalamus, preventing input from the pathway involving the hippocampus, mammillary bodies and the MTT, display forms of amnesia, supporting the anterior thalamus's involvement in episodic memory. However, although the hypothalamus projects to both the mammillary bodies and the anterior nuclei of the thalamus, the anterior nuclei receive input from hippocampal cells deep to the pyramidal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal_and_ventral, ventral projection of the thalamus where the thalamus connects with the optic nerve. There are two LGNs, one on the left and another on the right side of the thalamus. In humans, both LGNs have six layers of neurons (grey matter) alternating with optic fibers (white matter). The LGN receives information directly from the ascending retinal ganglion cells via the optic tract and from the reticular activating system. Neurons of the LGN send their axons through the optic radiation, a direct pathway to the primary visual cortex. In addition, the LGN receives many strong feedback connections from the primary visual cortex. In humans as well as other mammals, the two strongest pathways linking the eye to the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Reuniens
The nucleus reuniens is a region of the thalamic midline nuclear group. In the human brain, it is located in the interthalamic adhesion (''massa intermedia''). It is also known as the medioventral nucleus. The nucleus reuniens receives afferent input from a large number of structures, mainly from limbic and limbic-associated structures. It sends projections to the medial prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, perirhinal cortex, and entorhinal cortex The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in t ..., although there exist sparse connections to many other afferent structures as well. The unique medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampal connectivity allows reuniens to regulate neural traffic in this cortical network related to changes in an organism's attentiveness, making reuniens c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratenial Nucleus
The paratenial nucleus, or parataenial nucleus (), is a component of the midline nuclear group in the thalamus. It is sometimes subdivided into the nucleus parataenialis interstitialis and nucleus parataenialis parvocellularis (Hassler). It is located above the bordering paraventricular nucleus of thalamus and below the anterodorsal nucleus. The paratenial nucleus, like other midline nuclei, receives inputs from a large number of regions in the brainstem, hypothalamus and limbic system. It projects back to an equally wide range, but in a fairly specific manner (in the past, the midline nuclei have often been described as "nonspecific" because of their global effects). Particular targets include medial frontal polar cortex, the anterior cingulate, insula, the piriform and entorhinal cortices, the ventral subiculum, claustrum, the core and shell of nucleus accumbens, the medial striatum, the bed nucleus of stria terminalis, and caudal parts of the central and basal nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraventricular Nucleus Of Hypothalamus
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is a nucleus in the hypothalamus, located next to the third ventricle. Many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary where they secrete oxytocin, and a smaller amount of vasopressin. Other secretions are corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system, and target different neurons in the anterior pituitary. Dysfunctions of the PVN can cause hypersomnia in mice. In humans, the dysfunction of the PVN and the other nuclei around it can lead to drowsiness for up to 20 hours per day. The PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, wakefulness, and the response of the body to stress. Location The paraventricular nucleus lies adjacent to the third ventricle. It lies within the periventricular zone and is not to be confused with the periventricular nucleus, which occupies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraventricular Thalamus
The paraventricular thalamus (PVT) is a midline thalamic nucleus with broad connectivity with other brain structures such as the hypothalamus, striatum, and amygdala. Rodent studies suggest that the PVT plays a role in modulating reward-seeking behavior, threat avoidance, and wakefulness via the hypothalamic-thalamic-striatal circuit, while contributing to the retrieval of fear and the regulation of stress through other circuits. Anatomy The PVT is a nucleus in the midline nuclear group of the thalamus. It has an elongated ovoid shape and an approximate volume of 7 mm³. At the cellular level, the PVT is composed predominantly of glutamatergic neurons, neurons that release glutamate as the primary neurotransmitter. Connectivity The PVT is connected to several structures, including the brainstem, midbrain, striatum, and medial temporal lobe. For the brainstem and midbrain, the PVT receives inputs in the form of orexin from the hypothalamus, which are essential for regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub (network science), hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory neuron, sensory and motor neuron, motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, the thalami are paramedian symmetrical structures (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalami ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
The medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) or medial geniculate body (MGB) is part of the auditory thalamus and represents the thalamic relay between the inferior colliculus (IC) and the auditory cortex (AC). It is made up of a number of sub-nuclei that are distinguished by their neuronal morphology and density, by their afferent and efferent connections, and by the coding properties of their neurons. It is thought that the MGN influences the direction and maintenance of attention. Divisions The MGN has three major divisions; ventral (VMGN), dorsal (DMGN) and medial (MMGN). Whilst the VMGN is specific to auditory information processing, the DMGN and MMGN also receive information from non-auditory pathways. Ventral subnucleus Cell types There are two main cell types in the ventral subnucleus of the medial geniculate body (VMGN): * Thalamocortical relay cells (or principal neurons): The dendritic input to these cells comes from two sets of dendritic trees oriented on opposite poles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metathalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, the thalami are paramedian symmetrical structures (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalami are paired structures of gray matter about four centimetres long and ovoid in appearance, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Dorsal Nucleus
The medial dorsal nucleus (or mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus, dorsomedial nucleus, dorsal medial nucleus, or medial nucleus group) is a large nucleus in the thalamus. It is separated from the other thalamic nuclei by the internal medullary lamina. The medial dorsal nucleus is interconnected with the prefrontal cortex, therefore involved in prefrontal functions. Damage to the interconnected tract or the nucleus itself will result in similar damage to the prefrontal cortex. It is also believed to play a role in memory. Structure The medial dorsal nucleus relays inputs from the amygdala and olfactory cortex and projects to the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system, and in turn relays them to the prefrontal association cortex. As a result, it plays a crucial role in attention, planning, organization, abstract thinking, multi-tasking, and active memory. The connections of the medial dorsal nucleus have even been used to delineate the prefrontal cortex of the Göttingen minip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulvinar Nuclei
The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar (nuclei pulvinares) are the nuclei ( cell bodies of neurons) located in the thalamus (a part of the vertebrate brain). As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus (pulvinar thalami), usually just called the pulvinar. The pulvinar is usually grouped as one of the ''lateral thalamic nuclei'' in rodents and carnivores, and stands as an independent complex in primates. Pulvinar acts as an association nucleus that, along with medial dorsal nucleus, connected with parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes, but the function is largely unknown. No distinctive syndrome or obvious sensory deficit can be linked to either one. Structure By convention, the pulvinar is divided into four nuclei: Their connectomic details are as follows: * The ''lateral'' and ''inferior'' pulvinar nuclei have widespread connections with early visual cortical areas. * The dorsal part of the ''lateral'' pulvinar nucleus predominant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Nuclear Group
The lateral nuclear group is a collection of nuclei on the lateral side of the thalamus. This nucleus group is one of the three regions of the thalamus which result from trisection by the Y-shaped internal medullary lamina. The name "lateral nuclear group" is also given to a subset of the lateral group of nuclei which result from trisection by the internal medullary lamina. The lateral nuclear group consists of the following: * lateral dorsal nucleus * lateral posterior nucleus * pulvinar nuclei The lateral region of the thalamus which results from trisection by the internal medullary lamina also includes the ventral nuclear group and the lateral Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to: Biology and healthcare * Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side" * Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx * Lateral release ( ... and medial geniculate nuclei. References Thalamic nuclei {{Neuroana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |