|
Methyldiazonium
Methyldiazonium is an organic compound consisting of a methyl group attached to a diazo group. This cation is the conjugate acid of diazomethane, with an estimated p''K''a<10. : 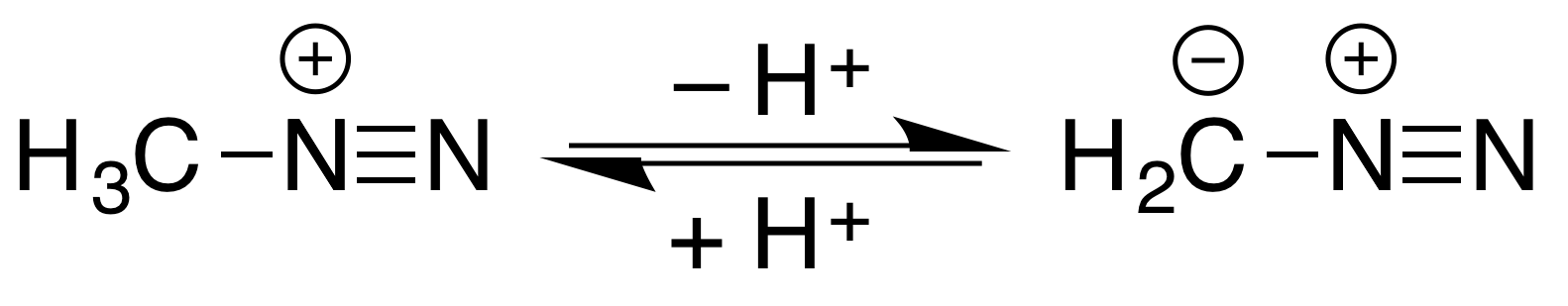 It is an intermediate in methylation reactions of diazomethane with acidic hydroxyl compounds, such as conversion of s to methyl esters and
It is an intermediate in methylation reactions of diazomethane with acidic hydroxyl compounds, such as conversion of s to methyl esters and
|
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether. The compound is a popular methylating agent in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane. Use For safety and convenience diazomethane is always prepared as needed as a solution in diethyl ether, ether and used as such. It converts carboxylic acids to methyl esters and phenols into their methyl ethers. The reaction is thought to proceed via proton transfer from carboxylic acid to diazomethane to give a methyldiazonium cation, which reacts with the carboxylate ion to give th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Ether
Methyl ether may refer to: * Any chemical compound of the ether class that includes a methyl group * Dimethyl ether, often simply called methyl ether See also *Methoxy group In organic chemistry, a methoxy group is the functional group consisting of a methyl group bound to oxygen. This alkoxy group has the formula . On a benzene ring, the Hammett equation classifies a methoxy substituent at the ''para'' position a ..., –OCH3 {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cations
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− (hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazo Compounds
In organic chemistry, the diazo group is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms at the terminal position. Overall charge-neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula . The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, . Diazo compounds () should not be confused with azo compounds () or with diazonium compounds (). Structure The electronic structure of diazo compounds is characterized by π electron density delocalized over the α-carbon and two nitrogen atoms, along with an orthogonal π system with electron density delocalized over only the terminal nitrogen atoms. Because all octet rule-satisfying resonance forms of diazo compounds have formal charges, they are members of a class of compounds known as 1,3-dipoles. Some of the most stable diazo compounds are α-diazo-β-diketones and α-diazo-β-diesters, in which the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenicity
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and Biological agent, biologic agents such as viruses and carcinogenic bacteria, bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked Cell division, cellular division. The specific mechanisms for carcinogenic activity is unique to each agent and cell type. Carcinogens can be broadly categorized, however, as activation-dependent and activation-independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Nitrosodimethylamine
''N''-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), also known as dimethylnitrosamine (DMN), is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NNO. It is one of the simplest members of a large class of nitrosamines. It is a volatile yellow oil. NDMA has attracted wide attention as being highly hepatotoxic and a known carcinogen in laboratory animals. Occurrence Drinking water Of more general concern, NDMA can be produced by water treatment by water chlorination, chlorination or chloramination. The question is the level at which it is produced. In the U.S. state of California, the allowable level is 10 nanograms/liter. The Canadian province of Ontario set the standard at 9 ng/L. The potential problem is greater for recycled water that can contain dimethylamine. Further, NDMA can form or be leached during treatment of water by ion exchange, anion exchange resins. Contamination of drinking water with NDMA is of particular concern due to the minute concentrations at which it is harmful and the dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid, sulfuric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
