|
Melithaea Albitincta
''Melithaea'' is a genus of octocorals in the family Melithaeidae. Members of the genus are commonly known as fan corals and are found in the tropical Indo-Pacific region. The type species is ''Melithaea ochracea''.''Melithaea'' Marine Species Identification Portal. Retrieved 2012-02-22. Description Members of the genus ''Melithaea'' are arborescent colonial corals forming fan, bush or tree shapes. The axis or main skeletal "trunk" is jointed, there being nodes, flexible horny joints, separated by internodes composed of hard, calcareous material. The branches divide off at the nodes which are often swollen. The minute calcareous spicules in the flexible membrane called the |
Henri Milne-Edwards
Henri Milne-Edwards (23 October 1800 – 29 July 1885) was a French zoologist. Biography Henri Milne-Edwards was the 27th child of William Edwards, an English planter and colonel of the militia in Jamaica and Elisabeth Vaux, a Frenchwoman. Henri was born in Bruges, in present-day Belgium, where his parents had retired; Bruges was then a part of the newborn French Republic. His father had been jailed for several years for helping some Englishmen in their escape to their country. Henri spent most of his life in France. He was brought up in Paris by his older brother Guillaume Frederic Edwards (1777–1842), a distinguished physiologist and ethnologist. His father was released after the fall of Napoleon. The whole family then moved to Paris. At first he turned his attention to medicine, in which he graduated as an MD at Paris in 1823. His passion for natural history soon prevailed, and he gave himself up to the study of the lower forms of animal life. He became a student of Geor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octocorallia
Octocorallia, along with Hexacorallia, is one of the two extant classes of Anthozoa. It comprises over 3,000 species of marine and brackish animals consisting of colonial polyps with 8-fold symmetry, commonly referred informally as "soft corals". It was previously known by the now unaccepted scientific names Alcyonacea and Gorgonacea, both deprecated , and by the also deprecated name of Alcyonaria, in earlier times. Its only two orders are Malacalcyonacea and Scleralcyonacea, which include corals such as those under the common names of blue corals, sea pens, and gorgonians (sea fans and sea whips). These animals have an internal skeleton secreted by their mesoglea, and polyps with tipically eight tentacles and eight mesenteries. As is the case with all cnidarians, their complex life cycle includes a motile, planktonic phase (a larva called planula), and a later characteristic sessile phase. Octocorals have existed at least since the Ordovician period, as shown by Maurit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melithaeidae
''Melithaeidae'' is a family of corals in the suborder Scleraxonia. Members of the family are commonly known as sea fans and are found on reefs in the tropical regions of the Indo-Pacific.Family Melithaeidae Marine Species Identification Portal. Retrieved 2012-02-22. Description Members of the family Melithaeidae are arborescent colonial corals forming fans, bushes or trees. The axis or main skeletal "trunk" is jointed, there being nodes, flexible horny joints, separated by internodes composed of hard, calcareous material. The branches divide dichotomously at the nodes and these are often swollen. The minute calcareous spicules in the flexible membrane call ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological Type (biology), type wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or specimens). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name with that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melithaea Ochracea
''Melithaea ochracea'' is a species of colonial soft coral in the family Melithaeidae, commonly known as knotted fan coral. It grows in tree-like fans on coral reefs in the South China Sea. It grows in tree-like fans on coral reefs in the South China Sea and is used in the jewelry industry under the name red spongy coral. Description Colonies of ''Melithaea ochracea'' are arborescent and usually grow to about long although much larger specimens can be found. They grow in one plane and have a branching, fan-shaped structure. The main skeletal stalk and branches are jointed, with swellings at the larger joints. The internodes are composed of hard, calcareous material while the joints are flexible and made of a horny material. The skeleton is covered by a flexible membrane, the mesoglea, which contains minute calcareous spicules or sclerites. The identity of these is important for distinguishing between different closely related species. In ''Melithaea ochracea'', they include ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony is composed of two or more Biological specificity#Conspecific, conspecific individuals living in close association with, or connected to, one another. This association is usually for mutual benefit such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Colonies can form in various shapes and ways depending on the organism involved. For instance, the bacterial colony is a cluster of identical cells (clones). These colonies often form and grow on the surface of (or within) a solid medium, usually derived from a single parent cell. Colonies, in the context of development, may be composed of two or more unitary (or solitary) organisms or be Modularity, modular organisms. Unitary organisms have determinate development (set life stages) from zygote to adult form and individuals or groups of individuals (colonies) are visually distinct. Modular organisms have indeterminate growth forms (life stages not set) through repeated iteration of genetically identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoglea
Mesoglea refers to the extracellular matrix found in cnidarians like coral or jellyfish as well as ctenophores that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. It is related to but distinct from mesohyl, which generally refers to extracellular material found in sponges. Description The mesoglea is mostly water. Other than water, the mesoglea is composed of several substances including fibrous proteins, like collagen and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. The mesoglea is mostly acellular, but in both Cnidaria and Ctenophora the mesoglea contains muscle bundles and nerve fibres. Other nerve and muscle cells lie just under the epithelial layers. The mesoglea also contains wandering amoebocytes that play a role in phagocytosing debris and bacteria. These cells also fight infections by producing antibacterial chemicals. The mesoglea may be thinner than either of the cell layers in smaller coelenterates like a hydra or may make up the bulk of the body in larger jellyfish. The mesoglea serves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerite
A sclerite (Greek language, Greek , ', meaning "hardness, hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal wikt:spicule, spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and Alcyonacea, soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates. Sclerites in combination Sclerites may occur practically isolated in an organism, such as the Stinger, sting of a Conus, cone shell. Also, they can be more or less scattered, such as tufts of defensive sharp, mineralised bristles as in many marine polychaetes. Or, they can occur as structured, but unconnected or loosely connected arrays, such as the mineral "teeth" in the radula of many Mollusca, the Valve (mollusc), valves of chit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
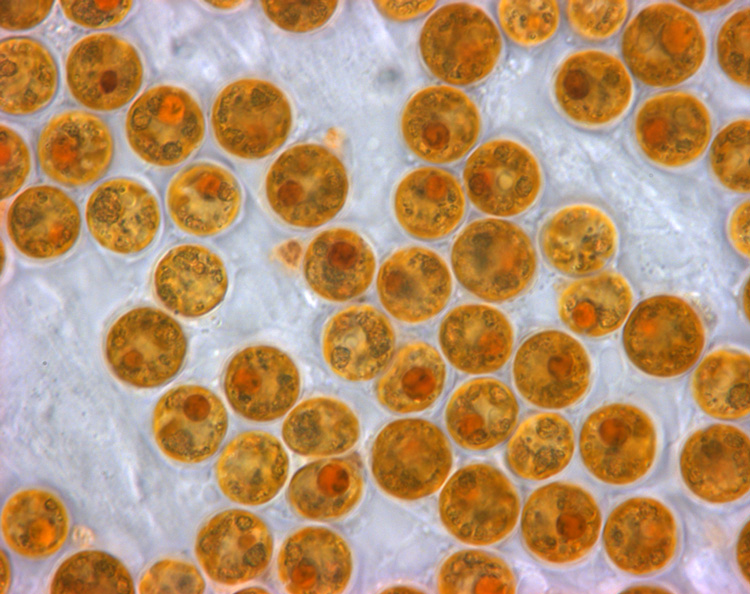
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae (; zooxanthella) is a colloquial term for single-celled photosynthetic organisms that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including corals, jellyfish, demosponges, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the dinoflagellate genus '' Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. "Zooxanthella" was originally a genus name (meaning literally "little yellow animal") given in 1881 by Karl Brandt to '' Zooxanthella nutricula'' (a mutualist of the radiolarian '' Collozoum inerme'') which has been placed in the Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |