|
Melanesian People
Melanesians are the predominant and indigenous inhabitants of Melanesia, in an area stretching from New Guinea to the Fiji Islands. Most speak one of the many languages of the Austronesian language family (especially ones in the Oceanic branch) or one of the many unrelated families of Papuan languages. There are several creoles of the region, such as Tok Pisin, Hiri Motu, Solomon Islands Pijin, Bislama, and Papuan Malay. Origin and genetics The origin of Melanesians is generally associated with the first settlement of Australasia by a lineage dubbed 'Australasians' or 'Australo-Papuans' during the Initial Upper Paleolithic, which is "ascribed to a population movement with uniform genetic features and material culture" ( Ancient East Eurasians), and sharing deep ancestry with modern East Asian peoples and other Asia-Pacific groups. It is estimated that people reached Sahul (the geological continent consisting of Australia and New Guinea) between 50,000 and 37,000 years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biak Language
Biak ( or 'Biak language'; or 'our language'; Indonesian: ), also known as Biak-Numfor, Noefoor, Mafoor, Mefoor, Nufoor, Mafoorsch, Myfoorsch and Noefoorsch, is an Austronesian language of the South Halmahera-West New Guinea subgroup of the Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages. According to ''Ethnologue'', it is spoken by about 70,000 people in Biak and Numfor and numerous small islands in the Schouten Islands, located in Papua province of Western New Guinea, northeastern Indonesia. Name The name ''Biak'' or ''Vyak'' refers to the island of the same name. It probably comes from an earlier form ''*Bat'', which is argued to have meant "the ground under one's feet, land" in Proto-Austronesian via the regular change of ''*t'' to ''k''. This is supported by the Ambel cognate ''Báyt''. Dialects There are a number of different dialects of Biak spoken on various different islands, the most well-known being Biak-Numfoor, spoken on the island of Numfoor. These dialect difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
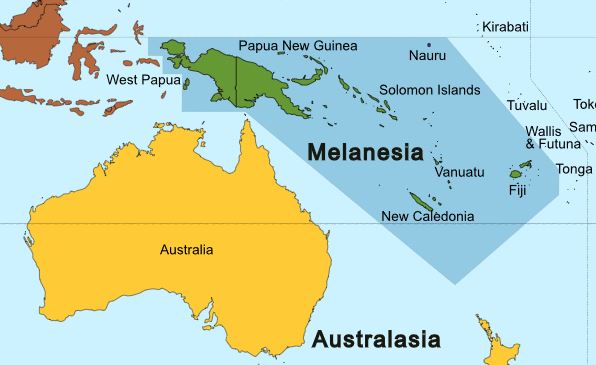
Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea. The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, and Papua New Guinea. It also includes the West New Guinea, Indonesian part of New Guinea, the French overseas collectivity of New Caledonia, and the Torres Strait Islands. Almost all of the region is in the Southern Hemisphere; only a few small islands that are not politically considered part of Oceania—specifically the northwestern islands of Western New Guinea—lie in the Northern Hemisphere. The name ''Melanesia'' (in French, ''Mélanésie'') was first used in 1832 by French navigator Jules Dumont d'Urville: he coined the terms ''Melanesia'' and ''Micronesia'' to go alongside the pre-existing ''Polynesia'' to designate what he viewed as the three main Ethnicity, ethnic and geographical regions forming the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
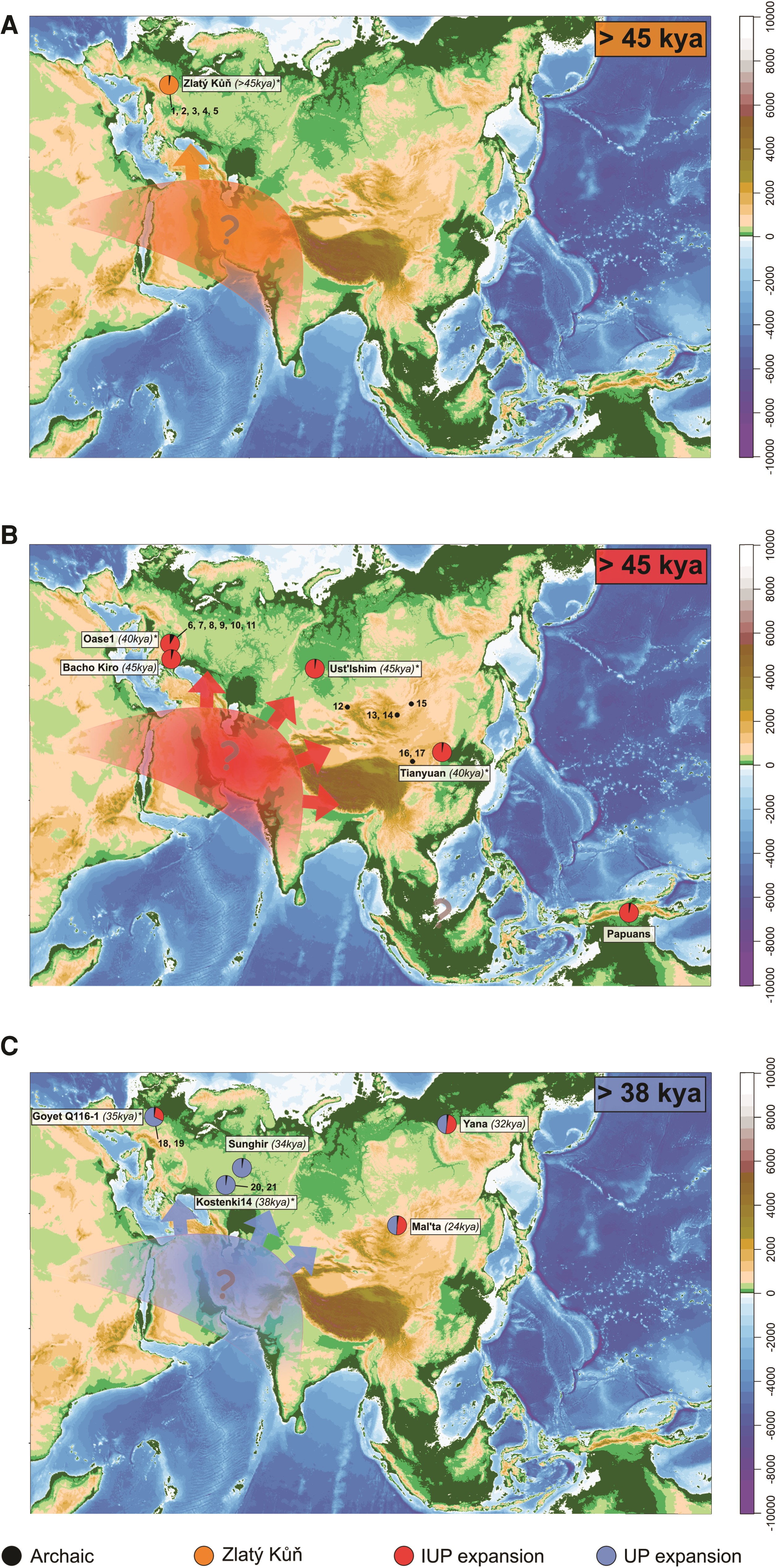
Ancient East Eurasians
The term Ancient East Eurasian, alternatively also known as East Eurasian or Eastern Eurasian, is used in population genomics to describe the genetic ancestry and phylogenetic relationship of diverse populations primarily living in the Asia-Pacific region, belonging to the "Eastern Eurasian clade" of human genetic diversity, and which can be associated with the Initial Upper Paleolithic (IUP) wave, following the Out of Africa migration at least 60,000 years ago. Early dispersals Ancient East Eurasians, modern humans of the Initial Upper Paleolithic (IUP) wave, are suggested to have diverged from Ancient West Eurasians around 48,000 years ago from a population hub likely on the Persian plateau, and expanded across Eurasia through a star-like expansion pattern at least 45,000 years ago. Ancient East Eurasians started to diversify among themselves as early as 45,000 years ago. This diversification may possibly be related to the development of two major IUP-affiliated types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initial Upper Paleolithic
The Initial Upper Paleolithic (also IUP, ) covers the first stage of the Upper Paleolithic, during which modern human populations expanded throughout Eurasia. Technology, art and distribution The Initial Upper Paleolithic period is characterized by a broadly shared material culture and tools associated with an early modern human dispersal >45kya. These IUP tools are characterized by a combination of elements of the Levallois technique (faceted platforms, hard hammer percussion, flat-faced cores). There are broadly two major IUP-affilated types: 'microlithic blades' (or microblades) and 'core & flakes' (or CAF assemblages). While most archaeologists agree on the existence of a shared set of traits, it remains unclear how much those can be related to a single demic diffusion event, or be explained by cultural transmission or convergence. The dispersal of IUP-affilated material culture into Europe, Central Asia and Siberia as well as Northwest China may stem from a distinct migr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Malay
Papuan Malay or Irian Malay is a Malay-based creole, Malay-based creole language spoken in the Papua (Indonesia), Indonesian part of New Guinea. It emerged as a contact language among tribes in Indonesian New Guinea (now Papua (Indonesian province), Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, West Papua (province), West Papua, and Southwest Papua) for trading and daily communication. Nowadays, it has a growing number of native speakers. More recently, the vernacular of Indonesian Indigenous people of New Guinea, Papuans has been influenced by Indonesian language, Standard Indonesian, the national standard language, standard dialect. It is spoken in Indonesian New Guinea alongside 274 other languages and functions as a lingua franca. Papuan Malay belongs to the Malayic sub-branch within the Western Malayo-Polynesian languages, Western-Malayo-Polynesian (WMP) branch of the Austronesian language family. Some linguists have suggested that Papuan Malay has its roots in North M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bislama
Bislama ( ; ; also known by its earlier French name, ) is an English-based creole language. It is the national language of Vanuatu, and one of the three official languages of the country, the other ones being English and French. Bislama is the first language of many of the "Urban ni-Vanuatu" (citizens who live in Port Vila and Luganville) and the second language of much of the rest of the country's residents. The lyrics of " Yumi, Yumi, Yumi", the country's national anthem, are composed in Bislama. More than 95% of Bislama words are of English origin, whilst the remainder comprises a few dozen words from French as well as some specific vocabulary inherited from various languages of Vanuatu—although these are essentially limited to flora and fauna terminology. While the influence of these vernacular languages is low on the vocabulary side, it is very high in the morphosyntax. As such, Bislama can be described simply as a language with an English vocabulary and an Oceanic gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pijin Language
Pijin (Solomon Islands Pidgin) is a language spoken in Solomon Islands. It is closely related to Tok Pisin of Papua New Guinea and Bislama of Vanuatu; the three varieties are sometimes considered to be dialects of a single Melanesian Pidgin language. It is also related to Torres Strait Creole of Torres Strait, though more distantly. In 1999 there were 307,000 second- or third-language speakers with a literacy rate in first language of 60%, a literacy rate in second language of 50%. History 1800–1860 During the early nineteenth century, an English jargon, known as Beach-la-Mar, developed and spread through the Western Pacific as a language used among traders (lingua franca) associated with the whaling industry at the end of the 18th century, the sandalwood trade of the 1830s, and the '' bêche-de-mer'' trade of the 1850s. 1860–1880 Between 1863 and 1906, blackbirding was used for the sugar cane plantation labour trade in Queensland, Samoa, Fiji and New Caledonia. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of its capital city, Port Moresby. It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian language family. Although it is strictly neither a pidgin nor a creole, it possesses some features from both language types. Phonological and grammatical differences make Hiri Motu not mutually intelligible with Motu. The languages are lexically very similar, and retain a common, albeit simplified, Austronesian syntactical basis. It has also been influenced to some degree by Tok Pisin. Even in the areas where it was once well established as a ''lingua franca'', the use of Hiri Motu has been declining in favour of Tok Pisin and English for many years. The language has some statutory recognition. Origins The term '' hiri'' is the name for the traditional trade voyages that created a culture and style of living for the Motu people. Hiri Motu becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tok Pisin
Tok Pisin ( ,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh ; ), often referred to by English speakers as New Guinea Pidgin or simply Pidgin, is an English-based creole languages, English creole language spoken throughout Papua New Guinea. It is an official Languages of Papua New Guinea, language of Papua New Guinea and the most widely used language in the country. In parts of the southern provinces of Western Province (Papua New Guinea), Western, Gulf Province, Gulf, Central Province (Papua New Guinea), Central, Oro Province, Oro, and Milne Bay Province, Milne Bay, the use of Tok Pisin has a shorter history and is less universal, especially among older people. Between five and six million people use Tok Pisin to some degree, though not all speak it fluently. Many now learn it as a first language, in particular the children of parents or grandparents who originally spoke different languages (for example, a mother from Madang and a father from Rabaul). Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they retain a rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |