|
Meerwein's Reagent
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic oxonium compound with the formula . It is often called Meerwein's reagent or Meerwein's salt after its discoverer Hans Meerwein. Also well known and commercially available is the related trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. The compounds are white solids that dissolve in polar organic solvents. They are strong alkylating agents. Aside from the salt, many related derivatives are available. Synthesis and reactivity Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is prepared from boron trifluoride, diethyl ether, and epichlorohydrin: : where the Et stands for ethyl. The trimethyloxonium salt is available from dimethyl ether via an analogous route. These salts do not have long shelf-lives at room temperature. They degrade by hydrolysis: : The propensity of trialkyloxonium salts for alkyl-exchange can be advantageous. For example, trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate, which reacts sluggishly due to its low solubility in most compatible solvents, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Group
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group (abbr. Et) is an alkyl substituent with the formula , derived from ethane (). ''Ethyl'' is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...'s nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated two-carbon moiety in a molecule, while the prefix "''eth-''" is used to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule. Ethylation Ethylation is the formation of a compound by introduction of the ethyl group. The most widely practiced example of this reaction is the ethylation of benzene with ethylene to yield ethylbenzene, a precursor to styrene, which is a precursor to polystyrene. Approximately 24.7 million tons of ethylbenzene were produced in 1999. :: Many ethyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagents For Organic Chemistry
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysis, catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrate (biochemistry), substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexafluorophosphate
Hexafluorophosphate is an fluoroanion, anion with chemical formula of . It is an Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, , and the Hexafluorosilicic acid, hexafluorosilicate dianion, , and fluoroantimonic acid, hexafluoroantimonate . In this anion, phosphorus has a Valence (chemistry), valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophile, nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion. Synthesis Hexafluorophosphate salts can be prepared by the reaction of phosphorus pentachloride and alkali or ammonium halide in a solution of hydrofluoric acid: : Hexafluorophosphoric acid can be prepared by direct reaction of hydrogen fluoride with phosphorus pentafluoride. It is a strong Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted acid that is typically generated ''In situ#Chemistry and chemical engineering, in situ'' immediately before its use. : These reactions require specialized e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroboric Acid
Fluoroboric acid or tetrafluoroboric acid (archaically, fluoboric acid) is an inorganic compound with the simplified chemical formula . Solvent-free tetrafluoroboric acid () has not been reported. The term "fluoroboric acid" usually refers to a range of compounds including hydronium tetrafluoroborate (), which are available as solutions. The ethyl ether solvate is also commercially available, where the fluoroboric acid can be represented by the formula , where ''n'' is 2. It is mainly produced as a precursor to other fluoroborate salts.Gregory K. Friestad, Bruce P. Branchaud "Tetrafluoroboric Acid" E-Eros Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. It is a strong acid. Fluoroboric acid is corrosive and attacks the skin. It is available commercially as a solution in water and other solvents such as diethyl ether. It is a strong acid with a weakly coordinating, non-oxidizing conjugate base. It is structurally similar to perchloric acid, but lacks the hazards associated with ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3, (sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor to other organic compounds and an aerosol propellant that is currently being demonstrated for use in a variety of fuel applications. Dimethyl ether was first synthesised by Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugene Péligot in 1835 by distillation of methanol and sulfuric acid. Production Approximately 50,000 tons were produced in 1985 in Western Europe by dehydration of methanol:Manfred Müller, Ute Hübsch, "Dimethyl Ether" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. : The required methanol is obtained from synthesis gas ( syngas). Other possible improvements call for a dual catalyst system that permits both methanol synthesis and dehydration in the same process unit, with no methanol isolation and purificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin (abbreviated ECH) is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscibility, miscible with most polar molecule, polar Organic compound, organic solvents. It is a chiral molecule generally existing as a racemic mixture of right-handed and left-handed enantiomers. Epichlorohydrin is a highly reactive electrophile, electrophilic compound and is used in the production of glycerol, plastics, Epoxy resin, epoxy glues and resins, epoxy diluents and elastomers. Production Epichlorohydrin is traditionally manufactured from allyl chloride in two steps, beginning with the addition of hypochlorous acid, which affords a mixture of two structural isomer, isomeric alcohols: : In the second step, this mixture is treated with base to give the epoxide: : In this way, more than 800,000 tons (1997) of epichlorohydrin are produced annually. Glycer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxonium Ion
In chemistry, an oxonium ion is any cation containing an oxygen atom that has three chemical bond, bonds and 1+ formal charge. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion (). Alkyloxonium Hydronium is one of a series of oxonium ions with the formula R''n''H3−''n''O+. Oxygen is usually pyramidal with an sp3 orbital hybridisation, hybridization. Those with ''n'' = 1 are called primary oxonium ions, an example being protonated alcohol (e.g. methanol). In acidic media, the oxonium functional group produced by protonating an alcohol can be a leaving group in the elimination reaction, E2 elimination reaction. The product is an alkene. Extreme acidity, heat, and dehydrating conditions are usually required. Other hydrocarbon oxonium ions are formed by protonation or alkylation of alcohol (chemistry), alcohols or ethers (R−C−−R1R2). Secondary oxonium ions have the formula R2OH+, an example being protonated ethers. Tertiary oxonium ions have the formula R3O+, an example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colourless, highly Volatility (chemistry), volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It belongs to the ether class of organic compounds. It is a common solvent and was formerly used as a general anesthetic. Production Most diethyl ether is produced as a byproduct of the vapor-phase Hydration reaction, hydration of ethylene to make ethanol. This process uses solid-supported phosphoric acid Catalysis, catalysts and can be adjusted to make more ether if the need arises: Vapor-phase Dehydration reaction, dehydration of ethanol over some Aluminium oxide, alumina catalysts can give diethyl ether yields of up to 95%. : Diethyl ether can be prepared both in laboratories and on an industrial scale by the acid ether synthesis. Uses The dominant use of diethyl ether is as a solvent. One particular application is in the production of cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
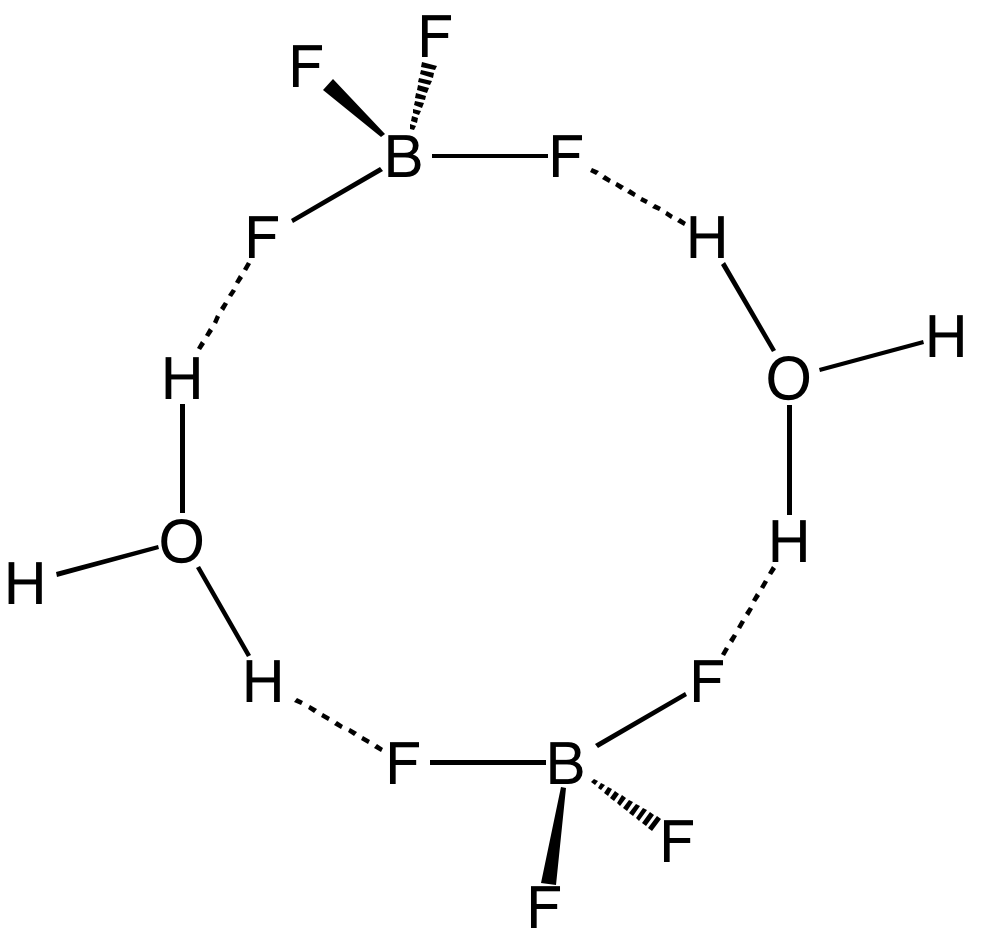
Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula . This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds. Structure and bonding The geometry of a molecule of is Trigonal planar molecular geometry, trigonal planar. Its D3h symmetry group, symmetry conforms with the prediction of VSEPR theory. The molecule has no dipole moment by virtue of its high symmetry. The molecule is isoelectronic with the carbonate anion, . is commonly referred to as "electron deficiency, electron deficient," a description that is reinforced by its exothermic reactivity toward Lewis bases. In the boron trihalides, , the length of the B–X bonds (1.30 Å) is shorter than would be expected for single bonds, and this shortness may indicate stronger B–X pi bond, π-bonding in the fluoride. A facile explanation invokes the symmetry-allowed overlap of a p orbital on the boron atom with the in-phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |