|
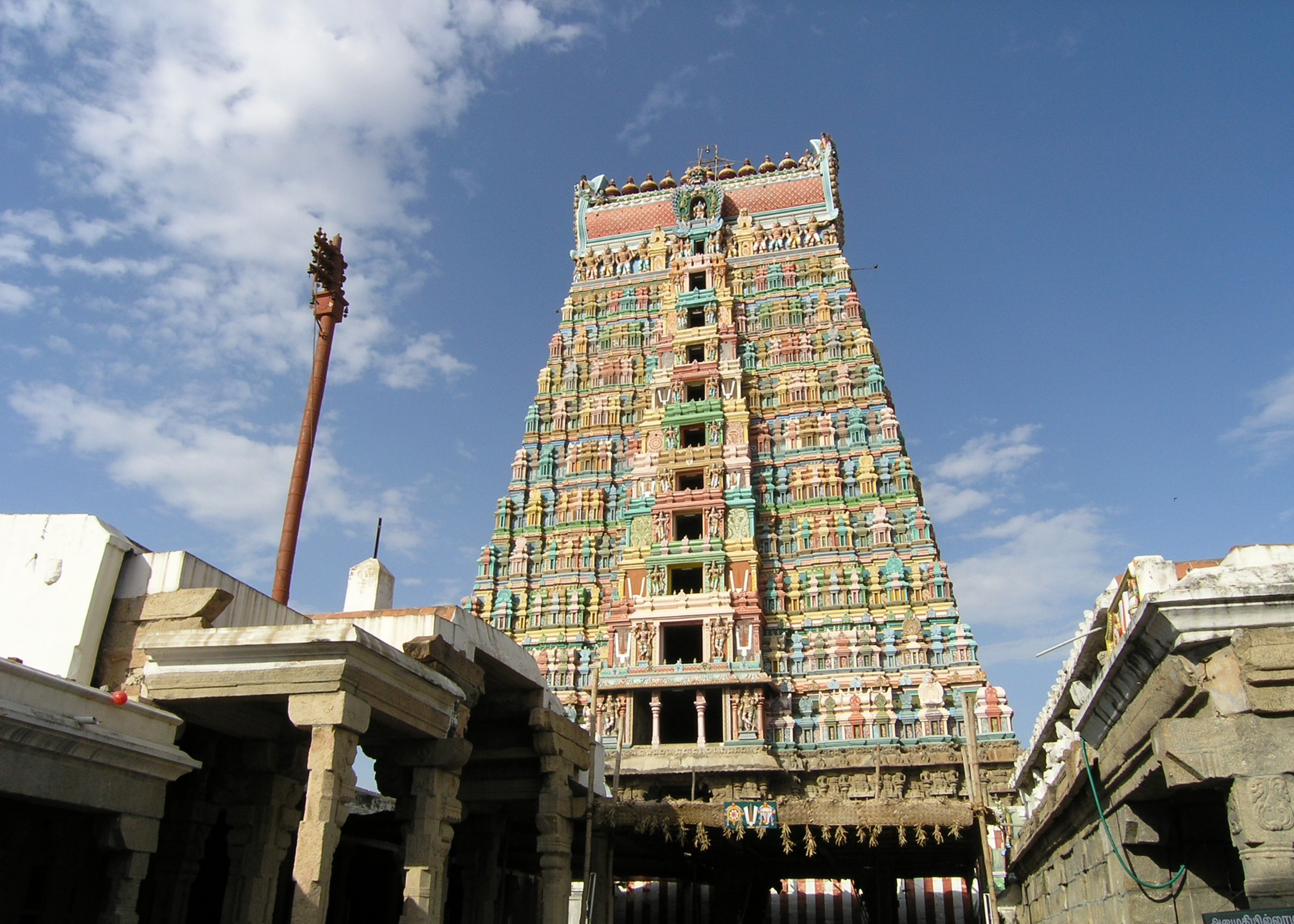
Meenakshi Temple
Arulmigu Meenakshi Sundareswarar Temple, also known as Arulmigu Meenakshi Amman Thirukkovil, is a historic Hindu temple located on the southern bank of the Vaigai River in the temple city of Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is dedicated to the goddess Meenakshi, a form of Parvati, her consort ''Sundareśvarar'', a form of Shiva and her brother ''Aḻagar'', a form of Vishnu. The temple is theologically significant as it represents a confluence of the Shaivism, Shaktism and Vaishnavism denominations of Hinduism. The temple is at the centre of the ancient temple city of Madurai mentioned in the Tamil Sangam literature, with the goddess temple mentioned in 6th-century CE texts. This temple is one of the Paadal Petra Sthalams, which are 275 temples of Shiva that are revered in the verses of Tamil Saiva Nayanars of the 6th-9th century CE. The west tower (''gopuram'') of the temple is the model on which the Tamil Nadu State Emblem is based. Madurai Meenakshi Sundareswarar temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandya Dynasty
The Pandya dynasty (), also referred to as the Pandyas of Madurai, was an ancient Tamil dynasty of South India, and among the four great kingdoms of Tamilakam, the other three being the Pallavas, the Cholas and the Cheras. Existing since at least the 4th to 3rd centuries BCE, the dynasty passed through two periods of imperial dominance, the 6th to 10th centuries CE, and under the 'Later Pandyas' (13th to 14th centuries CE). Under Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan I and Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I, the Pandyas ruled extensive territories including regions of present-day South India and northern Sri Lanka through vassal states subject to Madurai. The Pandya dynasty is the longest ruling dynasty in the world. The rulers of the three Tamil dynasties were referred to as the " three crowned rulers (the mu-ventar) of the Tamil Region" in the southern part of India. The origin and the timeline of the Pandya dynasty are difficult to establish. The early Pandya chieftains ruled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meenakshi Tirukalyanam
The Meenakshi Tirukalyanam festival, also known as Chithirai Tiruviḻa or Meenakshi Kalyanam, is an annual Tamil Hindu celebration in the city of Madurai during the month of April. The festival, celebrated during the Tamil month of Chithirai, is associated with the Meenakshi Temple, dedicated to the goddess Meenakshi, a form of Parvati and her consort Sundareshvara'','' a form of Shiva. The festival lasts for one month. The first 15 days mark the celebrations of the coronation of Meenakshi as the divine ruler of Madurai and her marriage to Sundareshvara. The next 15 days mark the celebrations of the journey of Kallaḻagar or Aḻagar (a form of the god Vishnu) from his temple to Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai. Legend As per the legend, Meenakshi was the daughter of the Pandya king Malayadhvaja Pandyan and queen Kanchana Malai. The royal couple did not have a child for a long time, so Malayadhvaja Pandyan performed special pujas and offered his prayers seek a son. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopuram
A ''gopuram'' or ''gopura'' ( Tamil: கோபுரம், Telugu: గోపురం, Kannada Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...: ಗೋಪುರ, Malayalam language, Malayalam: ഗോപുരം) is a monumental entrance tower, usually ornate, at the Entrance Hall, entrance of a Hindu temple, in the Dravidian architecture, South Indian architecture of the southern Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, and Telangana, and Sri Lanka. In other areas of India they are much more modest, while in Southern Indian temples they are very often by far the highest part of the temple. Ancient and early medieval temples feature smaller ''gopuram'', while in later temples they are a prominent feature of Hindu temple architecture, Hindu Tamil archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil language, Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam''), historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil language, Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ''), connotes the early classical Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition links it to Legendary Tamil Sangams, legendary literary gatherings around Madurai in the ancient Pandya dynasty, Pandya kingdom. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the historical Sangam literature era, also known as the Sangam period, spanned from 100 BCE to 250 CE, on the basis of linguistic, epigraphic, archaeological, numismatic and historical data; though some scholars give a broader range of 300 BCE to 300 CE. The Eighteen Greater Texts (Patiṉeṇmēlkaṇakku), along with the Tamil grammar work Tolkāppiyam, Tolkappiyam, are collectively considered as Sangam literature. These tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik Kafur
Malik Kafur (died February 1316), also known as Taj al-Din Izz al-Dawla, was a prominent general of the Delhi Sultanate ruler Alauddin Khalji. He was captured by Alauddin's general Nusrat Khan Jalesari, Nusrat Khan during the Alauddin Khalji's conquest of Gujarat, 1299 invasion of Gujarat, and rose to prominence in the 1300s. As a commander of Alauddin's forces, Kafur defeated the Mongol invasion of India, 1306, Mongol invaders in 1306. Subsequently, he led a series of expeditions in the southern part of India, against the Alauddin Khalji's conquest of Devagiri, Yadavas (1308), the Siege of Warangal, 1310, Kakatiyas (1310), the Siege of Dwarasamudra, Hoysalas (1311), and the Malik Kafur's invasion of the Pandya kingdom, Pandyas (1311). From these campaigns, he brought back many treasures, and many elephants and horses for the Delhi Sultanate. From 1313 to 1315, Kafur served as Alauddin's governor of Devagiri. When Alauddin fell seriously ill in 1315, Kafur was recalled to Delhi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
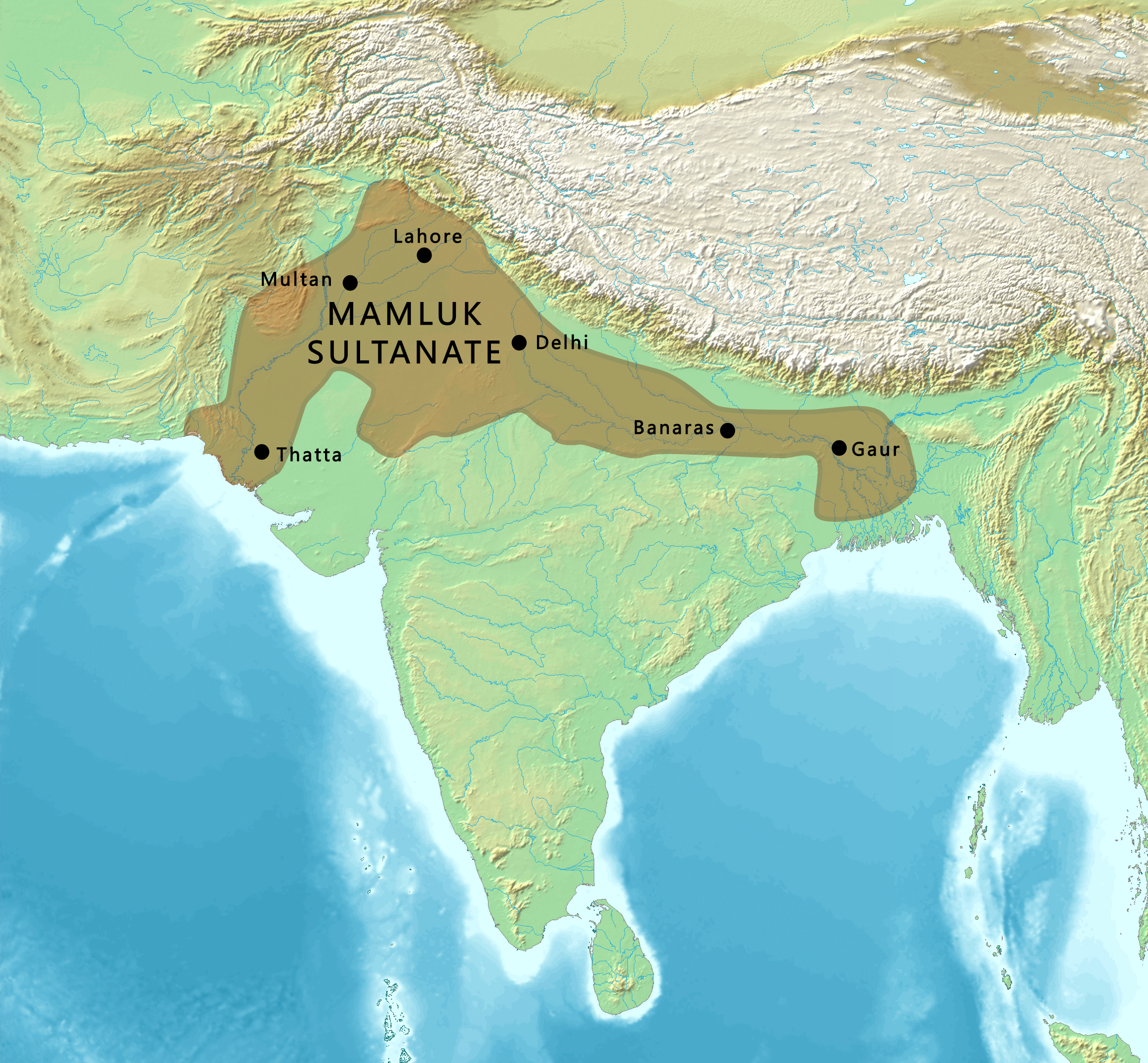
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumala Nayaka
Tirumala Nayaka (reigned 1623–16 February 1659) was the ruler of Madurai Nayak Dynasty in the 17th century. He ruled Madurai between 1623 and 1659. His contributions are found in the many splendid buildings and temples of Madurai. He belongs to Balija caste. His kingdom was under constant threat from the armies of Bijapur Sultanate and the other neighbouring Muslim kingdoms, which he managed to repulse successfully. His territories comprised much of the old Pandya territories which included Coimbatore, Tirunelveli, Madurai districts, Aragalur in southern Tamil Nadu and some territories of the Travancore kingdom. Tirumala Nayaka was a great patron of art and architecture and the Dravidian architecture evolved into the ''Madurai style''. He rebuilt and renovated a number of old temples of the Pandya dynasty, Pandya period. His palace, known as the Thirumalai Nayak Palace, Tirumala Nayaka Palace, is a notable architectural masterpiece. Wars with Mysore In the early years of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kali
Kali (; , ), also called Kalika, is a major goddess in Hinduism, primarily associated with time, death and destruction. Kali is also connected with transcendental knowledge and is the first of the ten Mahavidyas, a group of goddesses who provide liberating knowledge. Of the numerous Hindu goddesses, Kali is held as the most famous. She is the preeminent deity in the Hindu tantric and the Kalikula worship traditions, and is a central figure in the goddess-centric sects of Hinduism as well as in Shaivism. Kali is chiefly worshipped as the Divine Mother, Mother of the Universe, and Divine feminine energy. The origins of Kali can be traced to the pre-Vedic and Vedic era goddess worship traditions in the Indian subcontinent. Etymologically, the term ''Kali'' refers to one who governs time or is black. The first major appearance of Kali in the Sanskrit literature was in the sixth-century CE text '' Devi Mahatmya''. Kali appears in many stories, with the most popular one bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
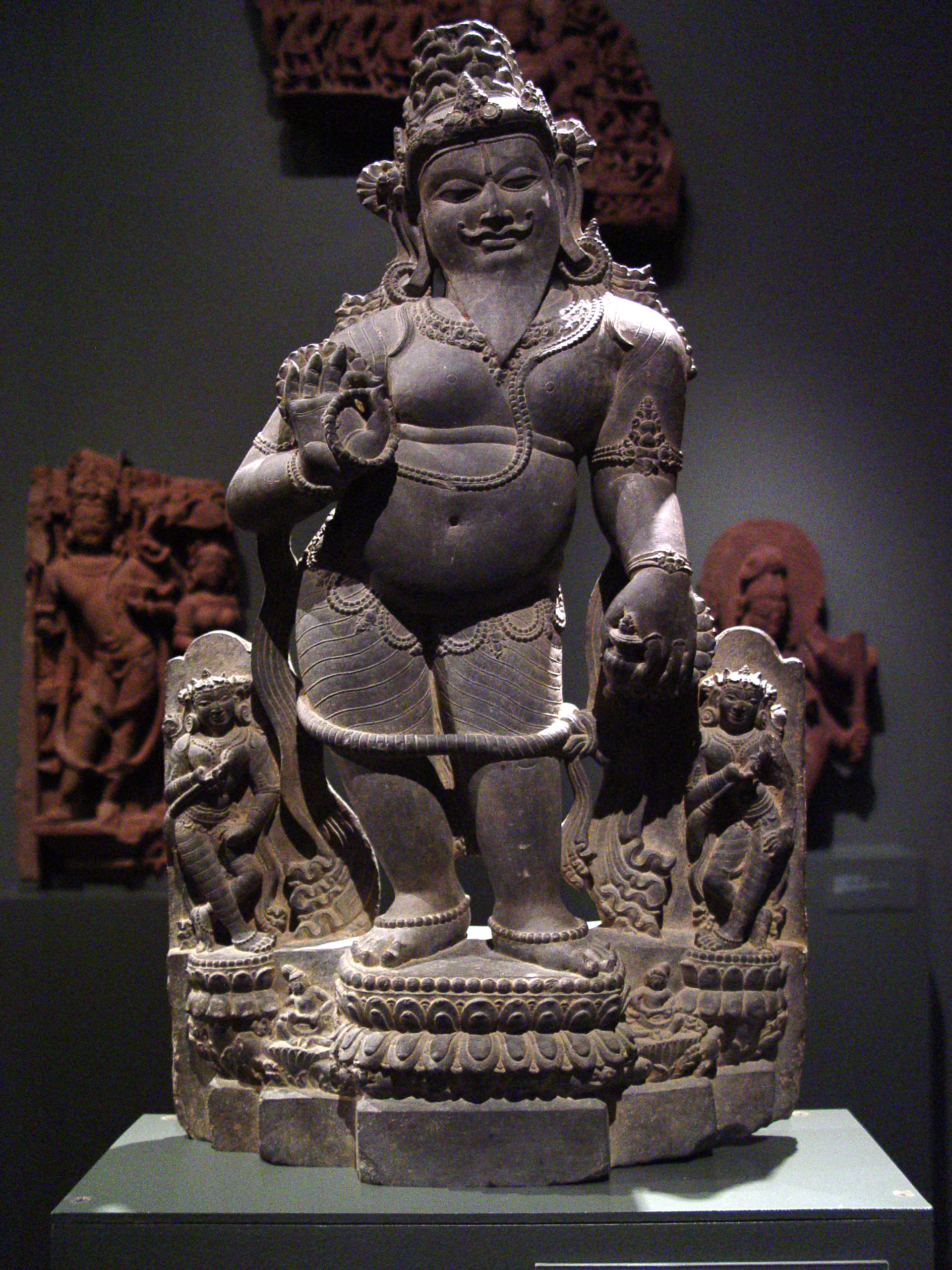
Ayyanar
Aiyanar (, ) is a Village deities of South India, Tamil folk deity venerated in South India and Sri Lanka. His worship is prevalent amongst rural Tamils, Tamil people. Some studies suggest that Ayyanar may have also been worshipped in Southeast Asian countries in the past. He is primarily worshipped as one of the village deities of Tamil Nadu. Temples to Aiyanar in the countryside are usually flanked by gigantic colourful statues of him and his companions riding horses or elephants. Etymology The Tamil language, Tamil word ''Ayyanār'' is derived from the root word ''Ayya'', a honorific used in a Tamil language to designate respected one.Indrapala, K., ''The evolution of an ethnic identity: The Tamils in Sri Lanka C. 300 BCE to C. 1200 CE'', p.# Some people propose that ''Aryan'' could be the Sanskrit version of Tamil word ''Aiyyan'' which means the same. There is a well known Aryankavu Sastha Temple, temple dedicated to Sastha situated in a village of Kerala, called "Aryanka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
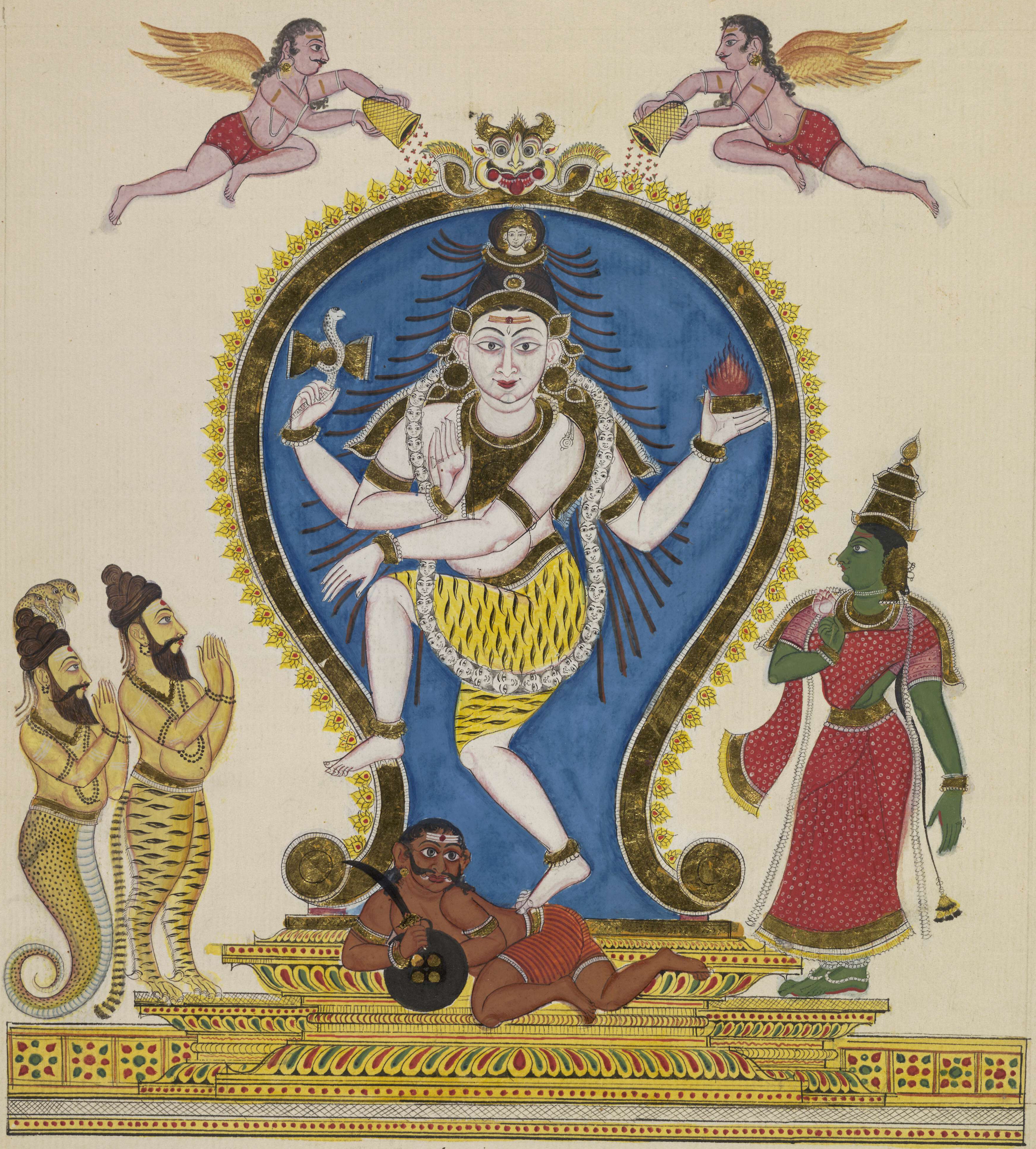
Nataraja
Nataraja (/ n̪əʈəɾɑd͡ʒᵊ/ ,, ; , ''Naṭarājar'' Telugu: నటరాజు,''Naṭarāju''), also known as Adalvallan (), is a depiction of Shiva, one of the main deities in Hinduism, as the divine cosmic dancer. His dance is called the tandava.''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2015) The pose and artwork are described in many Hindu texts such as the ''Tevaram'' and '' Thiruvasagam'' in Tamil and the ''Amshumadagama'' and ''Uttarakamika agama'' in Sanskrit and the Grantha texts. The dance ''murti'' is featured in all major Hindu temples of Shaivism, and is a well-known sculptural symbol in India and popularly used as a symbol of Indian culture, as one of the finest illustrations of Hindu art. This form is also referred to as Kuththan (), Sabesan (), and Ambalavanan () in various Tamil texts. The sculpture is symbolic of Shiva as the lord of dance and dramatic arts, with its style and proportions made according to Hindu texts on arts. Tamil devotional texts such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopuram
A ''gopuram'' or ''gopura'' ( Tamil: கோபுரம், Telugu: గోపురం, Kannada Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...: ಗೋಪುರ, Malayalam language, Malayalam: ഗോപുരം) is a monumental entrance tower, usually ornate, at the Entrance Hall, entrance of a Hindu temple, in the Dravidian architecture, South Indian architecture of the southern Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, and Telangana, and Sri Lanka. In other areas of India they are much more modest, while in Southern Indian temples they are very often by far the highest part of the temple. Ancient and early medieval temples feature smaller ''gopuram'', while in later temples they are a prominent feature of Hindu temple architecture, Hindu Tamil archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |