|
Max Bentele
Max Bentele (January 15, 1909 – May 19, 2006) was a German-born pioneer in the field of jet aircraft turbines and mechanical engineering. His contributions to the development of the Wankel engine earned him the title, "Father of the Wankel Engine in the United States". Bentele in Germany Bentele had been fascinated with engineering from an early age and graduated from the Technical University of Stuttgart in the fall of 1928 with a degree in mechanical and electrical engineering. Up until World War II he was working on turbine blade design for the Heinkel-Hirth, Germany's new jet engine. Bentele excelled at this task, and after the war he managed one of Heinkel-Hirth's few remaining machine shops, which had survived virtually unscathed. He excelled at this job and was approached to undertake the design and manufacture of much needed spare parts for Allied Jeeps. Bentele in the United States Bentele left his successful business at the request of the Americans and Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a " presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Orange GmbH
Woodward L'Orange GmbH is a German engineering manufacturing company headquartered in Stuttgart. It is one of the leading manufacturers of injection systems for large diesel engines worldwide. It developed and produced the first common-rail system for large diesel engines. Woodward L'Orange is a supplier to engine builders and has been part of Woodward since 2018. Previously the L'Orange GmbH belonged to the Rolls-Royce Power Systems AG. History On 9 September 1933, Rudolf L'Orange, son of Prosper L'Orange, together with his brother Harro, founded the ''Gebrüder L'Orange Motorzubehör GmbH'' (L'Orange Brothers Engine Accessories Company) in Stuttgart. Initially, they produced stamps, cylinders, needles and needle guides for injection pumps for aircraft and marine engines. His father had sold his inventions and manufacturing rights to the Robert Bosch AG, and this led to the foundation of the company. In Hamburg, L'Orange founded the ''Norddeutsche L'Orange GmbH Hamburg'' subsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wankel Cutaway
Wankel may refer to: * Wankel engine, a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric rotary design instead of reciprocating pistons * Wankel AG, a German company that produces Wankel engines for ultralight aircraft and racing cars People * Charlotte Wankel (1888–1969), Norwegian painter * Felix Wankel (1902–1988), German engineer; inventor of the Wankel engine * Georg Reinholdt Wankel (1843–1907), Norwegian politician * Heinrich Wankel (1821–1897), Czech palaeontologist See also * Wenkel Wenkel is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Max Wenkel (1864–1943), German automobile pioneer and inventor * Ortrun Wenkel (born 1942), German operatic contralto See also *Wankel *Wenzel Wenzel is a male given name (lo ..., a surname {{surname, Wankel German-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochoid
In geometry, a trochoid () is a roulette curve formed by a circle rolling along a line. It is the curve traced out by a point fixed to a circle (where the point may be on, inside, or outside the circle) as it rolls along a straight line. If the point is on the circle, the trochoid is called ''common'' (also known as a cycloid); if the point is inside the circle, the trochoid is ''curtate''; and if the point is outside the circle, the trochoid is ''prolate''. The word "trochoid" was coined by Gilles de Roberval. Basic description As a circle of radius rolls without slipping along a line , the center moves parallel to , and every other point in the rotating plane rigidly attached to the circle traces the curve called the trochoid. Let . Parametric equations of the trochoid for which is the -axis are :\begin & x = a\theta - b \sin \theta \\ & y = a - b \cos \theta \end where is the variable angle through which the circle rolls. Curtate, common, prolate If lies inside the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Wankel
Felix Heinrich Wankel (; 13 August 1902 – 9 October 1988) was a German mechanical engineer and inventor after whom the Wankel engine was named. Early life Wankel was born in 1902 in Lahr in what was then the Grand Duchy of Baden in the Upper Rhine Plain of present-day southwestern Germany. He was the only son of Gerty Wankel (née Heidlauff) and Rudolf Wankel, a forest assessor. His father died in World War I. Thereafter, the family moved to Heidelberg. He went to high schools in Donaueschingen, Heidelberg, and Weinheim, and left school without Abitur in 1921. He learned the trade of purchaser at the Carl Winter Press in Heidelberg and worked for the publishing house until June 1926. He and some friends had already run an unofficial afterwork machine shop in a backyard shed in Heidelberg since 1924. Wankel was now determined to receive unemployment benefits and to focus on the machine shop. One of his friends, who had graduated from university, gave his name and transforme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
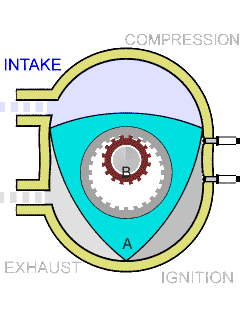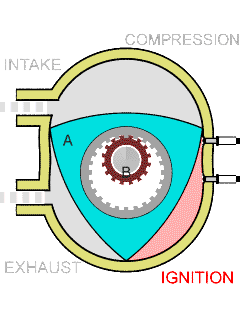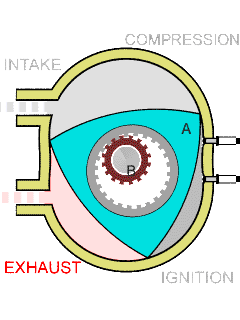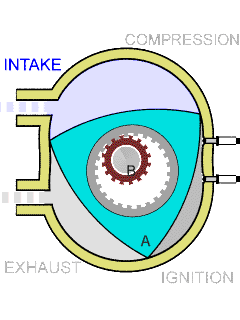
Wankel Rotary Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor rotates inside an oval-like epitrochoidal housing, around a central output shaft. The rotor spins in a hula-hoop fashion around the central output shaft, spinning the shaft via toothed gearing. Due to its inherent poor thermodynamics, the Wankel engine has a significantly worse thermal efficiency and worse exhaust gas behaviour when compared against the Otto engine or the Diesel engine, which is why the Wankel engine has seen limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, its advantages of compact design, smoothness, lower weight and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSU Motorenwerke AG
NSU Motorenwerke AG, or NSU, was a German manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles and pedal cycles, founded in 1873. Acquired by Volkswagen Group in 1969, VW merged NSU with Auto Union, creating Audi NSU Auto Union AG, ultimately Audi. The name NSU originated as an abbreviation of "Neckarsulm", the city where NSU was located. History Origin NSU originated as the "Mechanische Werkstätte zur Herstellung von Strickmaschinen", a knitting machine manufacturer established in 1873 by Christian Schmidt, a technically astute entrepreneur, in the town of Riedlingen on the Danube. The business relocated in 1880 to Neckarsulm. There followed a period of rapid growth and in 1886, the company began to produce bicycles, the first of them a 'high wheeler' or 'Penny-farthing' branded as the "Germania". By 1892, bicycle manufacturing had completely replaced knitting machine production. At about this time, the name NSU appeared as a brand name. The first NSU motorcycle appeared in 1901, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Studebaker-Packard Corporation
The Studebaker-Packard Corporation was the entity created in 1954 by the purchase of the Studebaker Corporation of South Bend, Indiana, by the Packard Motor Car Company of Detroit, Michigan. While Studebaker was the larger of the two companies, Packard's balance sheet and executive team were stronger than that of the South Bend company. In the spring of 1962, Studebaker-Packard reverted its name to "Studebaker Corporation". The following year, the South Bend plant was closed, while its Canadian plant in Hamilton, Ontario, continued to produce Studebaker cars until 1966. The South Bend plant would later be acquired by the Avanti Motor Company. Studebaker Corp. merged with Worthington Corporation one year later. Studebaker-Worthington was a diversified American manufacturer operating the various business units of Studebaker, Wagner Electric and Worthington Corporation. The company was in turn acquired by McGraw-Edison in 1979. Purposes of merger It was hoped that Packard wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine (that drives the compressor). The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s. Turbojets have poor efficiency at low vehicle speeds, which limits their usefulness in vehicles other than aircraft. Turbojet engines have been used in isolated cases to power vehicles other than aircraft, typically for attempts on land speed records. Where vehicles are "turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Hurley
Roy Leonard Hurley (August 12, 1922 – October 14, 1993) was an American professional basketball player. He spent two seasons in the National Basketball League (NBL) and one season in the Basketball Association of America (BAA). He played for the Indianapolis Kautskys (NBL, 1945–46), the Toronto Huskies (BAA, 1946–47), the Tri-Cities Blackhawks (NBL, 1947–48), and the Syracuse Nationals The Philadelphia 76ers are an American basketball team currently playing in the Atlantic Division of the Eastern Conference in the National Basketball Association (NBA). The 76ers are third in NBA history in wins and playoff appearances. 1946� ... (NBL, 1947–48). Hurley died on October 14, 1993. BAA career statistics Regular season References External links 1922 births 1993 deaths American expatriate basketball people in Canada American men's basketball players Forwards (basketball) Guards (basketball) Indianapolis Kautskys players Sportspeople from Arcadia, Calif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Curtiss
Glenn Hammond Curtiss (May 21, 1878 – July 23, 1930) was an American aviation and motorcycling pioneer, and a founder of the U.S. aircraft industry. He began his career as a bicycle racer and builder before moving on to motorcycles. As early as 1904, he began to manufacture engines for airships. In 1908, Curtiss joined the Aerial Experiment Association, a pioneering research group, founded by Alexander Graham Bell at Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, to build flying machines. Curtiss won a race at the world's first international air meet in France and made the first long-distance flight in the U.S. His contributions in designing and building aircraft led to the formation of the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company, which later merged into the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. His company built aircraft for the U.S. Army and Navy, and, during the years leading up to World War I, his experiments with seaplanes led to advances in naval aviation. Curtiss civil and military aircraft were so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |