|
MarkLogic Server
MarkLogic Server is a document-oriented database developed by MarkLogic. It is a NoSQL multi-model database that evolved from an XML database to natively store JSON documents and RDF triples, the data model for semantics. MarkLogic is designed to be a data hub for operational and analytical data. History MarkLogic Server was built to address shortcomings with existing search and data products. The product first focused on using XML as the document markup standard and XQuery as the query standard for accessing collections of documents up to hundreds of terabytes in size. Currently the MarkLogic platform is widely used in publishing, government, finance and other sectors. MarkLogic's customers are mostly Global 2000 companies. Technology MarkLogic uses documents without upfront schemas to maintain a flexible data model. In addition to having a flexible data model, MarkLogic uses a distributed, scale-out architecture that can handle hundreds of billions of documents and hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
MarkLogic
MarkLogic is an American software business that develops and provides an enterprise NoSQL database, which is also named ''MarkLogic''. They have offices in the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia. In February 2023, MarkLogic was acquired by Progress Software for $355 million. Overview Founded in 2001 by Christopher Lindblad and Paul Pedersen, MarkLogic Corporation is a privately held company with over 500 employees that was acquired by Vector Capital in October 2020. History MarkLogic was originally named Cerisent when it was founded in 2001 by Christopher Lindblad, who was the Chief Architect of the Ultraseek search engine at Infoseek, as well as Paul Pedersen, a professor of computer science at Cornell University and UCLA, and Frank R. Caufield, Founder of Darwin Ventures, to address shortcomings with existing search and data products. The product first focused on using XML document markup standard and XQuery as the query standard for accessing collections of documen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Database Index
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time said table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records. An index is a copy of selected columns of data, from a table, that is designed to enable very efficient search. An index normally includes a "key" or direct link to the original row of data from which it was copied, to allow the complete row to be retrieved efficiently. Some databases extend the power of indexing by letting developers create indexes on column values that have been transformed by functions or expressions. For example, an index could be created on upper(last_name), which would o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Graph Database
A graph database (GDB) is a database that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A key concept of the system is the graph (or edge or relationship). The graph relates the data items in the store to a collection of nodes and edges, the edges representing the relationships between the nodes. The relationships allow data in the store to be linked together directly and, in many cases, retrieved with one operation. Graph databases hold the relationships between data as a priority. Querying relationships is fast because they are perpetually stored in the database. Relationships can be intuitively visualized using graph databases, making them useful for heavily inter-connected data. Graph databases are commonly referred to as a NoSQL database. Graph databases are similar to 1970s network model databases in that both represent general graphs, but network-model databases operate at a lower level of abstraction and lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure, or just Azure ( /ˈæʒər, ˈeɪʒər/ ''AZH-ər, AY-zhər'', UK also /ˈæzjʊər, ˈeɪzjʊər/ ''AZ-ure, AY-zure''), is the cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. It has management, access and development of applications and services to individuals, companies, and governments through its global infrastructure. It also provides capabilities that are usually not included within other cloud platforms, including software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Microsoft Azure supports many programming languages, tools, and frameworks, including Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems. Azure was first introduced at the Professional Developers Conference (PDC) in October 2008 under the codename "Project Red Dog". It was officially launched as Windows Azure in February 2010 and later renamed to Microsoft Azure on March 25, 2014. Services Microsoft Azure uses large-scale virtualizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Fraud Prevention
In law, fraud is intentional deception to deprive a victim of a legal right or to gain from a victim unlawfully or unfairly. Fraud can violate civil law (e.g., a fraud victim may sue the fraud perpetrator to avoid the fraud or recover monetary compensation) or criminal law (e.g., a fraud perpetrator may be prosecuted and imprisoned by governmental authorities), or it may cause no loss of money, property, or legal right but still be an element of another civil or criminal wrong. The purpose of fraud may be monetary gain or other benefits, such as obtaining a passport, travel document, or driver's licence. In cases of mortgage fraud, the perpetrator may attempt to qualify for a mortgage by way of false statements. Terminology Fraud can be defined as either a civil wrong or a criminal act. For civil fraud, a government agency or person or entity harmed by fraud may bring litigation to stop the fraud, seek monetary damages, or both. For criminal fraud, a person may be prose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
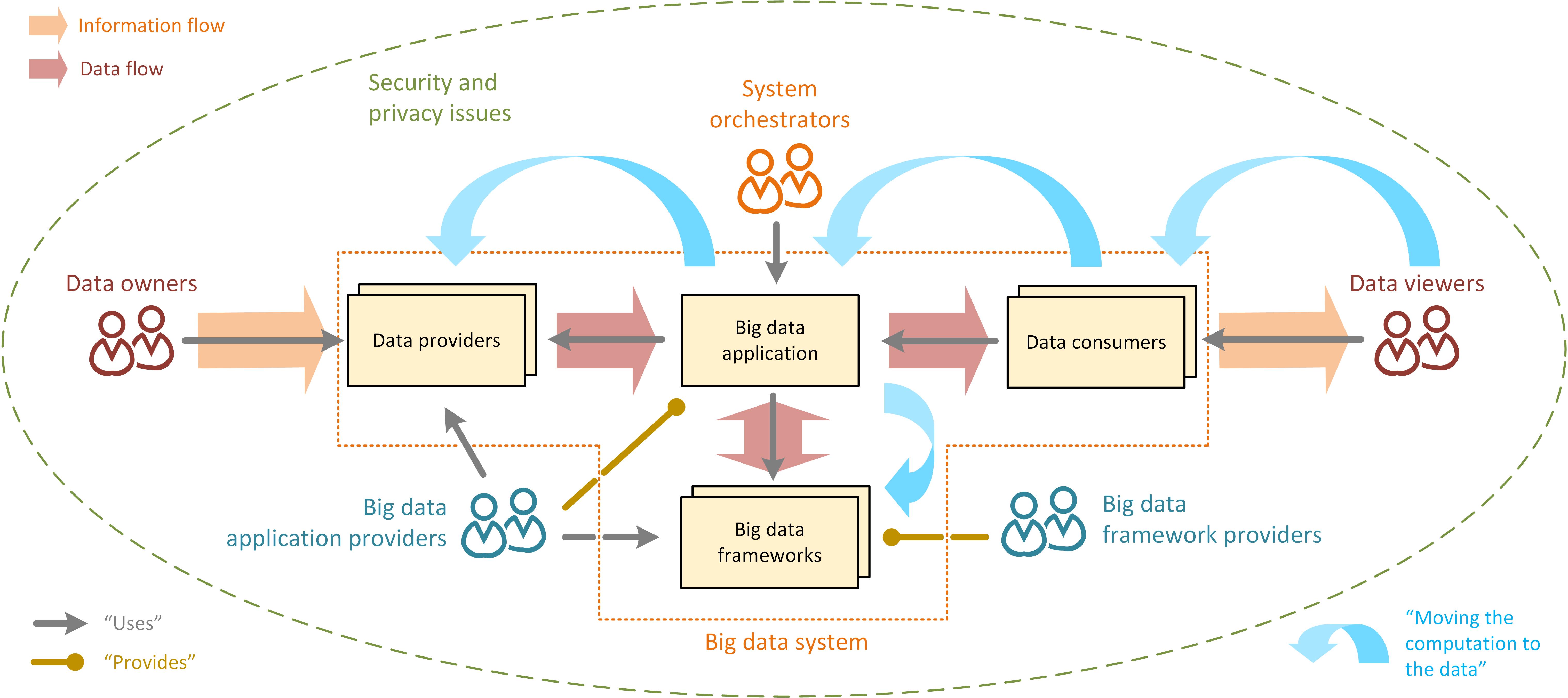 |
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets. As banks play an important role in financial stability and the economy of a country, most jurisdictions exercise a high degree of Bank regulation, regulation over banks. Most countries have institutionalized a system known as fractional-reserve banking, under which banks hold liquid assets equal to only a portion of their current liabilities. In addition to other regulations intended to ensure accounting liquidity, liquidity, banks are generally subject to minimum capital requirements based on an international set of capital standards, the Basel Accords. Banking in its modern sense evolved in the fourteenth century in the prosperous cities of Renaissance Italy but, in many ways, functioned as a continuation of ideas and concepts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Database Security
Database security concerns the use of a broad range of information security controls to protect databases against compromises of their confidentiality, integrity and availability. It involves various types or categories of controls, such as technical, procedural or administrative, and physical. Security risks to database systems include, for example: * Unauthorized or unintended activity or misuse by authorized database users, database administrators, or network/systems managers, or by unauthorized users or hackers (e.g. inappropriate access to sensitive data, metadata or functions within databases, or inappropriate changes to the database programs, structures or security configurations); * Malware infections causing incidents such as unauthorized access, leakage or disclosure of personal or proprietary data, deletion of or damage to the data or programs, interruption or denial of authorized access to the database, attacks on other systems and the unanticipated failure of databa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Sharding
A database shard, or simply a shard, is a horizontal partition of data in a database or search engine. Each shard may be held on a separate database server instance, to spread load. Some data in a database remains present in all shards, but some appears only in a single shard. Each shard acts as the single source for this subset of data. Database architecture Horizontal partitioning is a database design principle whereby '' rows'' of a database table are held separately, rather than being split into columns (which is what normalization and vertical partitioning do, to differing extents). Each partition forms part of a shard, which may in turn be located on a separate database server or physical location. There are numerous advantages to the horizontal partitioning of data. Since tables are divided and distributed into multiple servers, the total number of rows in each table in each database is reduced. This reduces index size, which generally improves search performance. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system. In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that a company can increase sales given increased resources. For example, a package delivery system is scalable because more packages can be delivered by adding more delivery vehicles. However, if all packages had to first pass through a single warehouse for sorting, the system would not be as scalable, because one warehouse can handle only a limited number of packages. In computing, scalability is a characteristic of computers, networks, algorithms, networking protocols, programs and applications. An example is a search engine, which must support increasing numbers of users, and the number of topics it indexes. Webscale is a computer architectural approach that brings the capabilities of large-scale cloud computing companies into enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
ACID
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Semantic Triple
A semantic triple, or RDF triple or simply triple, is the atomic data entity in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. As its name indicates, a triple is a sequence of three entities that codifies a statement about semantic data in the form of subject–predicate–object expressions (e.g., "Bob is 35", or "Bob knows John"). Subject, predicate and object This format enables knowledge to be represented in a machine-readable way. Particularly, every part of an RDF triple is individually addressable via unique URIs—for example, the statement "Bob knows John" might be represented in RDF as: http://example.name#BobSmith12 http://xmlns.com/foaf/spec/#term_knows http://example.name#JohnDoe34. Given this precise representation, semantic data can be unambiguously queried and reasoned about. The components of a triple, such as the statement "The sky has the color blue", consist of a subject ("the sky"), a predicate ("has the color"), and an object ("blue"). This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |