Graph database on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A graph database (GDB) is a
 A labeled-property graph model is represented by a set of nodes, relationships, properties, and labels. Both nodes of data and their relationships are named and can store properties represented by key–value pairs. Nodes can be labelled to be grouped. The edges representing the relationships have two qualities: they always have a start node and an end node, and are directed; making the graph a directed graph. Relationships can also have properties. This is useful in providing additional metadata and semantics to relationships of the nodes. Direct storage of relationships allows a constant-time traversal.
A labeled-property graph model is represented by a set of nodes, relationships, properties, and labels. Both nodes of data and their relationships are named and can store properties represented by key–value pairs. Nodes can be labelled to be grouped. The edges representing the relationships have two qualities: they always have a start node and an end node, and are directed; making the graph a directed graph. Relationships can also have properties. This is useful in providing additional metadata and semantics to relationships of the nodes. Direct storage of relationships allows a constant-time traversal.
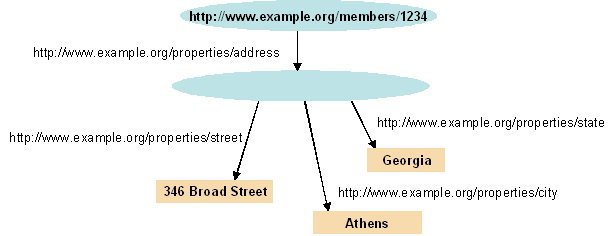 In an RDF graph model, each addition of information is represented with a separate node. For example, imagine a scenario where a user has to add a name property for a person represented as a distinct node in the graph. In a labeled-property graph model, this would be done with an addition of a name property into the node of the person. However, in an RDF, the user has to add a separate node called
In an RDF graph model, each addition of information is represented with a separate node. For example, imagine a scenario where a user has to add a name property for a person represented as a distinct node in the graph. In a labeled-property graph model, this would be done with an addition of a name property into the node of the person. However, in an RDF, the user has to add a separate node called
SELECT p2.person_name
FROM people p1
JOIN friend ON (p1.person_id = friend.person_id)
JOIN people p2 ON (p2.person_id = friend.friend_id)
WHERE p1.person_name = 'Jack';
The same query may be translated into --
* Cypher, a graph database query language
MATCH (p1:person )- FRIEND_WITH(p2:person)
RETURN p2.name
* SPARQL, an RDF graph database query language standardized by
PREFIX foaf:
** Short form
PREFIX foaf:
* SPASQL, a hybrid database query language, that extends SQL with SPARQL
SELECT people.name
FROM (
SPARQL PREFIX foaf:
The above examples are a simple illustration of a basic relationship query. They condense the idea of relational models' query complexity that increases with the total amount of data. In comparison, a graph database query is easily able to sort through the relationship graph to present the results.
There are also results that indicate simple, condensed, and declarative queries of the graph databases do not necessarily provide good performance in comparison to the relational databases. While graph databases offer an intuitive representation of data, relational databases offer better results when set operations are needed.
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A key concept of the system is the graph (or edge or relationship). The graph relates the data items in the store to a collection of nodes and edges, the edges representing the relationships between the nodes. The relationships allow data in the store to be linked together directly and, in many cases, retrieved with one operation. Graph databases hold the relationships between data as a priority. Querying relationships is fast because they are perpetually stored in the database. Relationships can be intuitively visualized using graph databases, making them useful for heavily inter-connected data.
Graph databases are commonly referred to as a NoSQL
NoSQL (originally meaning "Not only SQL" or "non-relational") refers to a type of database design that stores and retrieves data differently from the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which ...
database. Graph databases are similar to 1970s network model databases in that both represent general graphs, but network-model databases operate at a lower level of abstraction
Abstraction is a process where general rules and concepts are derived from the use and classifying of specific examples, literal (reality, real or Abstract and concrete, concrete) signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abstraction" ...
and lack easy traversal over a chain of edges.
The underlying storage mechanism of graph databases can vary. Relationships are first-class citizens in a graph database and can be labelled, directed, and given properties. Some depend on a relational engine and store the graph data in a table (although a table is a logical element, therefore this approach imposes a level of abstraction between the graph database management system and physical storage devices). Others use a key–value store or document-oriented database
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program and data storage system designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data.
Document-oriented databases are one ...
for storage, making them inherently NoSQL structures.
, no graph query language has been universally adopted in the same way as SQL was for relational databases, and there are a wide variety of systems, many of which are tightly tied to one product. Some early standardization efforts led to multi-vendor query languages like Gremlin, SPARQL, and Cypher. In September 2019 a proposal for a project to create a new standard graph query language (ISO/IEC 39075 Information Technology — Database Languages — GQL) was approved by members of ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1(ISO/IEC JTC 1). GQL is intended to be a declarative database query language, like SQL. In addition to having query language interfaces, some graph databases are accessed through application programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that des ...
s (APIs).
Graph databases differ from graph compute engines. Graph databases are technologies that are translations of the relational online transaction processing (OLTP) databases. On the other hand, graph compute engines are used in online analytical processing
In computing, online analytical processing (OLAP) (), is an approach to quickly answer multi-dimensional analytical (MDA) queries. The term ''OLAP'' was created as a slight modification of the traditional database term online transaction proces ...
(OLAP) for bulk analysis. Graph databases attracted considerable attention in the 2000s, due to the successes of major technology corporations in using proprietary graph databases, along with the introduction of open-source graph databases.
One study concluded that an RDBMS was "comparable" in performance to existing graph analysis engines at executing graph queries.
History
In the mid-1960s, navigational databases such asIBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
's IMS supported tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
-like structures in its hierarchical model, but the strict tree structure could be circumvented with virtual records.
Graph structures could be represented in network model databases from the late 1960s. CODASYL, which had defined COBOL in 1959, defined the Network Database Language in 1969.
Labeled graphs could be represented in graph databases from the mid-1980s, such as the Logical Data Model.
Commercial object databases (ODBMSs) emerged in the early 1990s. In 2000, the Object Data Management Group published a standard language for defining object and relationship (graph) structures in their ODMG'93 publication.
Several improvements to graph databases appeared in the early 1990s, accelerating in the late 1990s with endeavors to index web pages.
In the mid-to-late 2000s, commercial graph databases with ACID
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
guarantees such as Neo4j and Oracle Spatial and Graph became available.
In the 2010s, commercial ACID graph databases that could be scaled horizontally became available. Further, SAP HANA brought in-memory and columnar technologies to graph databases. Also in the 2010s, multi-model databases that supported graph models (and other models such as relational database or document-oriented database
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program and data storage system designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data.
Document-oriented databases are one ...
) became available, such as OrientDB, ArangoDB, and MarkLogic (starting with its 7.0 version). During this time, graph databases of various types have become especially popular with social network analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) ...
with the advent of social media companies. Also during the decade, cloud-based graph databases such as Amazon Neptune and Neo4j AuraDB became available.
Background
Graph databases portray the data as it is viewed conceptually. This is accomplished by transferring the data into nodes and its relationships into edges. A graph database is a database that is based ongraph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of ''graph (discrete mathematics), graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of ''Vertex (graph ...
. It consists of a set of objects, which can be a node or an edge.
* Nodes represent entities or instances such as people, businesses, accounts, or any other item to be tracked. They are roughly the equivalent of a record, relation, or row in a relational database, or a document in a document-store database.
* Edges, also termed ''graphs'' or ''relationships'', are the lines that connect nodes to other nodes; representing the relationship between them. Meaningful patterns emerge when examining the connections and interconnections of nodes, properties and edges. The edges can either be directed or undirected. In an undirected graph, an edge connecting two nodes has a single meaning. In a directed graph, the edges connecting two different nodes have different meanings, depending on their direction. Edges are the key concept in graph databases, representing an abstraction that is not directly implemented in a relational model
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data are represented in terms of t ...
or a document-store model.
* Properties are information associated to nodes. For example, if ''Wikipedia'' were one of the nodes, it might be tied to properties such as ''website'', ''reference material'', or ''words that starts with the letter w'', depending on which aspects of ''Wikipedia'' are germane to a given database.
Graph models
Labeled-property graph
Resource Description Framework (RDF)
 In an RDF graph model, each addition of information is represented with a separate node. For example, imagine a scenario where a user has to add a name property for a person represented as a distinct node in the graph. In a labeled-property graph model, this would be done with an addition of a name property into the node of the person. However, in an RDF, the user has to add a separate node called
In an RDF graph model, each addition of information is represented with a separate node. For example, imagine a scenario where a user has to add a name property for a person represented as a distinct node in the graph. In a labeled-property graph model, this would be done with an addition of a name property into the node of the person. However, in an RDF, the user has to add a separate node called hasName connecting it to the original person node. Specifically, an RDF graph model is composed of nodes and arcs. An RDF graph notation or a statement is represented by: a node for the subject, a node for the object, and an arc for the predicate. A node may be left blank, a literal and/or be identified by a URI. An arc may also be identified by a URI. A literal for a node may be of two types: plain (untyped) and typed. A plain literal has a lexical form and optionally a language tag. A typed literal is made up of a string with a URI that identifies a particular datatype. A blank node may be used to accurately illustrate the state of the data when the data does not have a URI.
Properties
Graph databases are a powerful tool for graph-like queries. For example, computing the shortest path between two nodes in the graph. Other graph-like queries can be performed over a graph database in a natural way (for example graph's diameter computations or community detection). Graphs are flexible, meaning it allows the user to insert new data into the existing graph without loss of application functionality. There is no need for the designer of the database to plan out extensive details of the database's future use cases.Storage
The underlying storage mechanism of graph databases can vary. Some depend on a relational engine and "store" the graph data in a table (although a table is a logical element, therefore this approach imposes another level of abstraction between the graph database, the graph database management system and the physical devices where the data is actually stored). Others use a key–value store ordocument-oriented database
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program and data storage system designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data.
Document-oriented databases are one ...
for storage, making them inherently NoSQL
NoSQL (originally meaning "Not only SQL" or "non-relational") refers to a type of database design that stores and retrieves data differently from the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which ...
structures. A node would be represented as any other document store, but edges that link two different nodes hold special attributes inside its document; a _from and _to attributes.
Index-free adjacency
Data lookup performance is dependent on the access speed from one particular node to another. Becauseindex
Index (: indexes or indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on the Halo Array in the ...
-free adjacency enforces the nodes to have direct physical RAM addresses and physically point to other adjacent nodes, it results in a fast retrieval. A native graph system with index-free adjacency does not have to move through any other type of data structures to find links between the nodes. Directly related nodes in a graph are stored in the cache once one of the nodes are retrieved, making the data lookup even faster than the first time a user fetches a node. However, such advantage comes at a cost. Index-free adjacency sacrifices the efficiency of queries that do not use graph traversal
In computer science, graph traversal (also known as graph search) refers to the process of visiting (checking and/or updating) each vertex in a graph. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the vertices are visited. Tree traversa ...
s. Native graph databases use index-free adjacency to process CRUD operations on the stored data.
Applications
Multiple categories of graphs by kind of data have been recognised. Gartner suggests the five broad categories of graphs: * Social graph: this is about the connections between people; examples includeFacebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
, Twitter
Twitter, officially known as X since 2023, is an American microblogging and social networking service. It is one of the world's largest social media platforms and one of the most-visited websites. Users can share short text messages, image ...
, and the idea of six degrees of separation
* Intent graph: this deals with reasoning and motivation.
* Consumption graph: also known as the "payment graph", the consumption graph is heavily used in the retail industry. E-commerce companies such as Amazon, eBay and Walmart use consumption graphs to track the consumption of individual customers.
* Interest graph: this maps a person's interests and is often complemented by a social graph. It has the potential to follow the previous revolution of web organization by mapping the web by interest rather than indexing webpages.
* Mobile graph: this is built from mobile data. Mobile data in the future may include data from the web, applications, digital wallets, GPS, and Internet of Things
Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communication networks. The IoT encompasse ...
(IoT) devices.
Comparison with relational databases
SinceEdgar F. Codd
Edgar Frank "Ted" Codd (19 August 1923 – 18 April 2003) was a British computer scientist who, while working for IBM, invented the relational model for database management, the theoretical basis for relational databases and relational database ...
's 1970 paper on the relational model
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data are represented in terms of t ...
, relational databases have been the de facto industry standard for large-scale data storage systems. Relational models require a strict schema and data normalization which separates data into many tables and removes any duplicate data within the database. Data is normalized in order to preserve data consistency and support ACID transactions. However this imposes limitations on how relationships can be queried.
One of the relational model's design motivations was to achieve a fast row-by-row access. Problems arise when there is a need to form complex relationships between the stored data. Although relationships can be analyzed with the relational model, complex queries performing many join operations on many different attributes over several tables are required. In working with relational models, foreign key
A foreign key is a set of attributes in a table that refers to the primary key of another table, linking these two tables. In the context of relational databases, a foreign key is subject to an inclusion dependency constraint that the tuples ...
constraints should also be considered when retrieving relationships, causing additional overhead.
Compared with relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
s, graph databases are often faster for associative data sets and map more directly to the structure of object-oriented applications. They can scale more naturally to large datasets as they do not typically need join operations, which can often be expensive. As they depend less on a rigid schema, they are marketed as more suitable to manage ad hoc and changing data with evolving schemas.
Conversely, relational database management systems are typically faster at performing the same operation on large numbers of data elements, permitting the manipulation of the data in its natural structure. Despite the graph databases' advantages and recent popularity over relational databases, it is recommended the graph model itself should not be the sole reason to replace an existing relational database. A graph database may become relevant if there is an evidence for performance improvement by orders of magnitude and lower latency.
Examples
The relational model gathers data together using information in the data. For example, one might look for all the "users" whose phone number contains the area code "311". This would be done by searching selected datastores, or tables, looking in the selected phone number fields for the string "311". This can be a time-consuming process in large tables, so relational databases offerindex
Index (: indexes or indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on the Halo Array in the ...
es, which allow data to be stored in a smaller sub-table, containing only the selected data and a unique key (or primary key) of the record. If the phone numbers are indexed, the same search would occur in the smaller index table, gathering the keys of matching records, and then looking in the main data table for the records with those keys. Usually, a table is stored in a way that allows a lookup via a key to be very fast.
Relational databases do not ''inherently'' contain the idea of fixed relationships between records. Instead, related data is linked to each other by storing one record's unique key in another record's data. For example, a table containing email addresses for users might hold a data item called userpk, which contains the primary key of the user record it is associated with. In order to link users and their email addresses, the system first looks up the selected user records primary keys, looks for those keys in the userpk column in the email table (or, more likely, an index of them), extracts the email data, and then links the user and email records to make composite records containing all the selected data. This operation, termed a join, can be computationally expensive. Depending on the complexity of the query, the number of joins, and indexing various keys, the system may have to search through multiple tables and indexes and then sort it all to match it together.
In contrast, graph databases directly store the relationships between records. Instead of an email address being found by looking up its user's key in the userpk column, the user record contains a pointer that directly refers to the email address record. That is, having selected a user, the pointer can be followed directly to the email records, there is no need to search the email table to find the matching records. This can eliminate the costly join operations. For example, if one searches for all of the email addresses for users in area code "311", the engine would first perform a conventional search to find the users in "311", but then retrieve the email addresses by following the links found in those records. A relational database would first find all the users in "311", extract a list of the primary keys, perform another search for any records in the email table with those primary keys, and link the matching records together. For these types of common operations, graph databases would theoretically be faster.
The true value of the graph approach becomes evident when one performs searches that are more than one level deep. For example, consider a search for users who have "subscribers" (a table linking users to other users) in the "311" area code. In this case a relational database has to first search for all the users with an area code in "311", then search the subscribers table for any of those users, and then finally search the users table to retrieve the matching users. In contrast, a graph database would search for all the users in "311", then follow the backlink
From the point of view of a given web resource (referent), a backlink is a regular hyperlink on another web resource (the referrer) that points to the referent. A ''web resource'' may be (for example) a website, web page, or web directory.
A ba ...
s through the subscriber relationship to find the subscriber users. This avoids several searches, look-ups, and the memory usage involved in holding all of the temporary data from multiple records needed to construct the output. In terms of big O notation
Big ''O'' notation is a mathematical notation that describes the asymptotic analysis, limiting behavior of a function (mathematics), function when the Argument of a function, argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a memb ...
, this query would be time – i.e., proportional to the logarithm of the size of the data. In contrast, the relational version would be multiple lookups, plus the time needed to join all of the data records.
The relative advantage of graph retrieval grows with the complexity of a query. For example, one might want to know "that movie about submarines with the actor who was in that movie with that other actor that played the lead in '' Gone With the Wind''". This first requires the system to find the actors in ''Gone With the Wind'', find all the movies they were in, find all the actors in all of those movies who were not the lead in ''Gone With the Wind'', and then find all of the movies they were in, finally filtering that list to those with descriptions containing "submarine". In a relational database, this would require several separate searches through the movies and actors tables, doing another search on submarine movies, finding all the actors in those movies, and then comparing the (large) collected results. In contrast, the graph database would walk from ''Gone With the Wind'' to Clark Gable
William Clark Gable (February 1, 1901November 16, 1960) was an American actor often referred to as the "King of Cinema of the United States, Hollywood". He appeared in more than 60 Film, motion pictures across a variety of Film genre, genres dur ...
, gather the links to the movies he has been in, gather the links out of those movies to other actors, and then follow the links out of those actors back to the list of movies. The resulting list of movies can then be searched for "submarine". All of this can be done via one search.
''Properties'' add another layer of abstraction
Abstraction is a process where general rules and concepts are derived from the use and classifying of specific examples, literal (reality, real or Abstract and concrete, concrete) signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abstraction" ...
to this structure that also improves many common queries. Properties are essentially labels that can be applied to any record, or in some cases, edges as well. For example, one might label Clark Gable as "actor", which would then allow the system to quickly find all the records that are actors, as opposed to director or camera operator. If labels on edges are allowed, one could also label the relationship between ''Gone With the Wind'' and Clark Gable as "lead", and by performing a search on people that are "lead" "actor" in the movie ''Gone With the Wind'', the database would produce Vivien Leigh, Olivia de Havilland
Dame Olivia Mary de Havilland (; July 1, 1916July 26, 2020) was a British and American actress. The major works of her cinematic career spanned from 1935 to 1988. She appeared in 49 feature films and was one of the leading actresses of her tim ...
and Clark Gable. The equivalent SQL query would have to rely on added data in the table linking people and movies, adding more complexity to the query syntax. These sorts of labels may improve search performance under certain circumstances, but are generally more useful in providing added semantic data for end users.
Relational databases are very well suited to flat data layouts, where relationships between data are only one or two levels deep. For example, an accounting database might need to look up all the line items for all the invoices for a given customer, a three-join query. Graph databases are aimed at datasets that contain many more links. They are especially well suited to social networking systems, where the "friends" relationship is essentially unbounded. These properties make graph databases naturally suited to types of searches that are increasingly common in online systems, and in big data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
environments. For this reason, graph databases are becoming very popular for large online systems like Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
, Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, Twitter
Twitter, officially known as X since 2023, is an American microblogging and social networking service. It is one of the world's largest social media platforms and one of the most-visited websites. Users can share short text messages, image ...
, and similar systems with deep links between records.
To further illustrate, imagine a relational model with two tables: a people table (which has a person_id and person_name column) and a friend table (with friend_id and person_id, which is a foreign key
A foreign key is a set of attributes in a table that refers to the primary key of another table, linking these two tables. In the context of relational databases, a foreign key is subject to an inclusion dependency constraint that the tuples ...
from the people table). In this case, searching for all of Jack's friends would result in the following SQL query.
W3C
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working together in ...
and used in multiple RDF Triple and Quad stores
** Long form List of graph databases
The following is a list of notable graph databases:Graph query-programming languages
* AQL (ArangoDB Query Language): a SQL-like query language used in ArangoDB for both documents and graphs *Cypher Query Language
Cypher is a declarative graph query language that allows for expressive and efficient data querying in a property graph.
Cypher was largely an invention of Andrés Taylor while working for Neo4j, Inc. (formerly Neo Technology) in 2011. Cypher wa ...
(Cypher): a graph query declarative language
In computer science, declarative programming is a programming paradigm—a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs—that expresses the logic of a computation without describing its control flow.
Many languages that app ...
for Neo4j that enables ad hoc and programmatic (SQL-like) access to the graph.
* GQL: proposed ISO standard graph query language
* GraphQL: an open-source data query and manipulation language for APIs. Dgraph implements modified GraphQL language called DQL (formerly GraphQL+-)
* Gremlin: a graph programming language that is a part of Apache TinkerPop open-source project
* SPARQL: a query language for RDF databases that can retrieve and manipulate data stored in RDF format
* regular path queries, a theoretical language for queries on graph databases
See also
* Graph transformation * Hierarchical database model * Datalog * Vadalog * Object database * RDF Database * Structured storage * Text graph * Wikidata is a Wikipedia sister project that stores data in a graph database. Ordinary web browsing allows for viewing nodes, following edges, and running SPARQL queries.References
{{Database models Database models