|
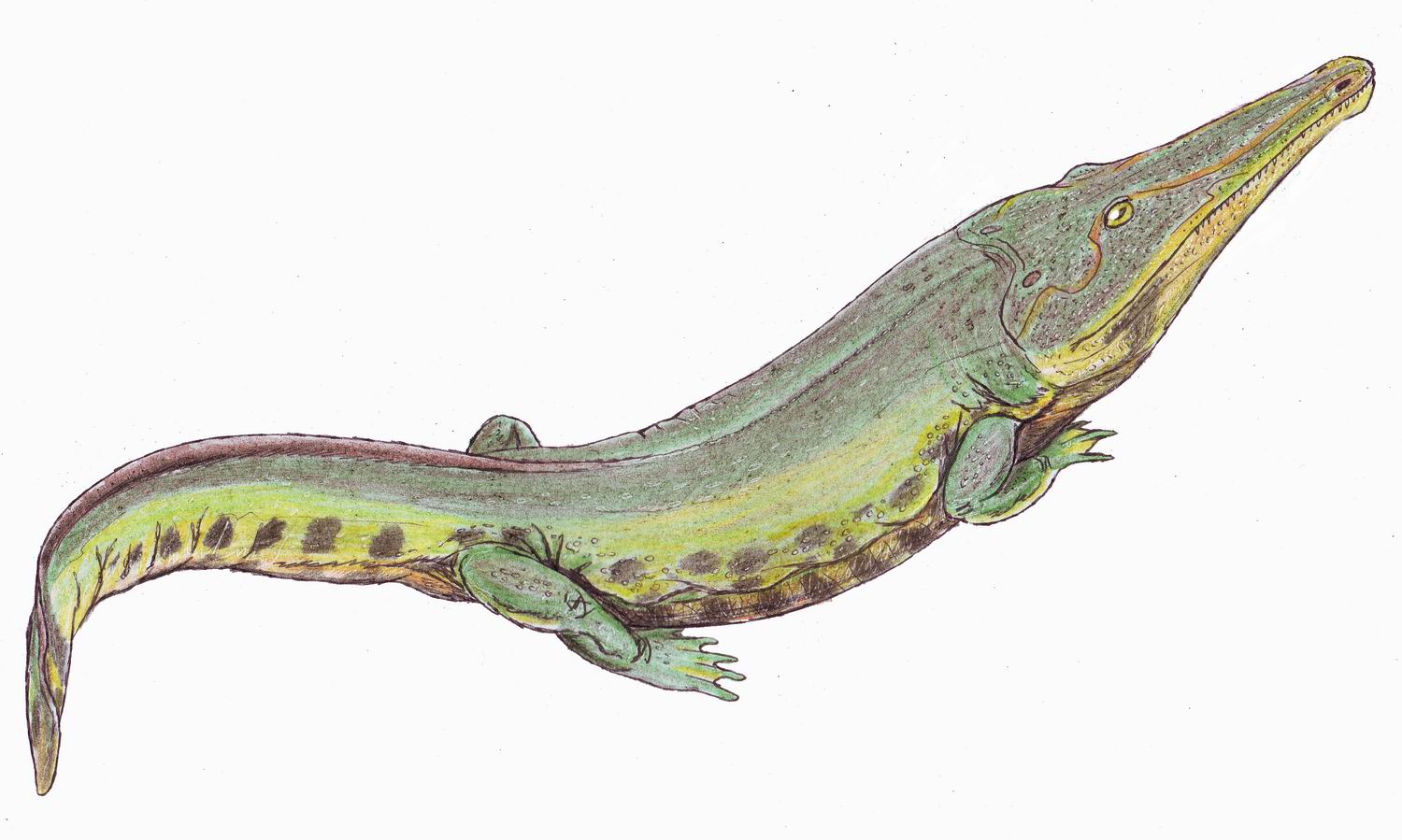
Marcianosuchus
''Marcianosuchus'' is an extinct genus of eucrocopodan archosauriforms from the Middle Triassic Röt Formation of Germany. The genus contains a single species, ''M. angustifrons'', known from a partial disarticulated skeleton. ''Marcianosuchus'' represents the first non- archosaurian archosauriform named from Central Europe. Discovery and naming The ''Marcianosuchus'' holotype specimen, SMNS 91318, was discovered in 1972 by Rupert Wild in talus deposits of the retired Kössig quarry, representing outcrops of the Röt Formation ( Buntsandstein Group) near Ebhausen in Calw district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The specimen consists of an associated, generally disarticulated, skeleton of a single individual. Known material includes several bones of the skull and lower jaws, teeth, pectoral and pelvic girdles, humeri, femora, an incomplete tibia and probable fibula, assorted autopodial bones, cervical, dorsal, and caudal vertebrae, associated osteoderms, ribs, and gastral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Röt Formation
The Röt Formation or Rötton Formation (German for Röt Shale), or Upper Buntsandstein, is a geologic formation of the Buntsandstein in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Middle Triassic Epoch (Anisian or Aegean or Bithynian in the regional stratigraphy).Röt Formation at .org The formation overlies the Plattenstein and Solling Formations and is overlain by the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2024 In Reptile Paleontology
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2024 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2024, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2024. Squamates Squamate research * A study on the biogeography of squamates throughout their evolutionary history, providing evidence of a localized Pangaean origin (Africa, Australia, Eurasia and Sundaland, Sunda) of the squamate crown group in the Jurassic followed by strong regionalization to Eurasia for subsequent Jurassic lineages, is published by Wilenzik, Barger & Pyron (2024). * New lizard assemblage, including fossil material of a pleurodontan iguanian, a Teiioidea, teiioid and a possible Scincoidea, scincoid, is described from the Upper Cretaceous (Campanian-Maastrichtian) Allen Formation (Argentina) by Garberoglio ''et al.'' (2024). * Revision of the fossil material of Paleocene lizards from the Walbeck fissure fillin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
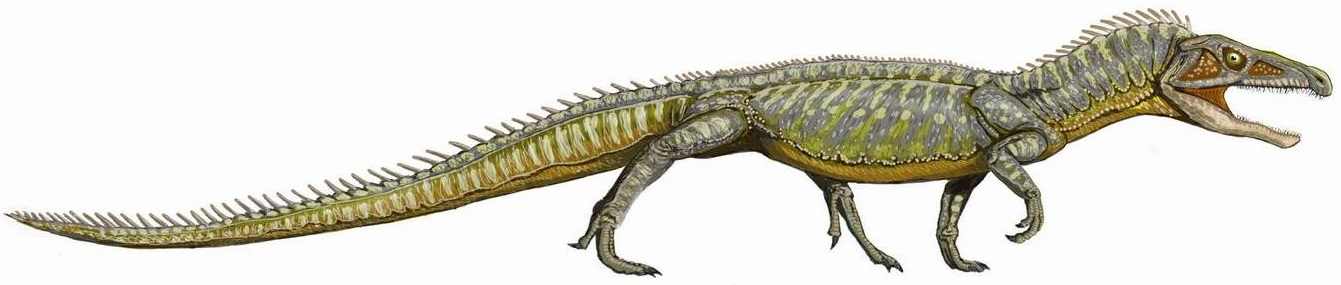
Eucrocopoda
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles encompassing archosaurs and some of their close relatives. It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria. Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing '' Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. Gauthier as part of the ''Phylonyms'' (2020) defined the clade as the last common ancestor of '' Gallus'', ''Alligator'', and '' Proterosuchus'', and all its descendants. Archosauriforms are a branch of archosauromorphs which originated in the Late Permian (roughly 252 million years ago) and persist to the present day as the two surviving archosaur groups: crocodilians and birds. Archosauriforms present several traits historically ascribed to the group Archosauria. These include serrated teeth set in deep sockets, a more active metabolism, and an antorbital fenestra (a hole in the skull in fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epoch (geology), epochs of the Triassic period (geology), period or the middle of three series (stratigraphy), series in which the Triassic system (stratigraphy), system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian age (geology), ages or stage (stratigraphy), stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of stratum, rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic life Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopodium
A limb (from Old English ''lim'', meaning "body part") is a jointed, muscled appendage of a tetrapod vertebrate animal used for weight-bearing, terrestrial locomotion and physical interaction with other objects. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods, who use their limbs for walking, running and jumping, swimming, climbing, grasping, touching and striking. All tetrapods have four limbs that are organized into two bilaterally symmetrical pairs, with one pair at each end of the torso, which phylogenetically correspond to the four paired fins (pectoral and pelvic fins) of their fish (sarcopterygian) ancestors. The cranial pair (i.e. closer to the head) of limbs are known as the forelimbs or ''front legs'', and the caudal (anatomical term), caudal pair (i.e. closer to the tail or coccyx) are the hindlimbs or ''back legs''. In animals with a more erect bipedal po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humeri
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes ( trochlea and capitulum), and 3 fossae ( radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from Late Latin , from Latin , meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic (shoulder) and Greek . Structure Upper extremity The upper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femora
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The top of the femur fits into a socket in the pelvis called the hip joint, and the bottom of the femur connects to the shinbone (tibia) and kneecap (patella) to form the knee. In humans the femur is the largest and thickest bone in the body. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle at which the femora converge is an important factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. In females, thicker pelvic bones cause the femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee), the femurs converge so much that the knees touch. The opposite condition, ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness), occurs when the femurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle bones, ankle. The tibia is found on the anatomical terms of location#Medial, medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute ''aulos, tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Vertebrae
Caudal vertebrae are the vertebrae of the tail in many vertebrates. In birds, the last few caudal vertebrae fuse into the pygostyle, and in apes, including humans, the caudal vertebrae are fused into the coccyx. In many reptiles, some of the caudal vertebrae bear ribs, the caudal ribs, though these are often fused with the vertebrae. The caudal vertebrae often articulate with haemal arches ventrally. The number of caudal vertebrae in animals can vary greatly. Anguid lizards have been reported to have as many as 111 caudal vertebrae, whereas as few as seven are present in the tail of the early therapsid ''Tapinocaninus''. In lepidosaurs and captorhinids, the caudal vertebrae possess fracture planes at mid-length that allow caudal autotomy. In frogs, the few caudal vertebrae are fused together to form part of the urostyle. References Skeletal system Vertebrate anatomy {{vertebrate-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |