|
Manis (other)
''Manis'' (" spirit") is a genus of South Asian and East Asian pangolins, the Asiatic pangolins, from subfamily Maninae, within family Manidae. Etymology Carl Linnaeus (1758) invented the Neo-Latin generic name ''Manis'' apparently as a feminine singular form of the Latin masculine plural Manes, the Ancient Roman name for a type of spirit, after the animal's strange appearance. Taxonomy * Subfamily: Maninae (Asiatic pangolins) ** Genus: ''Manis'' (Asiatic pangolins) *** ''Manis crassicaudata'' (Indian pangolin) *** '' Manis pentadactyla'' (Chinese pangolin) *** †'' Manis hungarica'' *** †'' Manis lydekkeri'' *** Subgenus: ''Paramanis'' **** '' Manis culionensis'' (Philippine pangolin) **** ''Manis javanica The Sunda pangolin (''Manis javanica''), also known as the Malayan or Javan pangolin, is a species of pangolin. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, including Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, and the islands of ...'' (Sunda pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manidae
Manidae is the only extant family of pangolins from superfamily Manoidea. This family comprises three genera (''Manis'' from subfamily Maninae, '' Phataginus'' from subfamily Phatagininae, and '' Smutsia'' from subfamily Smutsiinae), as well as extinct Fayum pangolin. Classification and phylogeny History of classification All species of living pangolin had been assigned to the genus ''Manis'' until the late 2000s, when research prompted the splitting of extant pangolins into three genera: ''Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. Taxonomy * Family: Manidae (pangolins) ** Subfamily: Maninae (Gray, 1821) *** Genus: ''Manis'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (Asiatic pangolins) **** ''Manis crassicaudata'' (Gray, 1827) (Indian pangolin) **** '' Manis pentadactyla'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (Chinese pangolin) **** ''Manis'' sp. (''Scale_H4'' & ''Scale_H8'')Jingyang Hu, Christian Roos, Xue Lv, Weimin Kuang, Li Yu (2020."Molecular Genetics Supports a Potential Fifth Asian Pangolin Species (Mammali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
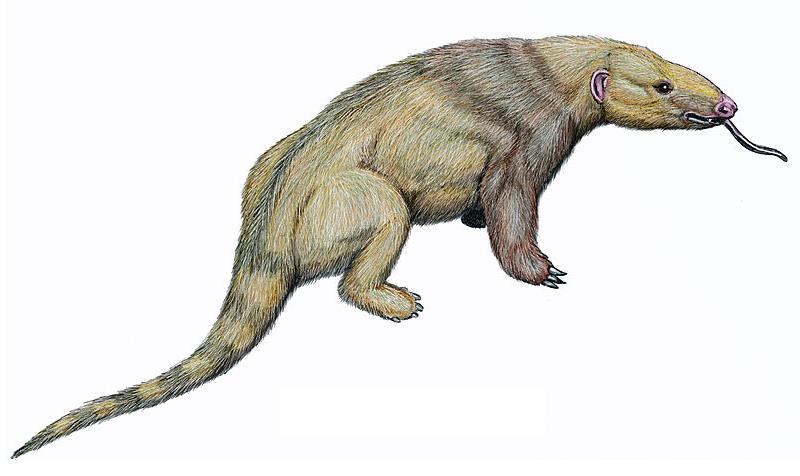
Necromanis
''Necromanis'' ("extinct pangolin") is an extinct genus of pangolin from superfamily Manoidea. It lived during the Oligocene and Miocene of Europe. It was originally placed within family Manidae, but was eventually removed from it as more fossil pholidotids from outside that family were found and studied more extensively (i.e., with the discovery and study of '' Eomanis'' and ''Patriomanis'').Gaudin, Timothy J., Robert J. Emry, and Brandon Pogue. "A new genus and species of pangolin (Mammalia, Pholidota) from the late Eocene of Inner Mongolia, China." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26.1 (2006): 146-159. Currently, ''Necromanis'' is placed as ''incertae sedis'' within the pholidotid superfamily Manoidea, together with the families Manidae and Patriomanidae. ''N. quercyi'' was originally placed within ''Teutomanis'' by Ameghino in 1905, but was later subsumed into ''Necromanis''. A new fossil humerus attributed to ''N. franconica'' from Quercy Quercy (; oc, Carcin , local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriomanidae
Patriomanidae ("fathers of pangolins") is a extinct family of pangolins from superfamily Manoidea that includes two extinct genera ''Patriomanis'' and '' Cryptomanis''. Taxonomy * Family: †Patriomanidae ** Genus: †'' Cryptomanis'' *** †''Cryptomanis gobiensis'' ** Genus: †''Patriomanis ''Patriomanis'' ("father of pangolins") is an extinct genus of pangolin from extinct family Patriomanidae. It lived during the Eocene of North America and it currently represents the only pangolin known from the Western Hemisphere. The genus c ...'' *** †''Patriomanis americana'' Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of family Patriomanidae within superfamily Manoidea. References Prehistoric pangolins Prehistoric mammal families {{Paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manoidea
Manoidea is a superfamily of pangolins from suborder Eupholidota that includes extant family Manidae, extinct family Patriomanidae and extinct genus '' Necromanis''. Taxonomy * Superfamily: Manoidea ** Family: Manidae (pangolins) ** Family: †Patriomanidae ** ''Incertae sedis ' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertain ...'' *** Genus: †'' Necromanis'' Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of superfamily Manoidea within suborder Eupholidota. References Pangolins Mammal superfamilies {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eomanis
''Eomanis'' ("dawn pangolin") is the earliest known true (and scaled) pangolin from extinct family Eomanidae (and extinct superfamily Eomanoidea) within suborder Eupholidota. It lived during the Eocene in Europe. ''Eomanis'' fossils found in the Messel Pit in Germany are very similar in size and anatomy to living pangolins of the genus ''Manis'', indicating that pangolins have remained largely unchanged in morphology and behavior for 50 million years. However, unlike modern pangolins, its tail and legs did not bear scales. According to the stomach contents of the excellently preserved Messel specimens, ''Eomanis’'' diet consisted of both insects and plant Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...s. Another early mammal discovered in the Messel Pit that was similar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupholidota
Eupholidota ("true pangolins") is a suborder of pangolins that includes two superfamilies: extant Manoidea and extinct Eomanoidea. Taxonomy * Suborder: Eupholidota (true pangolins) ** Superfamily: Manoidea *** Family: Manidae (pangolins) *** Family: †Patriomanidae *** ''Incertae sedis'' **** Genus: †''Necromanis ''Necromanis'' ("extinct pangolin") is an extinct genus of pangolin from superfamily Manoidea. It lived during the Oligocene and Miocene of Europe. It was originally placed within family Manidae, but was eventually removed from it as more foss ...'' ** Superfamily: † Eomanoidea *** Family: † Eomanidae Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of suborder Eupholidota within order Pholidota. References Pangolins {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotamandua
''Eurotamandua'' ("european ''Tamandua''") is an extinct genus of mammal from extinct family Eurotamanduidae that lived some 40-35 million years ago, during the middle Eocene. A single fossil is known, coming from the Messel Pit in southwestern Germany. ''Eurotamandua'' was about long. Most palaeontologists now classify ''Eurotamandua'' as a pangolin. When its fossils were first discovered, ''Eurotamandua'' was originally thought to be an anteater, as it lacked the characteristic fused-hair scales of other pangolins. ''Eurotamandua'' placement within the pangolins was made primarily because of a lack of the characteristic "xenarthran" joints found in all xenarthrans, including tamanduas. There is still much ambiguity in the taxonomy of all mammals prior to the Eocene, so there is the possibility that ''Eurotamandua'' was a primitive xenarthran. However, this is highly unlikely because all known fossil evidence indicates that xenarthrans existed exclusively in South America fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euromanis
''Euromanis'' ("european pangolin") is one of the earliest known pangolin genera. It lived during the Eocene in Europe. ''Euromanis'' fossils found in the Messel Pit in Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou .... Unlike modern pangolins, it did not bear scales on its body. Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of genus ''Euromanis'' within order Pholidota. References Prehistoric pangolins Eocene mammals Myrmecophagous mammals Prehistoric placental genera Cenozoic mammals of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1994 {{paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: ''Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises the four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . A number of extinct pangolin species are also known. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. They live in hollow trees or burrows, depending on the species. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacheiromys DB152-2
''Metacheiromys'' ("next to ''Cheiromys''") is an extinct genus of palaeanodont mammal from the paraphyletic subfamily Metacheiromyinae within paraphyletic family Metacheiromyidae, that lived in North America (what is now Wyoming) during the early to middle Eocene. ''Metacheiromys'' was a small creature, and measured around long. It had long claws and a narrow head similar in shape to that of an armadillo or an anteater (though it was actually related to the modern pangolins). The shape of its claws suggests that it probably dug through the soil in search of food, most likely small invertebrates. Unlike modern anteaters or pangolins, it had powerful canine teeth, but only a very few cheek teeth, instead using horny pads in its mouth to crush its food. The generic name means "next to ''Cheiromys''" because the scientist who saw the bones mistakenly thought that the animal was a primate with hands like those of the aye-aye (''Daubentonia madagascariensis''), one synonym being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeanodonta
Palaeanodonta ("ancient toothless animals") is an extinct clade of stem-pangolins. They were insectivorous, possibly fossorial, and lived from the Early Paleocene to Early Oligocene in North America, Europe and East Asia. While the taxonomic grouping of Palaeanodonta has been debated,Averianov, A. O. & Lopatin, A. V. (2014."High-level systematics of placental mammals: Current status of the problem."Biology Bulletin, 41(9), 801–816. it is widely thought that they are a sister group to pangolins. Anatomy Skull Palaeanodonts generally have low and caudally-broad skulls, with notable lambdoid crests and inflated bullae and squamosals. Teeth Despite the name of the group and contrary to their pangolin relatives, palaeanodonts are known to have had teeth. Early palaeanodonts retained minimal tribosphenic post-canines while later species had peglike or otherwise reduced molar crowns. Many also had large, characteristic cuspids. Classification and phylogeny Traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)