|
Manipur Valley
Imphal Valley ( /ˈɪmpɑːl/; ) or Manipur Valley () is located in the Indian state of Manipur and is an irregular almost oval shaped canyon that was formed as a result of the multiple small rivers that originate from neighbouring hill regions surrounding the valley and flow through it. The water in the Imphal valley is fetched from several rivers that flows via the valley, such as Imphal River, Iril River, Thoubal River, Khuga River and Sekmai river. Imphal River is the most prominent of the rivers which pass through the heart of the valley, and the river for which the entire valley is named. The Imphal valley is located in almost the centre of the state of Manipur and is surrounded by hills on all sides. Manipur has multi-topographical characteristics; it is a part of the eastern Himalayas, especially its lower hills, and it is an important feature of the landscape of Manipur. The hills forms one of the two main physical regions of the state, the other being the Manipur val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naga Hills
The Naga Hills, reaching a height of around , lie prominently on the border of India and Myanmar. They are part of a complex mountain system, and the parts of the mountain ranges inside the States and territories of India, Indian states of Nagaland, Manipur and the Administrative divisions of Burma, Burmese Naga Self-Administered Zone are called the Naga Hills. The highest point of the Naga hills is Mount Saramati (). Etymology The term "Naga" refers to the Naga people, who were called "Naga" or "Naka" in the Burmese language, meaning "people with pierced ears".Shimray, R. R. (1985), ''Origin and Culture of Nagas'', Pamleiphi Shimray, New Delhi, page 41, History In British India, the major part of the hills came under the Naga Hills District, British India, Naga Hills District. A part of the Naga Hills under the British India control was coalesced into a district in 1866. The boundaries of the Naga Hills District were gradually expanded by annexation of the territories of seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
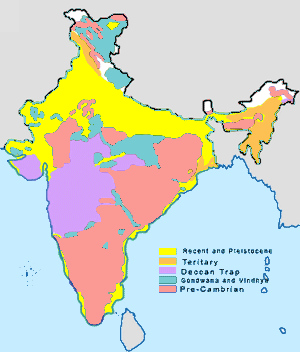
Geology Of India
The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of the Indian subcontinent contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently deposited alluvium that has yet to undergo diagenesis. Mineral deposits of great variety are found in the subcontinent in huge quantities. Even India's fossil record is impressive in which stromatolites, invertebrates, vertebrates and plant fossils are included. India's geographical land area can be classified into the Deccan Traps, Gondwana and Vindhyan. The Deccan Traps covers almost all of Maharashtra, a part of Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh marginally. During its journey northward after breaking off from the rest of Gondwana, the Indian Plate passed over a geologic hotspot, the Réunion hotspot, which caused extensive melting underneath the Indian Craton. The melting broke through the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valleys Of India
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms that may be global in use or else applied only locally. Forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manipur Articles Missing Geocoordinate Data
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically the Sagaing Region to the east and Chin State to the southeast. Covering an area of 22,330 square kilometers (8,621 mi²), the state consists mostly of hilly terrain with the 1813-square-kilometre (700 mi²) Imphal Valley inhabited by the Meitei (Manipuri) community, historically a kingdom. Surrounding hills are home to Naga and Kuki-Zo communities, who speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The official language and lingua franca, Meitei (Manipuri), also belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family. During the days of the British Raj, Manipur was one of the princely states. Prior to the British departure in 1947, Manipur acceded to the Dominion of India, along with roughly 550 other princely states. In September 1949, the ruler of Manipur signed a merger a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manipuris
The Meitei people, also known as Meetei people,P.20: "historically, academically and conventionally Manipuri prominently refers to the Meetei people."P.24: "For the Meeteis, Manipuris comprise Meeteis, Lois, Kukis, Nagas and Pangal." are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group native to the Indian State of Manipur. They form the largest and dominant ethnic group of Manipur in Northeast India. They speak the Meitei language (officially called Manipuri), one of the 22 official languages of the Republic of India and the sole official language of Government of Manipur. The Meiteis primarily settled in the Imphal Valley region in modern-day Manipur, though a sizeable population has settled in the other Indian states of Assam, Tripura, Nagaland, Meghalaya, and Mizoram. There is also a notable presence of Meiteis in the neighbouring countries of Myanmar and Bangladesh. The Meiteis represents about 53% of Manipur's population.Khomdan Singh Lisam, ''Encyclopaedia Of Manipur'', , pp. 322– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast India
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political Administrative divisions of India, administrative division of the country. It comprises eight States and union territories of India, states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state of Sikkim. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) (about 99 per cent of its total geographical boundary) with several neighbouring countries – it borders China to the north, Myanmar to the east, Bangladesh to the south-west, Nepal to the west, and Bhutan to the north-west. It comprises an area of , almost 8 per cent of that of India. The Siliguri Corridor connects the region to the Mainland India, rest of mainland India. The states of North Eastern Region are officially recognised under the North Eastern Council (NEC), co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacustrine Plain
A lacustrine plain or lake plain is a plain formed due to the past existence of a lake and its accompanying sedimentation, sediment accumulation. Lacustrine plains can be formed through one of three major mechanisms: glacial drainage, differential uplift, and inland lake creation and drainage. Lake plains can have various uses depending on where and how they form. Over time, in regions where a lake once existed, as water drains or evaporates from the lake, the deposited sediments are left behind, resulting in a level plain of land where the lake once existed. The soil of the plain may constitute fertile and productive farmland due to the previous accumulation of lacustrine sediments; in other cases, it may become a wetland or a desert. Background Lacustrine plains are plains formed when lakes filled with sediments are drained. There are several reasons why drainage might occur, but in all cases the water in the lake is lost, leaving behind a level land of sediments. The result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imphal
Imphal (; , ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (officially known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the former Kingdom of Manipur, surrounded by a moat. Spread over parts of the districts of Imphal West and Imphal East, the former contains the majority of the city's area and population. Imphal is part of the Smart Cities Mission under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs. Being a mega commercial hub, Imphal is known for its weaving, brass-ware, bronze-ware, and other cottage industries. Meitei language (officially known as Manipuri language) is the most widely spoken language in the city. '' INS Imphal'', the third ship of the ''Visakhapatnam''-class stealth guided missile destroyer of the Indian Navy, was named in recognition of the Indian soldiers who fought in Battle of Imphal during World War II, and is the first Indian Navy Ship (INS) named after a city in Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |