|
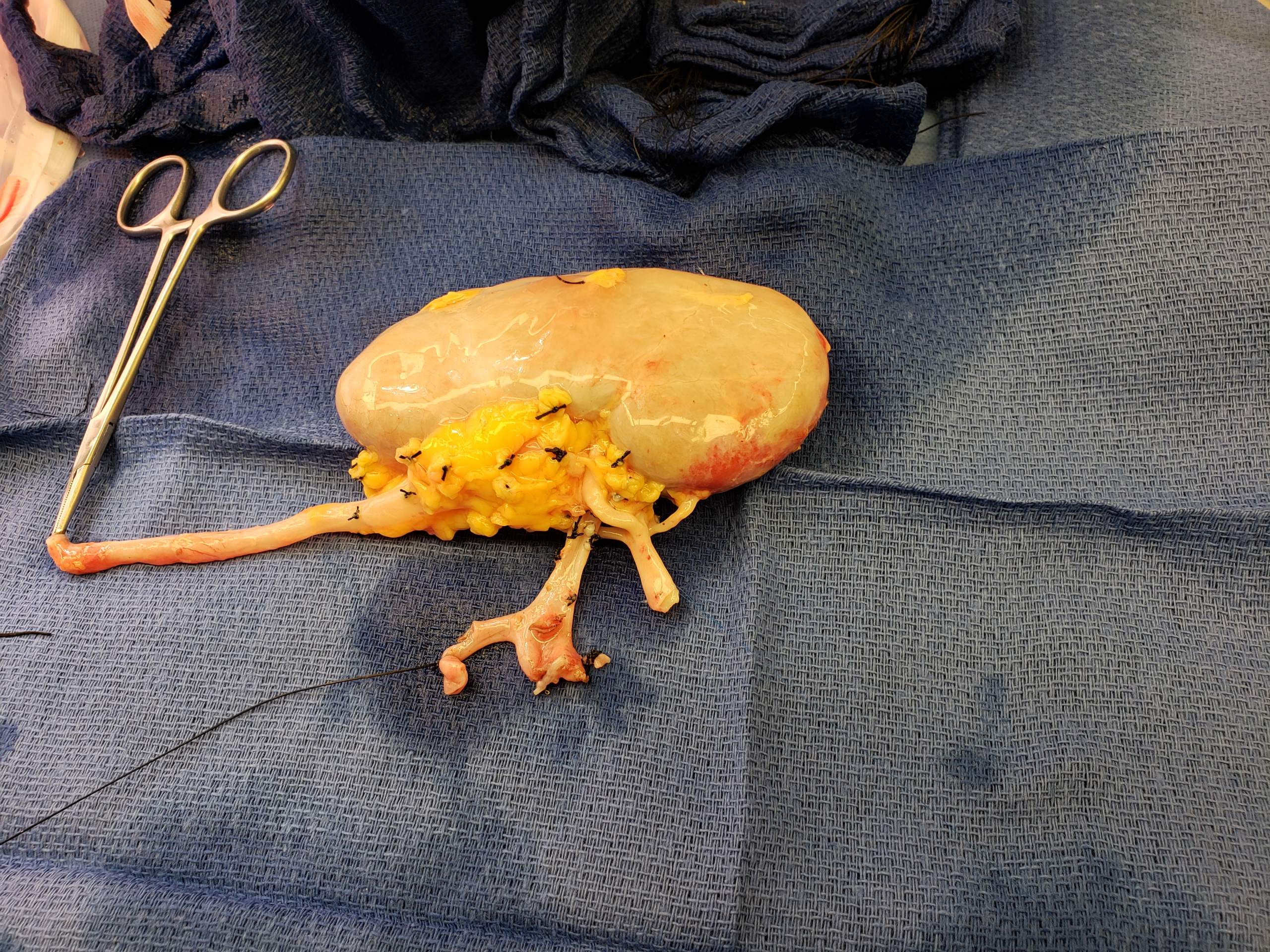
Malakoplakia
Malakoplakia (from Greek ''Malako'' "soft" + ''Plako'' "plaque") is a rare inflammatory condition which makes its presence known as a papule, plaque or ulceration that usually affects the genitourinary tract. However, it may also be associated with other bodily organs. It was initially described in the early 20th century as soft yellowish plaques found on the mucosa of the urinary bladder. Microscopically it is characterized by the presence of foamy histiocytes (called von Hansemann cells) with basophilic inclusions called Michaelis–Gutmann bodies. It usually involves gram-negative bacteria. Causes Malakoplakia is thought to result from the insufficient killing of bacteria by macrophages. Therefore, the partially digested bacteria accumulate in macrophages leading to deposition of iron and calcium. The impairment of bactericidal activity manifests itself as the formation of an ulcer, plaque or papule. Malakoplakia is associated with patients with a history of immunosuppression d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulcer (dermatology)
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the Epidermis (skin), epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as Decubitus ulcer, bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infection, infected, and pus forms. Signs and symptoms Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, travelers' diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, and cholera, among others. It is used both to treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in people with HIV/AIDS and other causes of immunosuppression. It can be given orally (swallowed by mouth) or intravenous infusion (slowly injected into a vein with an IV). Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 143rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridium
Phenazopyridine is a medication which, when excreted by the kidneys into the urine, has a local analgesic effect on the urinary tract. It is often used to help with the pain, irritation, or urgency caused by urinary tract infections, surgery, or injury to the urinary tract. In 2021, it was the 285th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 700,000 prescriptions. Medical uses Phenazopyridine is prescribed for its local analgesic effects on the urinary tract. It is sometimes used in conjunction with an antibiotic or other anti-infective medication at the beginning of treatment to help provide immediate symptomatic relief. Phenazopyridine does not treat infections or injury; it is only used for symptom relief during a UTI, following surgery, or injury to the urinary tract. It is recommended that it be used for no longer than the first two days of antibacterial treatment, as longer treatment cannot kill bacteria and may mask symptoms. UTI therapy sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptic
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery Antiseptic practices evolved in the 19th century through multiple individuals. Ignaz Semmelweis showed already in 1847-1848 that hand washing prior to delivery reduced puerperal fever. Despite this, many hospitals continued to practice surgery in unsanitary conditions, with some surgeons taking pride in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscope. These lenses let the physician focus on the inner surfaces of the urinary tract. Some cystoscopes use optical fibres (flexible glass fibres) that carry an image from the tip of the instrument to a viewing piece at the other end. Cystoscopes range from pediatric to adult and from the thickness of a pencil up to approximately 9 mm and have a light at the tip. Many cystoscopes have extra tubes to guide other instruments for surgical procedures to treat urinary problems. There are two main types of cystoscopy—flexible and rigid—differing in the flexibility of the cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is carried out with local anaesthesia on both sexes. Typically, a topical anesthetic, most often xylocaine gel (common brand names are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Culture
Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. ''Escherichia coli'' is the most common bacterium found. People without symptoms should generally not be tested for the condition. Differential diagnosis include contamination. If symptoms are present, treatment is generally with antibiotics. Bacteriuria without symptoms generally does not require treatment. Exceptions may include pregnant women, those who have had a recent kidney transplant, young children with significant vesicoureteral reflux, and those undergoing surgery of the urinary tract. Bacteriuria without symptoms is present in about 3% of otherwise healthy middle aged women. In nursing homes rates are as high as 50% among women and 40% in men. In those with a long term indwelling urinary catheter rates are 100%. Up to 10% of women have a urinary tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
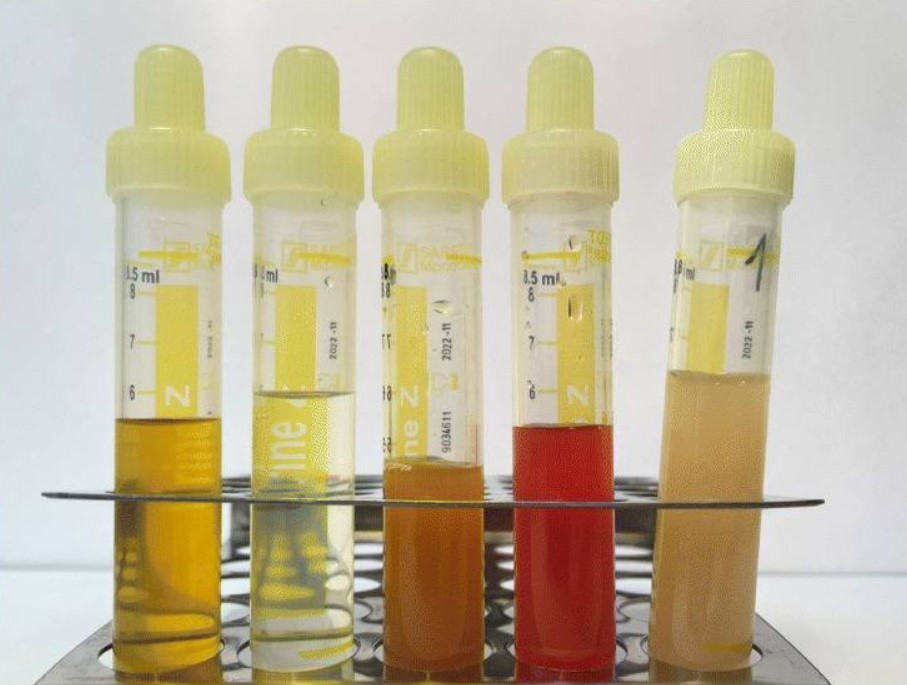
Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as Cell (biology), cells, urinary casts, Crystalluria, crystals, and organisms. Background Urine is produced by the filtration of blood in the kidneys. The formation of urine takes place in microscopic structures called nephrons, about one million of which are found in a normal human kidney. Blood enters the kidney though the renal artery and flows through the kidney's vasculature into the Glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus, a tangled knot of capillaries surrounded by Bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystitis
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra ( urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old). The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, catheterisation, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy, also known as pharmacological therapy or drug therapy, is defined as medical treatment that utilizes one or more pharmaceutical drugs to improve ongoing symptoms (symptomatic relief), treat the underlying condition, or act as a prevention for other diseases (prophylaxis). It can be distinguished from therapy using surgery (surgical therapy), radiation (radiation therapy), movement (physical therapy), or other modes. Among physicians, sometimes the term ''medical therapy'' refers specifically to pharmacotherapy as opposed to surgical or other therapy; for example, in oncology, medical oncology is thus distinguished from surgical oncology. Today's pharmacological therapy has evolved from a long history of medication use, and it has changed most rapidly in the last century due to advancements in drug discovery. The therapy is administered and adjusted by healthcare professionals according to the evidence-based guidelines and the patient's health condition. Perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Transplant
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 by a team including Joseph Murray, the recipient's surgeon, and Hartwell Harrison, surgeon for the donor. Murray was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1990 for this and other work. In 2018, an estimated 95,479 kidney transplants were performed worldwide, 36% of which came from living donors. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |