|
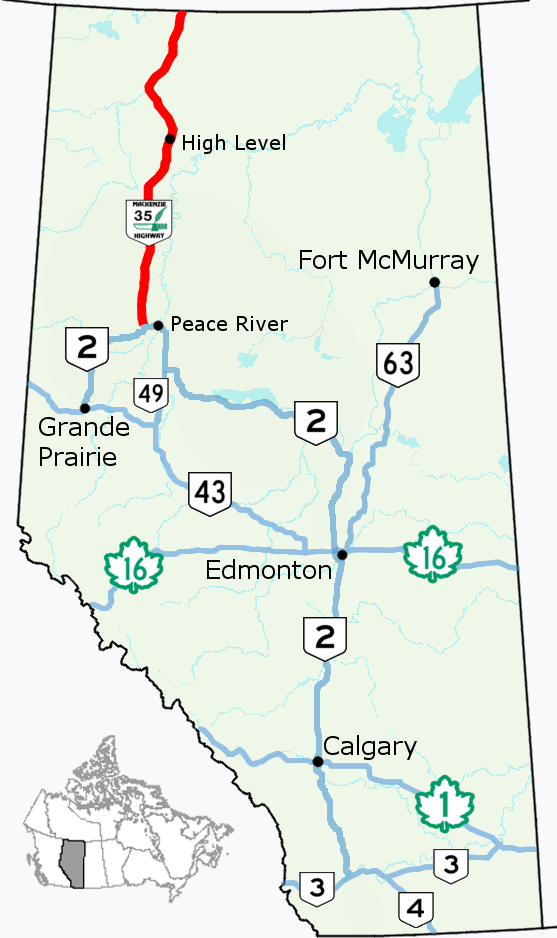
Mackenzie Highway
The Mackenzie Highway is a Canadian highway in northern Alberta and the Northwest Territories. It begins as Alberta Highway 2 at ''Mile Zero'' in Grimshaw, Alberta. After the first , it becomes Alberta Highway 35 for the balance of its length through Alberta and then becomes Northwest Territories Highway 1. Route description The Mackenzie Highway is designated as part of Canada's National Highway System, holding core route status from its terminus at Grimshaw to its intersection with the Yellowknife Highway, and northern/remote route status for the remainder of the route to its northern terminus at Wrigley. Originally begun in 1938, prior to World War II, the project was abandoned at the outbreak of war. It resumed in the late 1940s and completed to Hay River, Northwest Territories, in 1948/1949, but some sections, particularly in the vicinity of Steen River, remained difficult. In 1960, it was extended from Enterprise, approximately south of Hay River, to the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 35
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 35, commonly referred to as Highway 35, is a north–south highway in northwest Alberta, Canada that forms a portion of the Mackenzie Highway. Highway 35 is about long. From the south, Highway 35 begins at its intersection with Highway 2, approximately north of the Town of Grimshaw and west of the Town of Peace River, and ends at Alberta's boundary with the Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie .... It continues on as Northwest Territories Highway 1. It is one of only two highway-grade roads connecting the NWT with a province (the other being the Liard Highway), and the only one connecting the NWT with Alberta. Highway 35 passes through the towns of Manning and High Level. Major intersections From south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Providence
Fort Providence () is a hamlet in the South Slave Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. Located west of Great Slave Lake, it has all-weather road connections by way of the Yellowknife Highway (Great Slave Highway) branch off the Mackenzie Highway, and the Deh Cho Bridge opened November 30, 2012, near Fort Providence over the Mackenzie. The bridge replaced the ice bridge and ferry, enabling year-round crossing of the river. Fort Providence hosts the annual Mackenzie Days celebrations in August each year. History Fort Providence was founded in the 1860s as a Catholic mission site. By 1868, the Hudson's Bay Company, which previously has a trading post at Big Island at the source of the MacKenzie River, moved the post to the location of the mission site. From that moment, the settlement was known as Fort Providence. In 1867, the Grey Nuns opened a boarding school and an orphanage in the settlement. Instruction languages were English and French, and most of the nuns or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Communities In Alberta
The province of Alberta, Canada, is divided into ten types of Local government in Canada, local governments – urban municipalities (including List of cities in Alberta, cities, List of towns in Alberta, towns, List of villages in Alberta, villages and List of summer villages in Alberta, summer villages), List of specialized municipalities in Alberta, specialized municipalities, List of municipalities in Alberta#Rural municipalities, rural municipalities (including List of municipal districts in Alberta, municipal districts (often named as counties), List of communities in Alberta#Improvement districts, improvement districts, and List of communities in Alberta#Special areas, special areas), Métis in Alberta, Métis settlements, and Indian reserves. All types of municipalities are governed by local residents and were incorporated under various provincial acts, with the exception of improvement districts (governed by either the provincial or federal government), and List of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Nelson, British Columbia
Fort Nelson is a community in northeast British Columbia, Canada, within the Northern Rockies Regional Municipality (NRRM). It held town status prior to 6 February 2009, when it amalgamated with the former Northern Rockies Regional District to form the NRRM, becoming its administrative centre. The NRRM is the first regional municipality in the province. The community lies east of the northern Rocky Mountains in the Peace River region along the Alaska Highway at Mile 300. The town is approximately a four hour drive from the nearest urban centre, Fort St. John, but could potentially take six hours under winter driving conditions. The Alaska Highway both north and south of Fort Nelson is most often very well plowed in the winter and offers scenic views year round. According to the 2016 Canadian Census, the population was 3,366, a drop of 5.5% from the 2011 census. History Fort Nelson, named in honour of the British naval hero Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, was establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liard Highway
The Liard Highway (designated Highway 77 in British Columbia and Highway 7 in the Northwest Territories) is a 378 km two-lane highway in Canada that is the only direct road link between British Columbia and the Northwest Territories. Passing through sparsely populated areas of boreal forest of Canada, boreal forest, it serves as the sole land access route for the communities of Fort Liard and Nahanni Butte. Route The highway begins at a point on the Alaska Highway northwest of Fort Nelson, British Columbia, Fort Nelson and runs northeast through expanses of the Boreal forest of Canada, Canadian Boreal Forest to the border of British Columbia and the Northwest Territories. Beyond the border, it continues for as a very rough packed dirt and gravel road designated as Highway 7. It terminates at a junction with Territorial Mackenzie Highway, Highway 1 south of Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories, Fort Simpson. History The highway was built between 1975 and 1982 and was officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Road
An ice road or ice bridge is a human-made structure that runs on a frozen water surface (a river, a lake or a sea water expanse).Masterson, D. and Løset, S., 2011, ISO 19906: Bearing capacity of ice and ice roads, Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions (POAC), Montreal, Canada. Ice roads are typically part of a winter road, but they can also be simple stand-alone structures, connecting two shorelines.Goff, R.D. and Masterson, D.M., 1986, Construction of a sprayed ice island for exploration, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering (OMAE). The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), Tokyo, pp. 105–112. Ice roads may be planned, built and maintained so as to remain safe and effective, and a number of guidelines have been published with information in these regards. An ice road may be constructed year after year, for instance to service community needs d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferry
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus. Ferries form a part of the public transport systems of many waterside cities and islands, allowing direct transit between points at a capital cost much lower than bridges or tunnels. Ship connections of much larger distances (such as over long distances in water bodies like the Baltic Sea) may also be called ferry services, and many carry vehicles. History The profession of the ferryman is embodied in Greek mythology in Charon, the boatman who transported souls across the River Styx to the Underworld. Speculation that a pair of oxen propelled a ship having a water wheel can be found in 4th century Roman literature "''Anonymus De Rebus Bellicis''". Though impractical, there is no reason why it could not work and such a ferry, mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liard River
The Liard River of the Boreal forest of Canada, North American boreal forest flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows southeast through British Columbia, marking the northern end of the Rocky Mountains and then curving northeast back into Yukon and Northwest Territories, draining into the Mackenzie River at Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The river drains approximately of boreal forest and muskeg. Geography The river habitats are a subsection of the Lower Mackenzie Freshwater Ecoregion. The area around the river in Yukon is called the ''Liard River Valley'', and the Alaska Highway follows the river for part of its route. This surrounding area is also referred to as the ''Liard Plain'', and is a physiographic section of the larger Yukon–Tanana Uplands province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. The Liard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bear River
The Great Bear River, which drains the Great Bear Lake westward through marshes into the Mackenzie River, forms an important transportation link during its four ice-free months. It originates at south-west bay of the lake. The river has irregular meander pattern channel with average depth . Historic air photos show no evidence of bank erosion or channel migration in a 50-year period. The low discharge rate is due to small amount of precipitation in watershed area. Great Bear River contained open reaches that had melted out in place over 80 percent of its length in 1972 and 1974. The settlement of Tulita is located at the mouth of the river. Ecology Great Bear River hosts a number of aquatic species, with some of the most notable being Lake trout and Lake whitefish. Other animals regularly found in the Great Bear River include various fish species such as Arctic grayling, Burbot, Cisco (lake herring), Northern Pike, Nelma (inconnu), Walleye, Fourhorn sculpin, Slimy scul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dempster Highway
The Dempster Highway, also referred to as Yukon Highway 5 and Northwest Territories Highway 8, is a highway in Canada that connects the Klondike Highway in Yukon to Inuvik, Northwest Territories on the Mackenzie River delta. The highway crosses the Peel River (Canada), Peel and the Mackenzie rivers using a combination of seasonal ferry services and ice bridges. Year-round road access from Inuvik to Tuktoyaktuk opened in November 2017, with the completion of the Inuvik–Tuktoyaktuk Highway, creating the first all-weather road route connecting the Canadian road network with the Arctic Ocean. The highway is named for North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) officer William Dempster, who earned renown for discovering the fate of a lost NWMP patrol in 1911. Route description The highway begins east of Dawson City, Yukon on the Klondike Highway. There are no highway or major road intersections along the highway's route. It extends in a north-northeasterly direction to Inuvik, Northwest Terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Simpson
Fort Simpson (Slavey language: ''Łı́ı́dlı̨ı̨ Kų́ę́'' "place where rivers come together") is a village, the only one in the entire territory, in the Dehcho Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. The community is located on an island at the confluence of the Mackenzie and Liard rivers. It is approximately west of Yellowknife. Both rivers were traditionally trade routes for the Hudson's Bay Company and the native Dene people of the area. Fort Simpson is the regional centre of the Dehcho and is the gateway to the scenic South Nahanni River and the Nahanni National Park Reserve. Fort Simpson can be reached by air, water and road and has full secondary and elementary school service. The Mackenzie Highway was extended to Fort Simpson in 1970-71. The central section of the community is on an island near the south bank of the Mackenzie River, but industrial areas and rural residential areas are located along the highway as far as the Fort Simpson Airport, jus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories Highway 2
The Hay River Highway, officially Northwest Territories Highway 2, is the shortest numbered highway in the Northwest Territories and connects Hay River to the junction of Highway 1 at Enterprise. Its total length is , all of which is paved. south of downtown Hay River, there is a junction with Highway 5. The highway was originally a portion of the Mackenzie Highway; this status ended with the extension of the highway northwest from Enterprise, first as a route around Great Slave Lake to Yellowknife, and then west to Fort Simpson. The highway is one of the most "rural In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry are typically desc ...ized" highways in the N.W.T., with two subdivisions and one or two other clusters of homes. The highway is designated as a core route of Canada's National Highway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |