|
MSX-3
MSX-3 is a binding selectivity, selective adenosine adenosine A2A receptor, A2A receptor adenosine receptor antagonist, antagonist used in scientific research. Similarly to MSX-4, it is a water solubility, water-soluble ester prodrug of MSX-2. Medicinal chemistry MSX-3, MSX-4, and MSX-2 are xanthines and are chemical derivative, derivatives of the binding selectivity, non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist caffeine. MSX-2 has been extensively studied due to its high affinity (pharmacology), affinity and binding selectivity, selectivity for the adenosine A2A receptor, but use of MSX-2 itself has been limited by its poor water solubility. Whereas MSX-3 is a phosphate ester prodrug of MSX-2 that is suited best for intravenous administration and not for oral administration, MSX-4 is an amino acid ester (valine, L-valine) prodrug of MSX-2 that can be orally administered. Pharmacology MSX-2 has 500-fold higher affinity for the adenosine A2A receptor over the adenosine A1 re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSX-2
MSX-2 is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist used in scientific research. It is a xanthine and a derivative of the non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist caffeine. The affinities (Ki) of MSX-2 for the human adenosine receptors are 5.38 to 14.5nM for the adenosine A2A receptor, 2,500nM for the adenosine A1 receptor (172- to 465-fold lower than for the A2A receptor), and >10,000nM for the adenosine A2B and A3 receptors (>690-fold lower than for the A2A receptor). MSX-2 has poor water solubility, which has limited the use of MSX-2 itself. Water-soluble ester prodrugs of MSX-2, including MSX-3 (a phosphate ester prodrug) and MSX-4 (an amino acid ester prodrug), have been developed and used in place of MSX-2. MSX-3 is best-suited for use by intravenous administration, whereas MSX-4 can be administered by oral administration. MSX-3 and MSX-4 reverse motivational deficits in animals and hence have the capacity to produce pro-motivational effects. MSX-2 and MS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-motivational Agent
A motivation-enhancing drug, also known as a pro-motivational drug, is a drug which increases motivation. Drugs enhancing motivation can be used in the treatment of motivational deficits, for instance in depression, schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). They can also be used in the treatment of disorders of diminished motivation (DDMs), including apathy, abulia, and akinetic mutism, disorders that can be caused by conditions like stroke, traumatic brain injury (TBI), and neurodegenerative diseases. Motivation-enhancing drugs are used self-medication, non-medically by healthy people to increase motivation and productivity as well, for instance in education, educational contexts. There are limited clinical data on medications in treating motivational deficits and disorders. In any case, drugs used for pro-motivational purposes are generally dopaminergic agents, for instance dopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRIs) like methylphenidate and modafinil, dopam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine A2A Receptor
The adenosine A2A receptor, also known as ADORA2A, is an adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it. Structure This protein is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family which possess seven transmembrane alpha helices, as well as an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminus. Furthermore, located in the intracellular side close to the membrane is a small alpha helix, often referred to as helix 8 (H8). The crystallographic structure of the adenosine A2A receptor reveals a ligand binding pocket distinct from that of other structurally determined GPCRs (i.e., the beta-2 adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin).; Below this primary ( orthosteric) binding pocket lies a secondary ( allosteric) binding pocket. The crystal-structure of A2A bound to the antagonist ZM241385 (PDB code: 4EIY) showed that a sodium-ion can be found in this location of the protein, thus giving it the name 'sodium-ion binding pocket'. Heteromers The actions of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSX-4
MSX-4 is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist used in scientific research. It is a water-soluble amino acid ester prodrug of MSX-2, the active metabolite of the drug. MSX-4 reverses the motivational deficits induced by the dopamine D2 receptor antagonist eticlopride in animals and hence has the capacity to produce pro-motivational effects. MSX-4 was first described in the scientific literature by 2008. See also * Istradefylline Istradefylline, sold under the brand name Nourianz, is a medication used as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adults with Parkinson's disease (PD) experiencing "off" episodes. Istradefylline reduces "off" periods resulting from lon ... * MSX-3 References 3-Methoxyphenyl compounds Adenosine receptor antagonists Amino acids Esters Experimental drugs Pro-motivational agents Prodrugs Propargyl compounds Xanthines {{Pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG). History and etymology Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant. Nomenclature According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A1 Receptor
The adenosine A1 receptor is one member of the adenosine receptor group of G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as endogenous ligand. Biochemistry A1 receptors are implicated in sleep promotion by inhibiting wake-promoting cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain. A1 receptors are also present in smooth muscle throughout the vascular system. The adenosine A1 receptor has been found to be ubiquitous throughout the entire body. Signalling Activation of the adenosine A1 receptor by an agonist causes binding of Gi1/2/3 or Go protein. Binding of Gi1/2/3 causes an inhibition of adenylate cyclase and, therefore, a decrease in the cAMP concentration. An increase of the inositol triphosphate/diacylglycerol concentration is caused by an activation of phospholipase C, whereas the elevated levels of arachidonic acid are mediated by DAG lipase, which cleaves DAG to form arachidonic acid. Several types of potassium channels are activated but N-, P-, and Q-type calcium channels are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A2B Receptor
The adenosine A2B receptor, also known as ADORA2B, is a G-protein coupled adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human adenosine A2b receptor gene which encodes it. Mechanism This integral membrane protein stimulates adenylate cyclase activity in the presence of adenosine. This protein also interacts with netrin-1, which is involved in axon elongation. Gene The gene is located near the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Ligands Research into selective A2B ligands has lagged somewhat behind the development of ligands for the other three adenosine receptor subtypes, but a number of A2B-selective compounds have now been developed, and research into their potential therapeutic applications is ongoing. Agonists * BAY 60-6583 * NECA (N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine) * (S)-PHPNECA - high affinity and efficacy at A2B, but poor selectivity over other adenosine receptor subtypes * LUF-5835 * LUF-5845 - partial agonist Antagonists and inverse agonists * Compound 38: antagonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A3 Receptor
The adenosine A3 receptor, also known as ADORA3, is an adenosine receptor, but also denotes the human gene encoding it. Function Adenosine A3 receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that couple to Gi/Gq and are involved in a variety of intracellular signaling pathways and physiological functions. It mediates a sustained cardioprotective function during cardiac ischemia, it is involved in the inhibition of neutrophil degranulation in neutrophil-mediated tissue injury, it has been implicated in both neuroprotective and neurodegenerative effects, and it may also mediate both cell proliferation and cell death. Recent publications demonstrate that adenosine A3 receptor antagonists (SSR161421) could have therapeutic potential in bronchial asthma (17,18). Gene Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Therapeutic implications An adenosine A3 receptor agonist (CF-101) is in clinical trials for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Receptor
The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: A1, A2A, A2B and A3; each is encoded by a different gene. The adenosine receptors are commonly known for their antagonists caffeine and theophylline, whose action on the receptors produces the stimulating effects of coffee, tea and chocolate. Pharmacology Each type of adenosine receptor has different functions, although with some overlap. For instance, both A1 receptors and A2A play roles in the heart, regulating myocardial oxygen consumption and coronary blood flow, while the A2A receptor also has broader anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body. These two receptors also have important roles in the brain, regulating the release of other neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate, while the A2B and A3 receptors are located mainly peripherally and are involved in proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building blocks of RNA (and its derivative deoxyadenosine is a building block of DNA), which are essential for all life. Its derivatives include the energy carriers adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is pervasive in signal transduction. Adenosine is used as an intravenous medication for some cardiac arrhythmias. Adenosyl (abbreviated Ado or 5'-dAdo) is the chemical group formed by removal of the 5′-hydroxy (OH) group. It is found in adenosylcobalamin (an active form of vitamin B12) and as a radical in radical SAM enzymes. Medical uses Supraventricular tachycardia In individuals with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify and convert t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
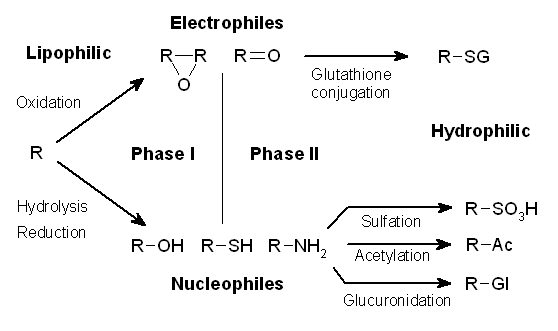
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is called pharmacokinetics. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important aspect of pharmacology and medicine. For example, the rate of metabolism determines the duration and intensity of a drug's pharmacologic action. Drug metabolism also affects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid ''residues'' form the second-largest component ( water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |