|
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG). History and etymology Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant. Nomenclature According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Amino Acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms, the nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidine. Six other amino acids are considered conditionally essential in the human diet, meaning their synthesis can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions, such as prematurity in the infant or individuals in severe catabolic distress. These six are arginine, cysteine, glycine, glutamine, proline, and tyrosine. Six amino acids are non-essential (dispensable) in humans, meaning they can be synthesized in sufficient quantities in the body. These six are alanine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, serine, and selenocysteine (considered the 21st amino acid). Py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid ''residues'' form the second-largest component ( water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetolactate Synthase
The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme (also known as acetohydroxy acid or acetohydroxyacid synthase, abbr. AHAS) is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids ( valine, leucine, and isoleucine). A human protein of yet unknown function, sharing some sequence similarity with bacterial ALS, is encoded by the ILVBL (ilvB-like) gene. Structure Gene Human ILVBL gene has 17 exons resides on chromosome 19 at q13.1. Protein The catalytic peptide of ALS in '' Arabidopsis thaliana'' (mouse-eared cress) is a chloroplastic protein consisting of 670 residues, the last 615 of which form the active form. Three main domains are found, with two thiamine pyrophosphate sandwiching a DHS-like NAD/FAD-binding domain. In SCOP assignment, these subunits are named d1yhya1, d1yhya2, and d1yhya3 from the N-terminal to the C-termianl. The structure of acetolactate synthase that was used for the picture on this pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
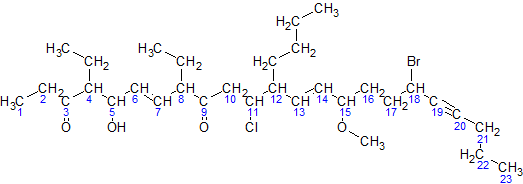
Skeletal Formula
The skeletal formula, or line-angle formula or shorthand formula, of an organic compound is a type of molecular structural formula that serves as a shorthand representation of a molecule's bonding and some details of its molecular geometry. A skeletal formula shows the skeletal structure or skeleton of a molecule, which is composed of the skeletal atoms that make up the molecule. It is represented in two dimensions, as on a piece of paper. It employs certain conventions to represent carbon and hydrogen atoms, which are the most common in organic chemistry. An early form of this representation was first developed by organic chemist August Kekulé, while the modern form is closely related to and influenced by the Lewis structure of molecules and their valence electrons. Hence they are sometimes termed Kekulé structures or Lewis–Kekulé structures. Skeletal formulae have become ubiquitous in organic chemistry, partly because they are relatively quick and simple to draw, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC Nomenclature Of Organic Chemistry
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the '' Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry'' (informally called the Blue Book). Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry. To avoid long and tedious names in normal communication, the official IUPAC naming recommendations are not always followed in practice, except when it is necessary to give an unambiguous and absolute definition to a compound. IUPAC names can sometimes be simpler than older names, as with ethanol, instead of ethyl alcohol. For relatively simple molecules they can be more easily understood than non-systematic names, which must be learnt or looked over. However, the common or trivial name is often substanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transamination
Transamination is a chemical reaction that transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids. This pathway is responsible for the deamination of most amino acids. This is one of the major degradation pathways which convert essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (amino acids that can be synthesized de novo by the organism). Transamination in biochemistry is accomplished by enzymes called transaminases or aminotransferases. α-ketoglutarate acts as the predominant amino-group acceptor and produces glutamate as the new amino acid. : Aminoacid + α-ketoglutarate ↔ α-keto acid + glutamate Glutamate's amino group, in turn, is transferred to oxaloacetate in a second transamination reaction yielding aspartate. : Glutamate + oxaloacetate ↔ α-ketoglutarate + aspartate Mechanism of action Transamination catalyzed by aminotransferase occurs in two stages. In the first step, the α amino group of an amino acid is transferred to the enzyme, prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroxyacid Dehydratase
The enzyme dihydroxy-acid dehydratase () catalyzes the chemical reaction :2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate \rightleftharpoons 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H2O This enzyme participates in valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis and pantothenate and coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of lyase In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking (an elimination reaction) of various chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bon ...s, specifically the hydro-lyases, which cleave carbon-oxygen bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate hydro-lyase (3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate-forming). Other names in common use include * acetohydroxyacid dehydratase, * α,β-dihydroxyacid dehydratase, * 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate dehydratase, * α,β-dihydroxyisovalerate dehydratase, * dihydroxy acid dehydras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketol-acid Reductoisomerase
In enzymology, a ketol-acid reductoisomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :(R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP+ \rightleftharpoons (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH + H+ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate and NADP+, whereas its 3 products are (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate, NADPH, and H+. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate:NADP+ oxidoreductase (isomerizing). Other names in common use include dihydroxyisovalerate dehydrogenase (isomerizing), acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase, ketol acid reductoisomerase, alpha-keto-beta-hydroxylacyl reductoisomerase, 2-hydroxy-3-keto acid reductoisomerase, acetohydroxy acid reductoisomerase, acetolactate reductoisomerase, dihydroxyisovalerate (isomerizing) dehydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Amination
Reductive amination (also known as reductive alkylation) is a form of amination that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine. The carbonyl group is most commonly a ketone or an aldehyde. It is considered the most important way to make amines, and a majority of amines made in the pharmaceutical industry are made this way. Reaction process In this organic reaction, the amine first reacts with the carbonyl group to form a hemiaminal species, which subsequently loses one molecule of water in a reversible manner by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution, to form the imine. The equilibrium between aldehyde/ketone and imine can be shifted toward imine formation by removal of the formed water through physical or chemical means. This intermediate imine can then be isolated and reduced with a suitable reducing agent (e.g., sodium borohydride). This method is sometimes called indirect reductive amination. In a separate approach, imine formation and redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-Ketoisovaleric Acid
α-Ketoisovaleric acid is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2H. It is a ketoacid. With a melting point just above room temperature, it is usually an oil or semi-solid. The compound is colorless. It is a metabolite of valine and a precursor to pantothenic acid, a prosthetic group found in several cofactors. In the biological context, is usually encountered as its conjugate base ketoisovalerate, (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2−. Synthesis and reactions α-Ketoisovalerate undergoes hydroxymethylation to give ketopantoate: :(CH3)2CHC(O)CO2− + CH2O → HOCH2(CH3)2CC(O)CO2− This conversion is catalyzed by ketopantoate hydroxymethyltransferase. Like many α-ketoacids, α-ketoisovaleric acid is prone to decarboxylation to give isobutyraldehyde: :(CH3)2CHC(O)CO2H → (CH3)2CHCHO + CO2 Genetic engineering has been used to produce the biofuel isobutanol Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |