|
MSPI (nerve Agent)
MSPI is an irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. MSPI reacts with the acetylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme th ... to form an aged enzyme adduct that can't be reactivated by cholinesterase reactivators. See also * EA-2192 * Guanitoxin References Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Imidazolium compounds Methyl esters Phosphoramidothioates Zwitterions Nerve agents {{Neurotoxin-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
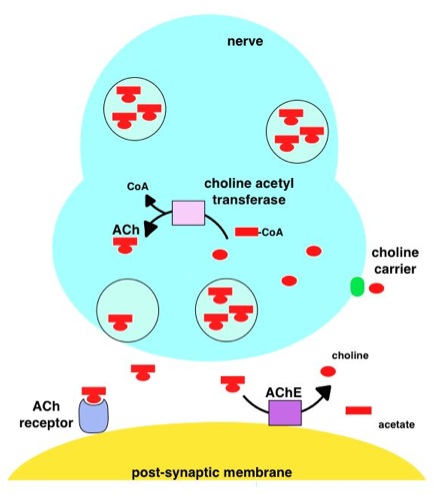
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate cholinergic neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 5,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholinesterase Reactivator
Cholinesterase reactivators are drugs that reverse the inhibition of cholinesterase by organophosphates or sulfonates. They are used as antidote for treating organophosphate insecticide and nerve agent poisoning. Organophosphates are used industrially in agricultural pesticides, and globally as agents of chemical warfare. Discovered in 1955, Pralidoxime was the first cholinesterase reactivator used as an antidote to OP neurotoxicity and remains the most commonly used reactivator. Cholinesterase reactivators are indicated for anticholinesterase toxicity and cholinergic crisis, the signs of which are contained within the mnemonic ''DUMBELS'' : Diarrhea/diaphoresis, urinary frequency, miosis, bronchospasm/bronchorrhea, emesis, lacrimation, and salivation. Death may occur due to the blockage of nicotinic receptors of muscle fibers at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the muscles of respiration. Mechanism of action Organophosphates lead to toxicity by forming a stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EA-2192
EA-2192 is an extremely toxic degradation product of the VX, a very potent nerve agent. It is a white solid that is very soluble and stable in water. EA-2192 is an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is almost as toxic as VX itself. EA-2192 instantly ages acetylcholinesterase as it is the dealkylated form of VX and can also not be reversed with common oxime reactivators. See also *Nerve agent Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemistry, organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (ACh ... References V-series nerve agents Phosphonothioates Phosphonic acids Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Diisopropylamino compounds {{alkanederivative-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanitoxin
Guanitoxin (GNT), formerly known as anatoxin-a(S) "Salivary", is a naturally occurring cyanotoxin commonly isolated from cyanobacteria (specifically of the genus ''Anabaena''). It is a potent covalent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, and thus a potent rapid acting neurotoxin which in cases of severe exposure can lead to death. Guanitoxin was first structurally characterized in 1989, and consists of a cyclic ''N''-hydroxyguanidine organophosphate with a phosphate ester moiety. Toxicity and treatment The main mechanism of action for guanitoxin is by irreversibly inhibiting the active site of acetylcholinesterase leading to excess acetylcholine in the parasympathetic and peripheral nervous systems; inducing poisoning via nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptor stimulation. The clinical signs of high level guanitoxin exposure consists mainly of excessive salivation, lacrimation, chromodacryorrhea (in rats), urinary incontinence, muscular weakness, muscle twitching, convulsion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from Hydrolysis, breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, Autonomic ganglion, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being Butyrylcholinesterase#Inhibitors, butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase, cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP, tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imidazolium Compounds
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula . It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. It can be classified as a heterocycle, specifically as a diazole. Many natural products, especially alkaloids, contain the imidazole ring. These imidazoles share the 1,3-C3N2 ring but feature varied substituents. This ring system is present in important biological building blocks, such as histidine and the related hormone histamine. Many drugs contain an imidazole ring, such as certain antifungal drugs, the nitroimidazole series of antibiotics, and the sedative midazolam. When fused to a pyrimidine ring, it forms a purine, which is the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing Heterocyclic compound, heterocycle in nature. The name "imidazole" was coined in 1887 by the German chemist Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch (1857–1935). Structure and properties Imidazole is a planar 5-membered ring, that exists in two equivalent tautomeric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Esters
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom chemical bond, bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In chemical formula, formulas, the group is often skeletal formula#Pseudoelement symbols, abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (chemistry), radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwitterions
In chemistry, a zwitterion ( ; ), also called an inner salt or dipolar ion, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively and negatively charged functional groups. : (1,2- dipolar compounds, such as ylides, are sometimes excluded from the definition.) Some zwitterions, such as amino acid zwitterions, are in chemical equilibrium with an uncharged "parent" molecule. Betaines are zwitterions that cannot isomerize to an all-neutral form, such as when the positive charge is located on a quaternary ammonium group. Similarly, a molecule containing a phosphonium group and a carboxylate group cannot isomerize. Amino acids Tautomerism of amino acids follows this stoichiometry: : The ratio of the concentrations of the two species in solution is independent of pH. It has been suggested, on the basis of theoretical analysis, that the zwitterion is stabilized in aqueous solution by hydrogen bonding with solvent water molecules. Analysis of neutron diffraction data for glycin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |