|
MIMIC Simulator
MIMIC Simulator is a product suite from Gambit Communications consisting of simulation software in the network and systems management space. The MIMIC Simulator Suite has several components related to simulation of managed networks and data centers for the purposes of software development, software testing or training, sales and marketing of network management applications (see). MIMIC SNMP simulator solves a classical simulation problem: network management or operations support system software typically manages large networks. Traditionally, in order to set up such networks for the above purposes, physical equipment had to be separately purchased and assembled in laboratories. To reduce the expense, most of the network can be simulated (e.g. see). The principle behind SNMP simulation is that the SNMP protocol is an interface that can be simulated. SNMP requests carry data values for MIB objects, which can be shaped at will by the simulator, thus representing any device which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNMP Simulator
An SNMP simulator is a type of computer simulation, that simulates the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent. Contrary to network simulation, which models the behavior of a network within a computer, the SNMP simulator actually interfaces with outside systems, for example network management application software. An SNMP simulator fools the network management application software into believing it is talking via the SNMP protocol to one or more devices, just like a flight simulator allows a pilot to believe they are flying a plane. Uses SNMP Simulators are used for development, testing, and training of network management system software. Before the advent of simulators, actual physical equipment was used. The scalability of simulators dramatically reduces the cost in this area. Features in this area vary widely, from the no-cost to commercial offerings. It is not uncommon for higher-end simulators to simulate thousands of devices on common PC hardware or virtual mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Management Information Base
A management information base (MIB) is a database used for managing the entities in a communication network. Most often associated with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), the term is also used more generically in contexts such as in OSI/ ISO Network management model. While intended to refer to the complete collection of management information available on an entity, it is often used to refer to a particular subset, more correctly referred to as MIB-module. Objects in the MIB are defined using a subset of Abstract Syntax Notation One ( ASN.1) called "Structure of Management Information Version 2 (SMIv2)" . The software that performs the parsing is a MIB compiler. The database is hierarchical (tree-structured) and each entry is addressed through an object identifier (OID). Internet documentation RFCs discuss MIBs, notably , "Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP based internets", and its two companions, , "Management Information Base f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOAP
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, and precursors to catalysts. When used for cleaning, soap solubilizes particles and grime, which can then be separated from the article being cleaned. In hand washing, as a surfactant, when lathered with a little water, soap kills microorganisms by disorganizing their membrane lipid bilayer and denaturing their proteins. It also emulsifies oils, enabling them to be carried away by running water. Soap is created by mixing fats and oils with a base. A similar process is used for making detergent which is also created by combining chemical compounds in a mixer. Humans have used soap for millennia. Evidence exists for the production of soap-like materials in ancient Babylon around 280 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CoAP
Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) is a specialized Internet application protocol for constrained devices, as defined iRFC 7252 It enables those constrained devices called "nodes" to communicate with the wider Internet using similar protocols. CoAP is designed for use between devices on the same constrained network (e.g., low-power, lossy networks), between devices and general nodes on the Internet, and between devices on different constrained networks both joined by an internet. CoAP is also being used via other mechanisms, such as SMS on mobile communication networks. CoAP is an application-layer protocol that is intended for use in resource-constrained Internet devices, such as wireless sensor network nodes. CoAP is designed to easily translate to HTTP for simplified integration with the web, while also meeting specialized requirements such as multicast support, very low overhead, and simplicity. Multicast, low overhead, and simplicity are important for Internet of things ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MQTT
MQTT (originally an initialism of MQ Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight, publish-subscribe, machine to machine network protocol for Message queue/Message queuing service. It is designed for connections with remote locations that have devices with resource constraints or limited network bandwidth. It must run over a transport protocol that provides ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections—typically, TCP/IP. It is an open OASIS standard and an ISO recommendation (ISO/IEC 20922). History Andy Stanford-Clark ( IBM) and Arlen Nipper (then working for Eurotech, Inc.) authored the first version of the protocol in 1999. It was used to monitor oil pipelines within the SCADA industrial control system. The goal was to have a protocol that is bandwidth-efficient, lightweight and uses little battery power, because the devices were connected via satellite link which, at that time, was extremely expensive. Historically, the "MQ" in "MQTT" came from the IBM MQ (then 'MQSeries' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Of Things
The Internet of things (IoT) describes physical objects (or groups of such objects) with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. Internet of things has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet, they only need to be connected to a network and be individually addressable. The field has evolved due to the convergence of multiple technologies, including ubiquitous computing, commodity sensors, increasingly powerful embedded systems, as well as machine learning.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Fault-tolerant cooperative navigation of networked UAV swarms for forest fire monitoring Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022. Traditional fields of embedded systems, wireless sensor networks, control systems, automation (including home and building automation), independently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMTF
Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) is a 501(c)(6) nonprofit industry standards organization that creates open manageability standards spanning diverse emerging and traditional IT infrastructures including cloud, virtualization, network, servers and storage. Member companies and alliance partners collaborate on standards to improve interoperable management of information technologies. Based in Portland, Oregon, the DMTF is led by a board of directors representing technology companies including: Broadcom Inc., Cisco, Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Intel Corporation, Lenovo, NetApp, Positive Tecnologia S.A., and Verizon. History Founded in 1992 as the Desktop Management Task Force, the organization’s first standard was the now-legacy Desktop Management Interface (DMI). As the organization evolved to address distributed management through additional standards, such as the Common Information Model (CIM), it changed its name to the Distributed Management Task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Platform Management Interface
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware (BIOS or UEFI) and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SFlow
sFlow, short for "sampled flow", is an industry standard for packet export at Layer 2 of the OSI model. sFlow was originally developed by InMon Corp. It provides a means for exporting truncated packets, together with interface counters for the purpose of network monitoring. Maintenance of the protocol is performed by the sFlow.org consortium, the authoritative source of the sFlow protocol specifications. The current version of sFlow is v5. Operation sFlow uses mandatory sampling to achieve scalability and is, for this reason, applicable to high speed networks (gigabit per second speeds and higher). sFlow is supported by multiple network device manufacturers and network management software vendors. An sFlow system consists of multiple devices performing two types of sampling: random sampling of packets or application layer operations, and time-based sampling of counters. The sampled packet/operation and counter information, referred to as ''flow samples'' and ''counter samples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
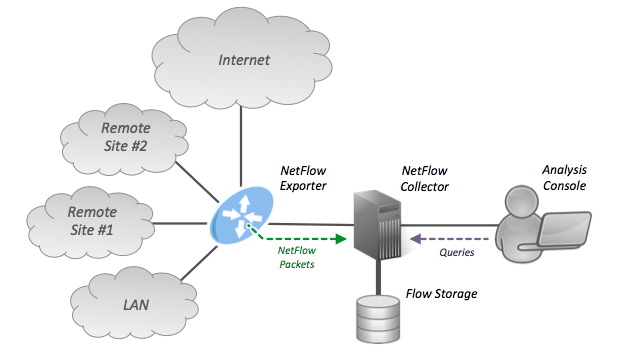
NetFlow
NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on Cisco routers around 1996 that provides the ability to collect IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. By analyzing the data provided by NetFlow, a network administrator can determine things such as the source and destination of traffic, class of service, and the causes of congestion. A typical flow monitoring setup (using NetFlow) consists of three main components: * Flow exporter: aggregates packets into flows and exports flow records towards one or more flow collectors. * Flow collector: responsible for reception, storage and pre-processing of flow data received from a flow exporter. * Analysis application: analyzes received flow data in the context of intrusion detection or traffic profiling, for example. Protocol description Routers and switches that support NetFlow can collect IP traffic statistics on all interfaces where NetFlow is enabled, and later export those statistics as NetFlow records toward at least on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisco IOS
The Internetworking Operating System (IOS) is a family of proprietary network operating systems used on several router and network switch models manufactured by Cisco Systems. The system is a package of routing, switching, internetworking, and telecommunications functions integrated into a multitasking operating system. Although the IOS code base includes a cooperative multitasking kernel, most IOS features have been ported to other kernels, such as Linux and QNX, for use in Cisco products. Not all Cisco networking products run IOS. Exceptions include some Cisco Catalyst switches, which run IOS XE, and Cisco ASR routers, which run either IOS XE or IOS XR; both are Linux-based operating systems. For data center environments, Cisco Nexus switches (Ethernet) and Cisco MDS switches (Fibre Channel) both run Cisco NX-OS, also a Linux-based operating system. History The IOS network operating system was created from code written by William Yeager at Stanford University, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command Line Interface
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and providing information to them as to what actions they are to perform. In some cases the invocation is conditional based on conditions established by the user or previous executables. Such access was first provided by computer terminals starting in the mid-1960s. This provided an interactive environment not available with punched cards or other input methods. Today, many users rely upon graphical user interfaces and menu-driven interactions. However, some programming and maintenance tasks may not have a graphical user interface and use a command line. Alternatives to the command-line interface include text-based user interface menus (for example, IBM AIX SMIT), keyboard shortcuts, and various desktop metaphors centered on the pointer (usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)