|
Luopingosaurus Holotype
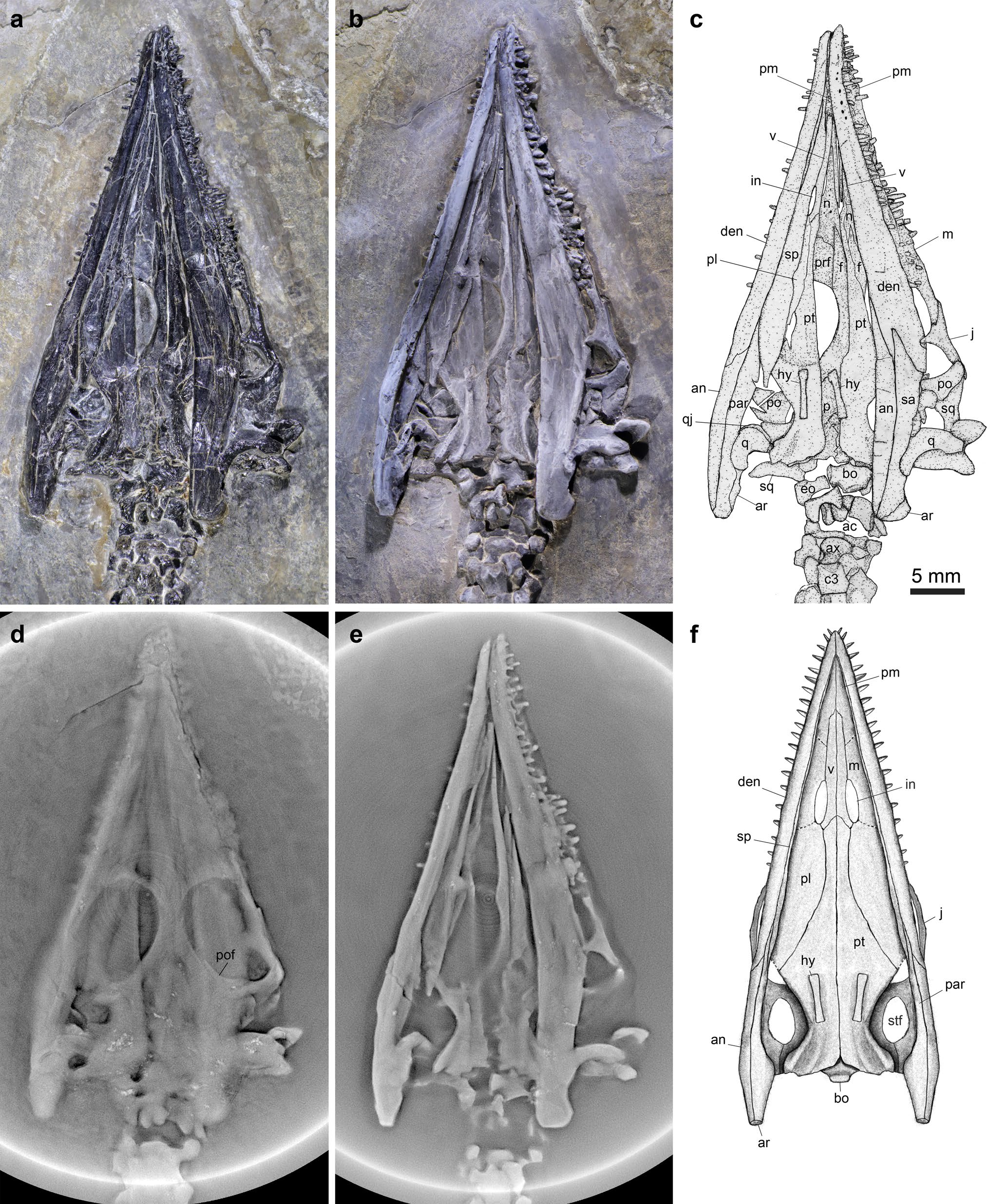
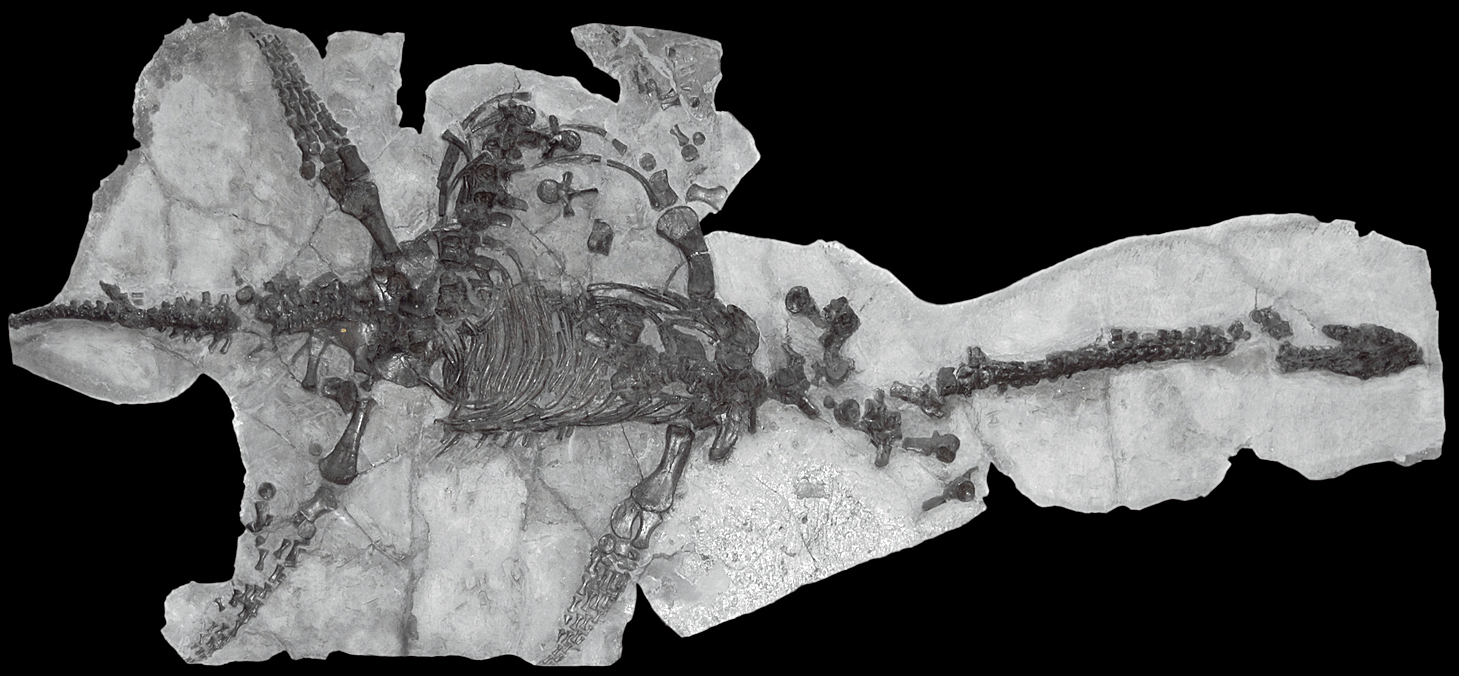
''Luopingosaurus'' (meaning "Luoping lizard") is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaurid sauropterygian from the Middle Triassic Guanling Formation of Yunnan Province, China. The genus contains a single species, ''L. imparilis'', known from a well-preserved, nearly complete skeleton. Discovery and naming The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen, Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, IVPP V19049, was discovered in sediments of the Guanling Formation, dated to the Anisian age (Pelsonian substage) of the middle Triassic period, in Luoping County, Yunnan Province, China. This specimen consists of a nearly complete, ventrally-exposed, Joint, articulated individual, lacking only the end of the tail. The preserved portion of the skeleton measures long. In 2023, Xu et al. Species description, described ''Luopingosaurus imparilis'', a new genus and species of pachypleurosaurid, based on these fossil remains. The Genus, generic name, "''Luopingosaurus''", combines a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epoch (geology), epochs of the Triassic period (geology), period or the middle of three series (stratigraphy), series in which the Triassic system (stratigraphy), system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian age (geology), ages or stage (stratigraphy), stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of stratum, rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic life Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic, when they became extinct as part of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Other than being diapsids, their affinities to other reptiles have long been contentious. Sometimes suggested to be closely related to turtles, other proposals have considered them most closely related to Lepidosauromorpha or Archosauromorpha, and/or the marine reptile groups Thalattosauria and Ichthyosauromorpha. Origins an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanosaurus
''Hanosaurus'' is an extinct genus of marine reptiles that existed during the Triassic period in what is now China. The type species is ''Hanosaurus hupehensis''. It was a small animal, with specimens measuring long in total body length, which likely fed on soft-bodied prey. Discovery ''Hanosaurus'' (lizard of Han River) was discovered from the Sonshugo locality of Hubei, China. It was found at the second member of the Jialingjiang Formation. The type specimen consisted of a skull, complete hindlimbs and pelvis, incomplete shoulder girdle represented by coracoid and clavicle, and an articulated but incomplete vertebral column. It was initially described as a thalattosaur but subsequent research showed it was more likely to be a sauropterygia. A more complete referred specimen was described in 2022 from the Yingzishan locality of Hubei, China. The specimen was also found at the second member of the Jialingjiang formation. It consisted of almost the entire skeleton preserved w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodontia
Placodonts ("Tablet (pharmacy), tablet tooth, teeth") are an Extinction, extinct order (biology), order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes Plesiosauria, plesiosaurs. Placodonts were generally between in length, with some of the largest measuring long. The first specimen was discovered in 1830. They have been found throughout central Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and China. Palaeobiology The earliest forms, like ''Placodus'', which lived in the early to middle Triassic, resembled barrel-bodied lizards superficially similar to the marine iguana of today, but larger. In contrast to the marine iguana, which feeds on algae, the placodonts ate Mollusca, molluscs and so their teeth were flat and tough to crush shells. In the earliest periods, their size was probably enough to keep away the top sea predators of the time: the sharks. However, as time passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honghesaurus
''Honghesaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaur from the Anisian-age Guanling Formation of China. The type specimen measures about in total body length. Classification The cladogram below follows Xu and colleagues (2022), when they used ''Youngina'' as a reference point for rooting the tree. Using a selection of placodont Placodonts (" tablet teeth") are an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes plesiosaurs. Placodonts were generall ...s resulted in a less resolved topology. References Triassic sauropterygians Pachypleurosauria Fossil taxa described in 2022 Anisian life {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades. Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and synapomorphy all mean a trait shared between species because they share an ancestral species. Apomorphic and synapomorphic characteristics convey much information about evolutionary clades and can be used to define taxa. However, plesiomorphic and symplesiomorphic characteristics cannot. The term ''symplesiomorphy'' was introduced in 1950 by German entomologist Willi Hennig. Examples A backbone is a plesiomorphic trait shared by birds and mammals, and does not help in placing an animal in one or the other of these two clades. Birds and mammals share this trait because both clades are descended from the same far distant ancestor. Other clades, e.g. snakes, lizards, turtles, fish, frogs, all have backbones and none are either birds n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keichousaurids
Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles from the Triassic period. Pachypleurosaurs vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, with elongate forms ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species ''Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, with the only other discovery of such an event having been made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were traditionally included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more recent cladistic classifications, however, (Rieppel 2000), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wumengosaurus
''Wumengosaurus'' is an extinct aquatic reptile from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) Guanling Formation of Guizhou, southwestern China. It was originally described as a basal eosauropterygian and usually is recovered as such by phylogenetic analyses, although one phylogeny has placed it as the sister taxon to Ichthyosauromorpha while refraining from a formal re-positioning. It was a relatively small reptile, measuring in total body length. In 2021, Qin ''et al''. described an additional specimen from Guizhou ( Panzhou District) as a new species of ''Wumengosaurus'', ''W. rotundicarpus''. Classification In the 2023 description of '' Luopingosaurus'', Xu ''et al''. recovered ''Wumengosaurus'' as a derived pachypleurosaurid, as the sister taxon to the clade formed by ''Luopingosaurus'' and ''Honghesaurus''. The results of their phylogenetic analyses are shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |