Luopingosaurus Holotype on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Luopingosaurus'' (meaning "Luoping lizard") is an extinct genus of
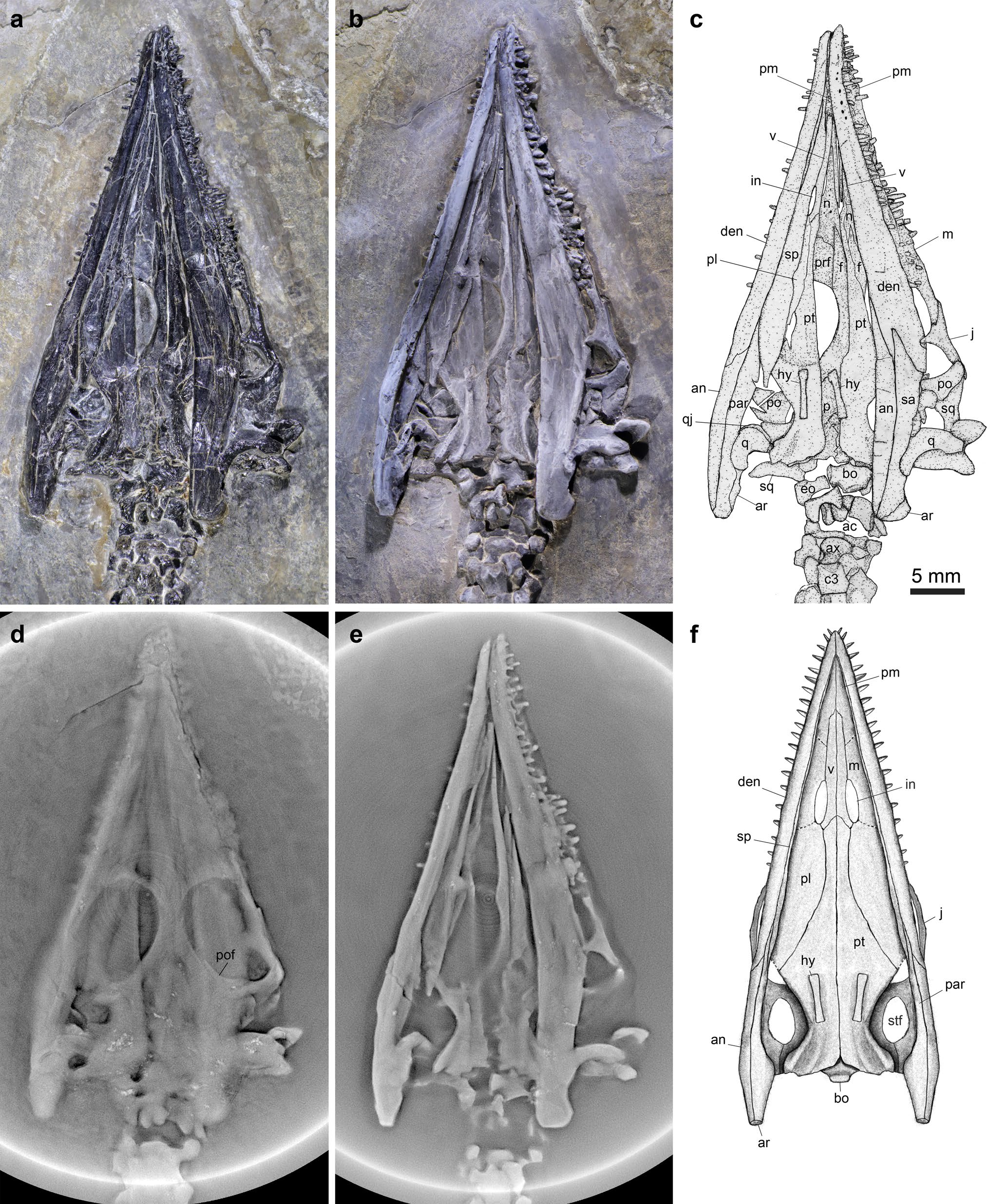 The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen,
The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen,
 ''Luopingosaurus'' is one of the largest pachypleurosauroids, with an estimated total body length of . It also has an unusually long snout compared to other pachypleurosaurids; the only related taxon with a longer snout is ''
''Luopingosaurus'' is one of the largest pachypleurosauroids, with an estimated total body length of . It also has an unusually long snout compared to other pachypleurosaurids; the only related taxon with a longer snout is ''
pachypleurosaurid
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus''
Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , ...
sauropterygian
Sauropterygia (" lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria bec ...
from the Middle Triassic Guanling Formation
The Guanling Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian or Pelsonian in the regional chronostratigraphy) geologic formation in southwestern China.
Description
The formation encompasses two members. The first member is primarily calcareous mudston ...
of Yunnan Province, China. The genus contains a single species, ''L. imparilis'', known from a well-preserved, nearly complete skeleton.
Discovery and naming
 The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen,
The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen, IVPP The Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP; ) of China is a research institution and collections repository for fossils, including many dinosaur and pterosaur specimens (many from the Yixian Formation). As its name suggest ...
V19049, was discovered in sediments of the Guanling Formation
The Guanling Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian or Pelsonian in the regional chronostratigraphy) geologic formation in southwestern China.
Description
The formation encompasses two members. The first member is primarily calcareous mudston ...
, dated to the Anisian age (Pelsonian substage) of the middle Triassic period, in Luoping County, Yunnan Province, China. This specimen consists of a nearly complete, ventrally-exposed, articulated individual, lacking only the end of the tail. The preserved portion of the skeleton measures long.
In 2023, Xu ''et al''. described ''Luopingosaurus imparilis'', a new genus and species of pachypleurosaurid
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus''
Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , ...
, based on these fossil remains. The generic name, "''Luopingosaurus''", combines a reference to the type locality in Luoping County with the Greek word "saurus", meaning "lizard". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
, "''imparilis''", means "peculiar" and "unusual" in Latin.
Description
 ''Luopingosaurus'' is one of the largest pachypleurosauroids, with an estimated total body length of . It also has an unusually long snout compared to other pachypleurosaurids; the only related taxon with a longer snout is ''
''Luopingosaurus'' is one of the largest pachypleurosauroids, with an estimated total body length of . It also has an unusually long snout compared to other pachypleurosaurids; the only related taxon with a longer snout is ''Wumengosaurus
''Wumengosaurus'' is an extinct aquatic reptile from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) Guanling Formation of Guizhou, southwestern China. It was originally described as a basal eosauropterygian and usually is recovered as such by phyloge ...
'', which has occasionally been placed outside of Pachypleurosauroidea
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus''
Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , ...
by other authors. The evolution of this feature alongside the shorter-snouted keichousaurids
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus''
Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , ...
may have occurred due to differences in foraging and feeding specializations. The elongated snout may have allowed ''Luopingosaurus'' to more effectively catch and hold prey.
''Luopingosaurus'' represents the only known instance of hyperphalangy (an increase in the number of phalanges) in Pachypleurosauroidea, having five phalanges in the third digit as opposed to the plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and ...
condition of four.
Classification
Xu ''et al''. (2023) recovered ''Luopingosaurus'' as a derived pachypleurosaurid member of the Pachypleurosauroidea, as the sister taxon to ''Honghesaurus
''Honghesaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaur from the Anisian-age Guanling Formation of China. The type specimen measures about in total body length.
Classification
The cladogram below follows Xu and colleagues (2022), when they used ...
''. Their results are shown in the cladogram below:
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q116041293 Pachypleurosaurs Triassic sauropterygians Guanling Formation Anisian genera Fossils of China Extinct animals of China Fossil taxa described in 2023 Prehistoric reptile genera