|
Lukka Lands
The term Lukka lands (sometimes Luqqa lands), in Hittite language texts from the 2nd millennium BC, is a collective term for states formed by the Lukka people in south-west Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). The Lukka were never subjugated long-term by the Hittites, who generally viewed them as hostile. It is commonly accepted that the Bronze Age toponym Lukka is cognate with the Lycia of classical antiquity (8th century BC to 5th century AD). Location There are two somewhat different hypotheses with regard to the extent of the Lukka lands. The maximalist hypothesis is upheld by Trevor Bryce, who discusses the occurrences of Lukka in Bronze Age texts. "From these texts we can conclude the Lukka, or Lukka lands, referred to regions extending from the western end of Pamphylia, through Lycaonia, Pisidia and Lycia". The minimalist hypothesis is upheld by Ilya Yakubovich, who concludes based on the analysis of textual evidence: " have positive philological arguments for the presence of Bron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tahtalı Dağı
Tahtalı Dağı, also known as Lycian Olympus, is a mountain near Kemer, a seaside resort on the Turkish Riviera in Antalya Province, Turkey. It was known as Olympus ( grc, Ὄλυμπος; also transliterated as Olympos) and Phoenicus or Phoinikous ( grc, Φοινικοῦς) in ancient times. It is part of the Beydağları Coastal National Park. Visitors can ascend the summit with the Olympos Aerial Tram. The Lycian Way long distance trail traverses the mountain. Geography Tahtalı Dağı lies on the east coast of the Teke Peninsula (Lycian Peninsula), dominating the landscape around Kemer. Located between Antalya and Finike and the dominant peak of the mountain range ''Bey Dağları'' (Turkish: '' Bey Mountains''). From it, the start of the Taurus Mountains can be seen. Its close proximity to the coast of the Mediterranean Sea also make it visible from afar to mariners. It is the highest mountain in the Natural Park of Olympos - Beydağları - Milli Park. From November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycians
Lycians is the name of various peoples who lived, at different times, in Lycia, a geopolitical area in Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). History The earliest known inhabitants of the area were the '' Solymoi'' (or ''Solymi''), also known as the Solymians, who may have spoken a Semitic language. Later in prehistory, another people, known as the Milyae (or Milyans) migrated to the same area; they spoke an Anatolian language (Indo-European) language known as Milyan and the area was known as Milyas. According to Herodotus, Milyas was subsequently settled by a people originating in Crete, whose endonym was ''trm̃mili'' – the hellenized form of this name was Termilae (Τερμίλαι). Under a leader named Sarpedon, the Termilae had been driven out of Crete (according to Herodotus) by Minos and settled in a large part of Milyas. Subsequently, the Milyae were concentrated increasingly in the adjoining mountains, whereas the Termilae remained a maritime people. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assuwa
Assuwa ( hit, 𒀸𒋗𒉿, translit=aš-šu-wa, link=yes; gmy, 𐀀𐀯𐀹𐀊, translit=a-si-wi-ja, link=yes) was a confederation of 22 states in western Anatolia around 1400 BC. The confederation formed to oppose the Hittite Empire, but was defeated under Tudhaliya I/II. The name was recorded in various centres in Mycenaean Greece as ''Asswia'', which latter acquired the form ''Asia''. Etymology Assuwa is identified most conclusively in Hittite records as ''aš-šu-wa'' and also as ''a-si-wi-ja'', ''a-si-wi-jo'', ''a-si-ja-ti-ja'', ''a-''𐁗''-ja'', and ''a-''𐁗-''jo'' in the Linear B script of Mycenaean Greece. Less conclusive is the ''a-su-ja'' in the Linear A script of the Minoans, though it is considered as containing “Greek-like elements” and possibly related to the Linear B form.Cline, Eric H. “Achilles in Anatolia: Myth, History, and the Assuwa Rebellion,” in Crossing Boundaries and Linking Horizons: Studies in Honor of Michael Astour on His 80th Birthday, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arzawa
Arzawa was a region and a political entity (a " kingdom" or a federation of local powers) in Western Anatolia in the second half of the 2nd millennium BC (roughly from the late 15th century BC until the beginning of the 12th century BC). The core of Arzawa is believed to be along the Kaystros River (now known as Küçük Menderes River), with its capital at Apasa, later known as Ephesus. When the Hittites conquered Arzawa, it was divided into three Hittite provinces: a southern province called Mira along the Maeander River, which would later become known as Caria; a northern province called the Seha River Land, along the Gediz River, which would later become known as Lydia; and an eastern province called Hapalla.J. David Hawkins (1998). ‘Tarkasnawa King of Mira: Tarkendemos, Boğazköy Sealings, and Karabel.’ ''Anatolian Studies'' 48:1–31. It succeeded the Assuwa league, which also included parts of western Anatolia, but was conquered by the Hittites c. 1400 BC. Arza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Regions Of Anatolia
The following is a list of regions of Ancient Anatolia, also known as "Asia Minor," in the present day Anatolia region of Turkey in Western Asia. Late Bronze Age regions (circa 1200 BC) *Alasiya / Alashiya (later Cyprus in the Classical Age, to the south of mainland Anatolia or Asia Minor) * Assuwa, roughly most part of West Asia Minor / Anatolia, it was a confederation (or league) of 22 ancient Anatolian states that formed some time before 1400 BC (may have been the origin of the name Asia) ** Adadura ** Alatra ** Assuwa Proper **Dura ** Dunda ** Ḥalluwa ** Ḥuwallušiya ** Karakisa / Karkiya (later Caria in the Classical Age) ** Kispuwa ** Kuruppiya ** Land of Mount Pahurina ** Luissa, a name ending in -luišša (or the whole name Luišša) **Lukka / Lugga (later Lycia in the Classical Age) ** Parista ** Pasuhalta ** Taruisa (later Troas / Troad? in the Classical Age) (Wilusa / Wilusiya was the capital, has been identified with the city called Ilion / Troy by the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia (around 1650 BC). This empire reached its height during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed an area that included most of Anatolia as well as parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Empire of Hattusa—in modern times conventionally called the Hittite Empire—came into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empire and the empire of Mitanni for control of the Near East. The Middle Assyrian Empire eventually emerged as the dominant power and annexed much of the Hittite Empire, while the remainder was sacked by Phrygian newcomers to the region. After BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse, the Hittites splintered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
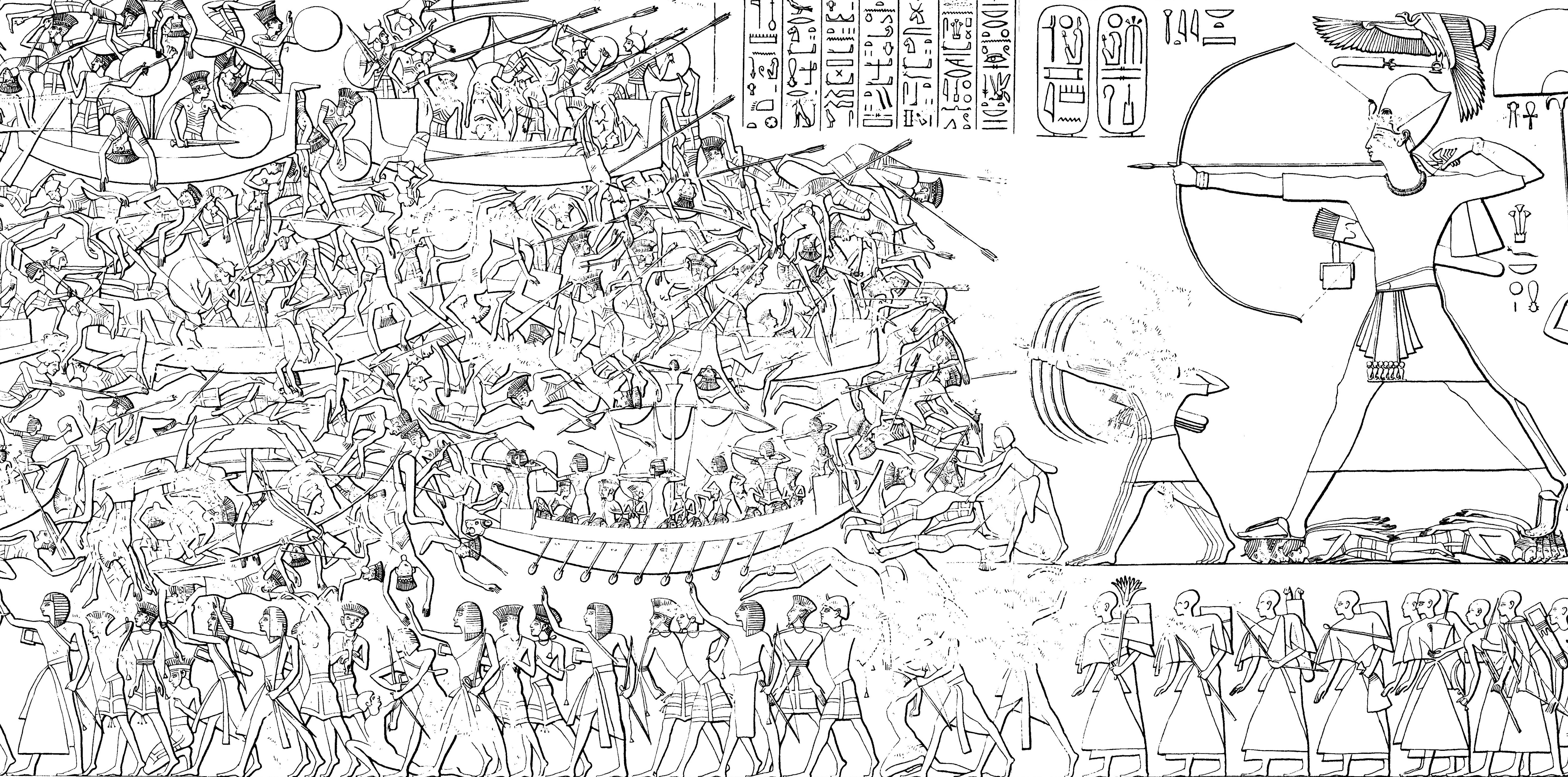
Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom, itself the most powerful period of Ancient Egypt. The name ''Ramesses'' is pronounced variously . Other spellings include Rameses and Ramses; in grc-koi, Ῥαμέσσης, Rhaméssēs. He is known as Ozymandias in Greek sources ( grc-koi, Ὀσυμανδύας, translit=Osymandýas), from the first part of Ramesses's regnal name, , "The Maat of Ra is powerful, Chosen of Ra". His successors and later Egyptians called him the "Great Ancestor". At age fourteen, he was appointed prince regent by his father, Seti I. Most Egyptologists today believe he assumed the throne on 31 May 1279 BC, based on his known accession date of III Season of the Harvest, day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh or Battle of Qadesh took place between the forces of the New Kingdom of Egypt under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II at the city of Kadesh on the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs near the modern Lebanon–Syria border. The battle is generally dated to 1274 BC from the Egyptian chronology, and is the earliest pitched battle in recorded history for which details of tactics and formations are known. It is believed to have been the largest chariot battle ever fought, involving between 5,000 and 6,000 chariots in total. As a result of discovery of multiple Kadesh inscriptions and the Egyptian–Hittite peace treaty, it is the best documented battle in all of ancient history. Background After expelling the Hyksos' 15th Dynasty around 1550 BC, the Egyptian New Kingdom rulers became more aggressive in reclaiming control of their state's borders. Thutmose I, Thutmose III and his son and coregent Amenhotep II fought batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Türkei.jpg)





_in_the_Battle_of_Khadesh.jpg)